Work Done (maths) Presentation
| Introduction to Work Done | ||
|---|---|---|
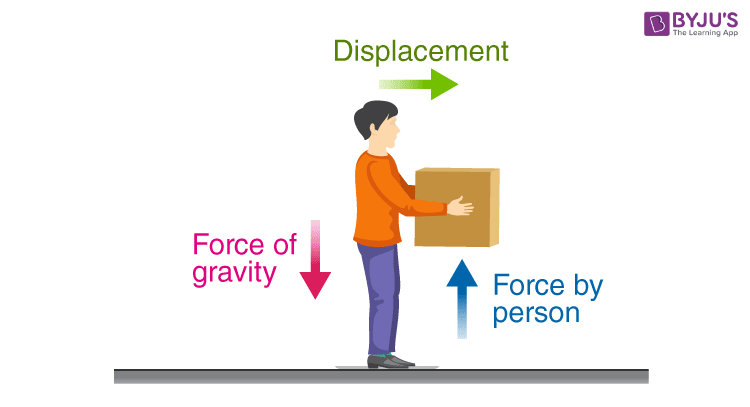
| Work done is a concept in mathematics that relates to the amount of effort exerted in moving an object. It is defined as the product of the force applied on an object and the distance over which the force is applied. Work done is measured in joules (J) or foot-pounds (ft-lb). | ||
| 1 | ||
| Formula for Work Done | ||
|---|---|---|
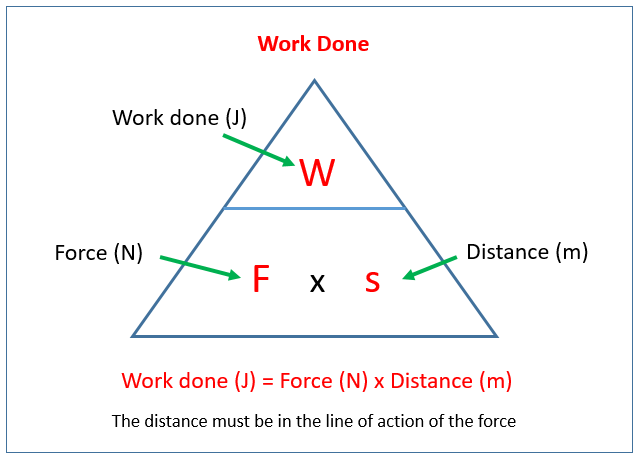
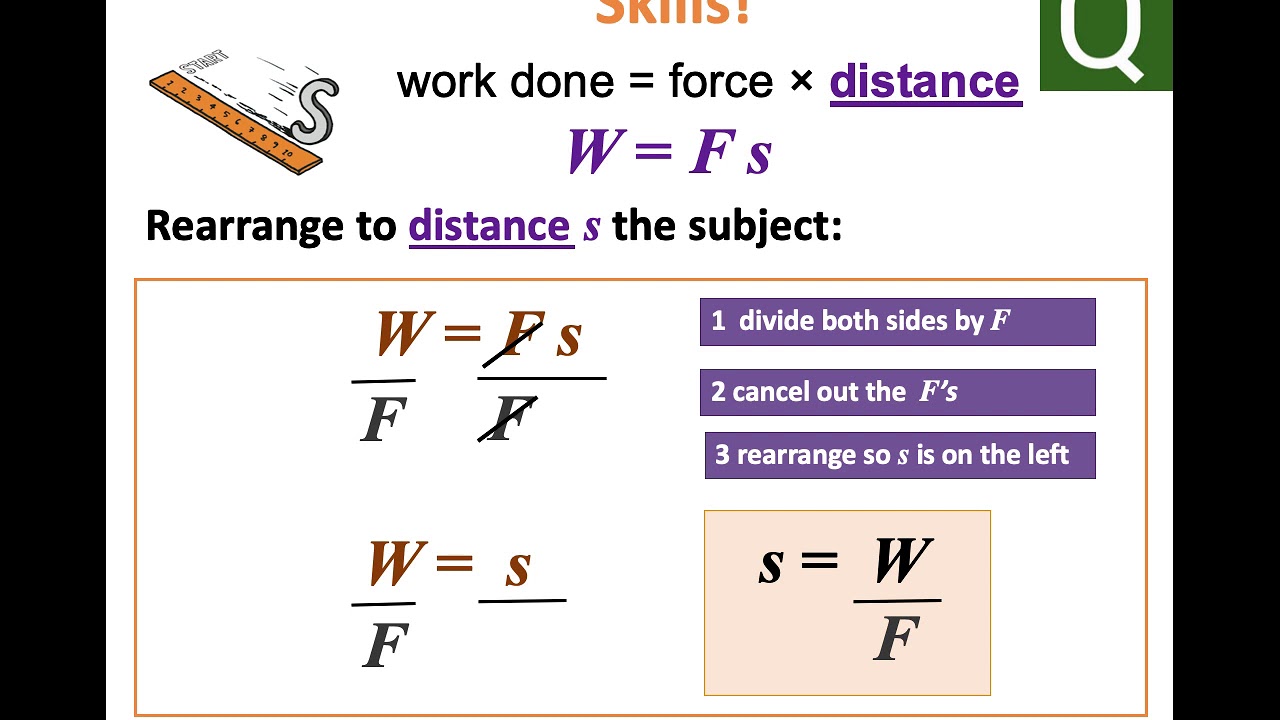
| The formula for calculating work done is: Work = Force × Distance × cos(θ). Force represents the magnitude of the applied force in Newtons (N) or pounds (lb). Distance is the displacement of the object in meters (m) or feet (ft). | ||
| 2 | ||
| Positive and Negative Work Done | ||
|---|---|---|
| When the angle between the applied force and the direction of motion is 0° (or 180°), work done is positive. Positive work occurs when the force applied and the direction of motion are in the same direction. When the angle is 90° (or 270°), work done is zero as there is no displacement. | ||
