Tense Presentation
| Introduction to Tense | ||
|---|---|---|
| Tense is a grammatical concept that expresses time and refers to the way verbs are used to indicate when an action occurred. Tense helps us understand the timeline of events in a sentence or a passage. The three main tenses in English are past, present, and future. | ||
| 1 | ||
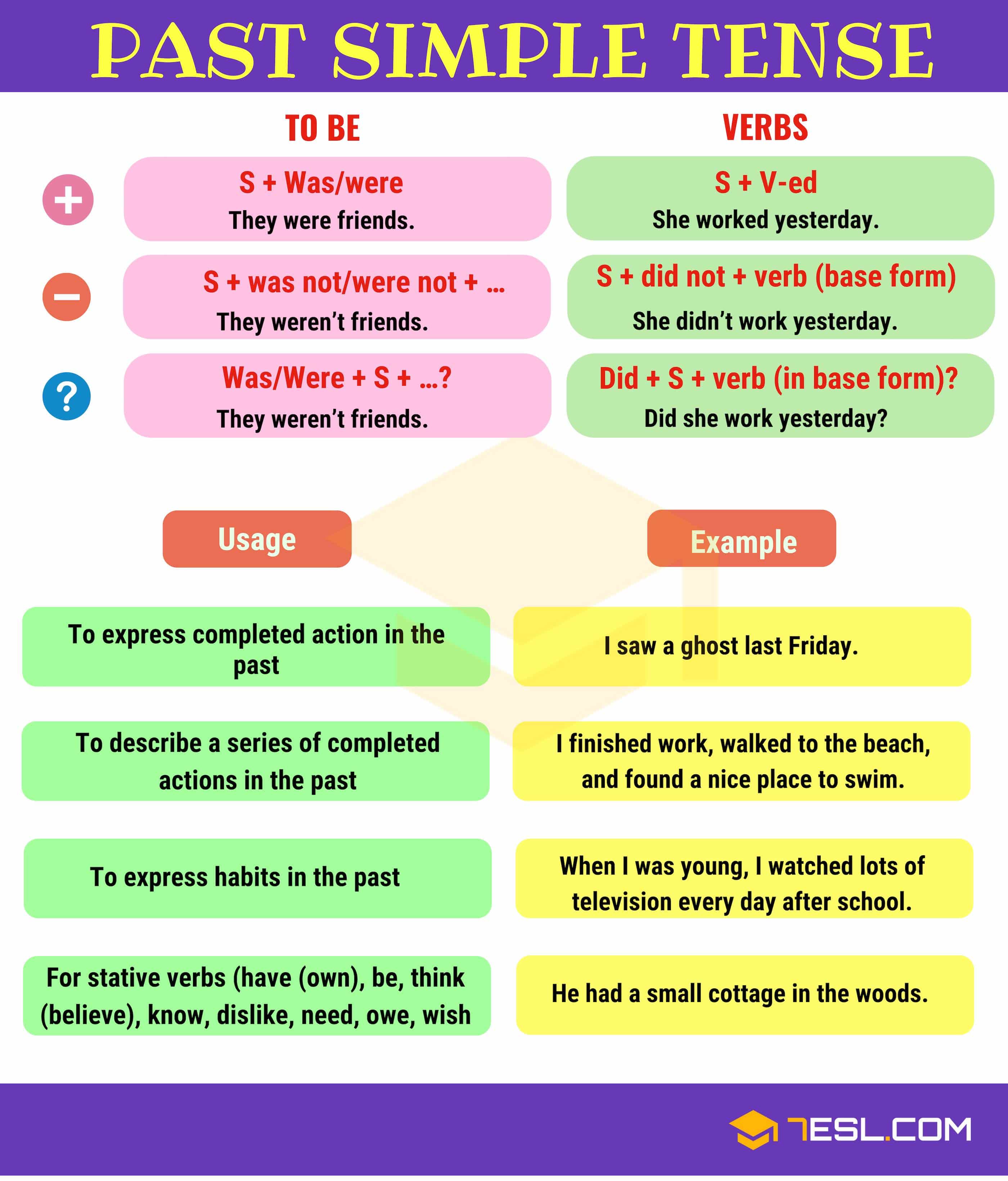
| Past Tense | ||
|---|---|---|
| Past tense is used to describe actions or events that happened in the past. It is formed by adding "-ed" to regular verbs or using irregular verb forms. Examples: She walked to the store. They ate dinner together. | ||
| 2 | ||
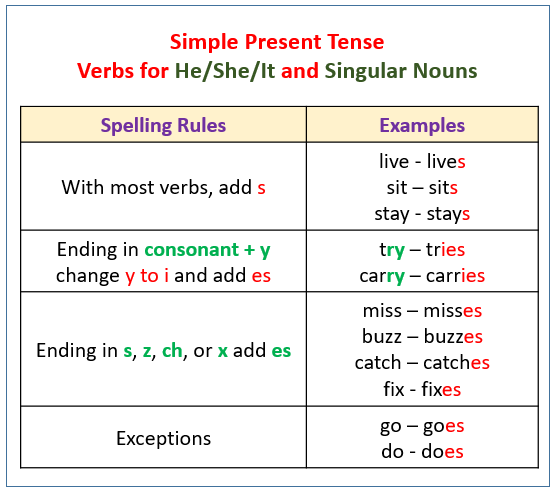
| Present Tense | ||
|---|---|---|
| Present tense is used to describe actions or events happening now or regularly. It is formed by using the base form of the verb (without adding "-ed" or "-s"). Examples: He plays soccer every weekend. I enjoy reading books. | ||
| 3 | ||
| Future Tense | ||
|---|---|---|
| Future tense is used to describe actions or events that will happen in the future. It is formed by using "will" or "shall" before the base form of the verb. Examples: They will visit their grandparents tomorrow. I shall complete the project by Friday. | ||
| 4 | ||
| Simple Tense | ||
|---|---|---|
| Simple tense refers to actions or events that are complete and not ongoing. It is used to state facts, general truths, or single completed actions. Examples: She wrote a book last year. The sun rises in the east. | ||
| 5 | ||
| Continuous Tense | ||
|---|---|---|
| Continuous tense refers to actions or events that are ongoing or in progress. It is used to describe actions happening at a specific time or over a period. Examples: I am studying for my exam. They were playing in the park. | ||
| 6 | ||
| Perfect Tense | ||
|---|---|---|
| Perfect tense refers to actions or events that are completed before a certain point in time. It is used to show the relationship between past, present, and future. Examples: She has already finished her homework. They will have arrived by 6 PM. | ||
| 7 | ||
| Perfect Continuous Tense | ||
|---|---|---|
| Perfect continuous tense refers to actions or events that started in the past, continued in the present, and may continue in the future. It is used to describe the duration of an action. Examples: I have been waiting for an hour. They will have been studying for the whole day. | ||
| 8 | ||
| Tense Consistency | ||
|---|---|---|
| Tense consistency refers to maintaining the same tense throughout a sentence or a paragraph. It helps to ensure clarity and coherence in writing or speaking. Example: Incorrect - She went to the store and buys some fruits. Correct - She went to the store and bought some fruits. | ||
| 9 | ||
| Conclusion | ||
|---|---|---|
| Tense is a crucial aspect of grammar that helps us convey the timing and sequence of events. By understanding and using different tenses correctly, we can communicate effectively in English. Practice and exposure to various examples are key to mastering the usage of tense. | ||
| 10 | ||




(80).jpg)