| 3 | ||
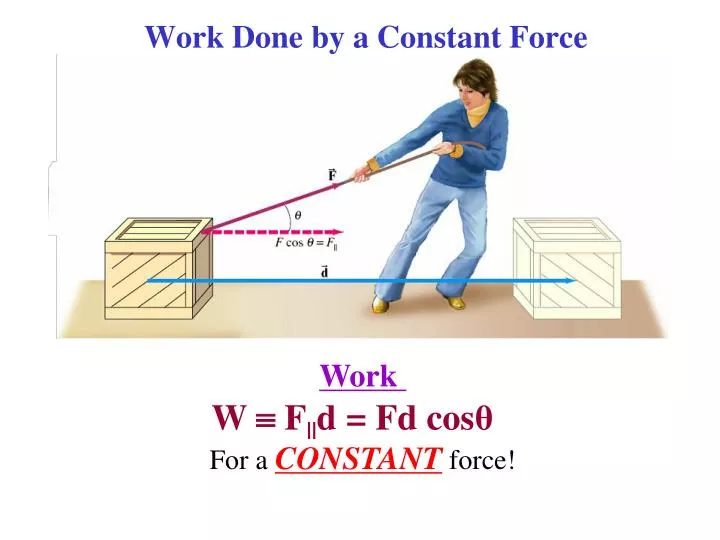
| Work Done by a Constant Force | ||
|---|---|---|
| Work done by a constant force can be calculated as: Work = Force × Distance. In this case, the angle between the applied force and the direction of motion is 0°. The magnitude of work done is given by the product of force and distance. | ||
| 4 | ||
| Work Done by a Variable Force | ||
|---|---|---|
| Work done by a variable force can be determined using integration. The force is considered a function of displacement, and the integral of force with respect to displacement gives the work done. The integral is evaluated over the range of displacement. | ||
| 5 | ||
| Examples of Work Done | ||
|---|---|---|
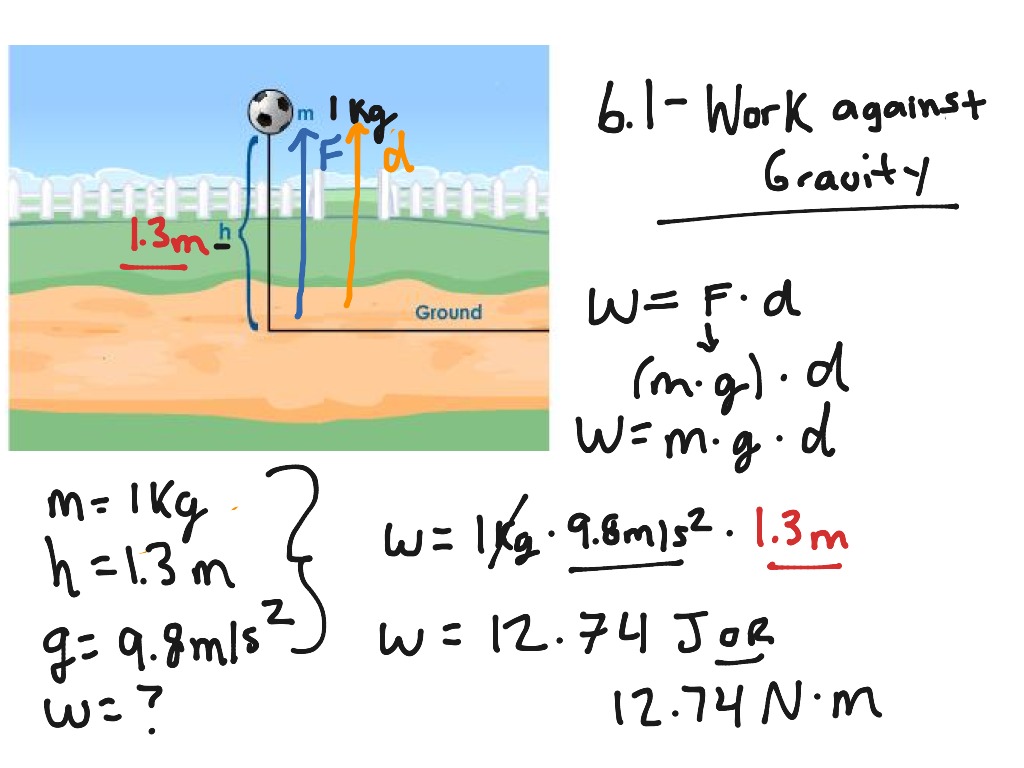
| Lifting a box against gravity requires work to be done. Pushing a car to move it forward also involves work done. Stretching a spring or compressing a gas is another example of work done. | ||
| 6 | ||
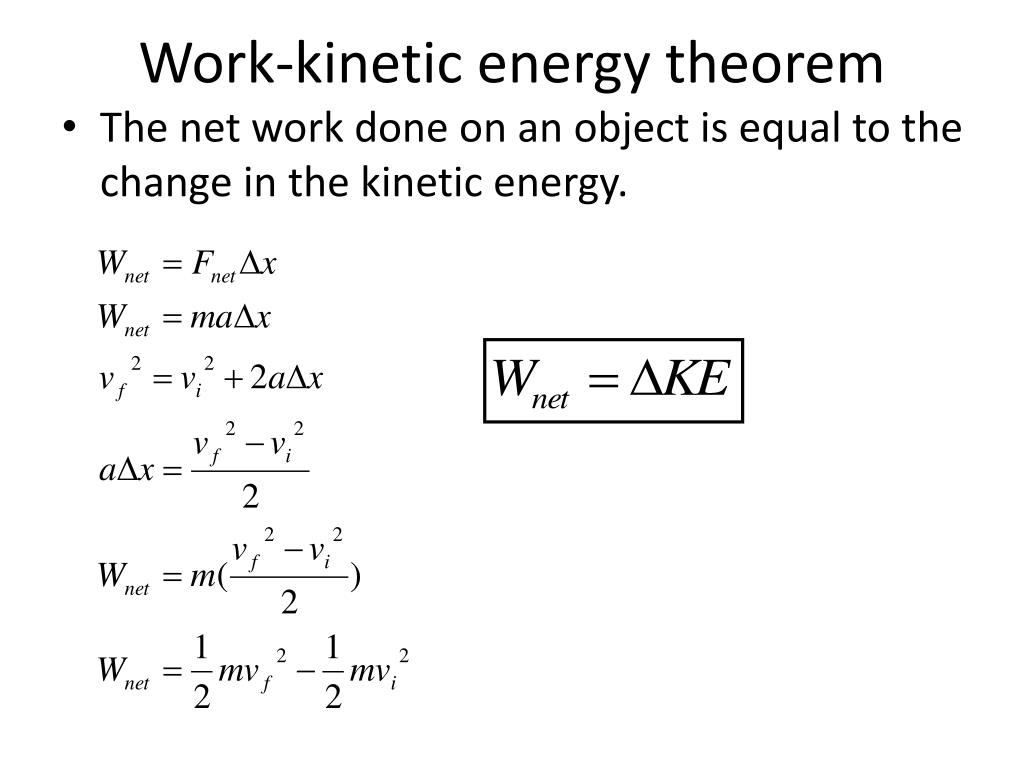
| Work-Energy Theorem | ||
|---|---|---|
| The work-energy theorem states that the work done on an object is equal to the change in its kinetic energy. This theorem allows us to relate work done to the energy of an object. It is based on the principle of conservation of energy. | ||
| 7 | ||
| Applications of Work Done | ||
|---|---|---|
| Understanding work done is crucial in engineering and physics to analyze mechanical systems. Calculating work done helps in determining the amount of energy transferred or stored in a system. Work done is utilized in designing machines, analyzing forces, and optimizing efficiency. | ||
| 8 | ||
| Summary | ||
|---|---|---|
| Work done is the product of force and distance. Positive work occurs when the force and direction of motion are the same, while negative work occurs when they are opposite. Constant force work is calculated using the formula Work = Force × Distance. | ||
| 9 | ||
| Conclusion | ||
|---|---|---|
| Work done is a fundamental concept in mathematics, physics, and engineering. It helps us understand the relationship between force, distance, and energy transfer. By calculating work done, we can analyze and optimize systems, design machines, and solve real-world problems. | ||
| 10 | ||