Postpartum Haemorrhage Presentation
| Introduction to Postpartum Haemorrhage | ||
|---|---|---|
| Postpartum haemorrhage (PPH) is defined as excessive bleeding after childbirth. It is a leading cause of maternal mortality and morbidity worldwide. PPH can occur both immediately after delivery or up to 6 weeks postpartum. | ||
| 1 | ||
| Risk Factors for Postpartum Haemorrhage | ||
|---|---|---|
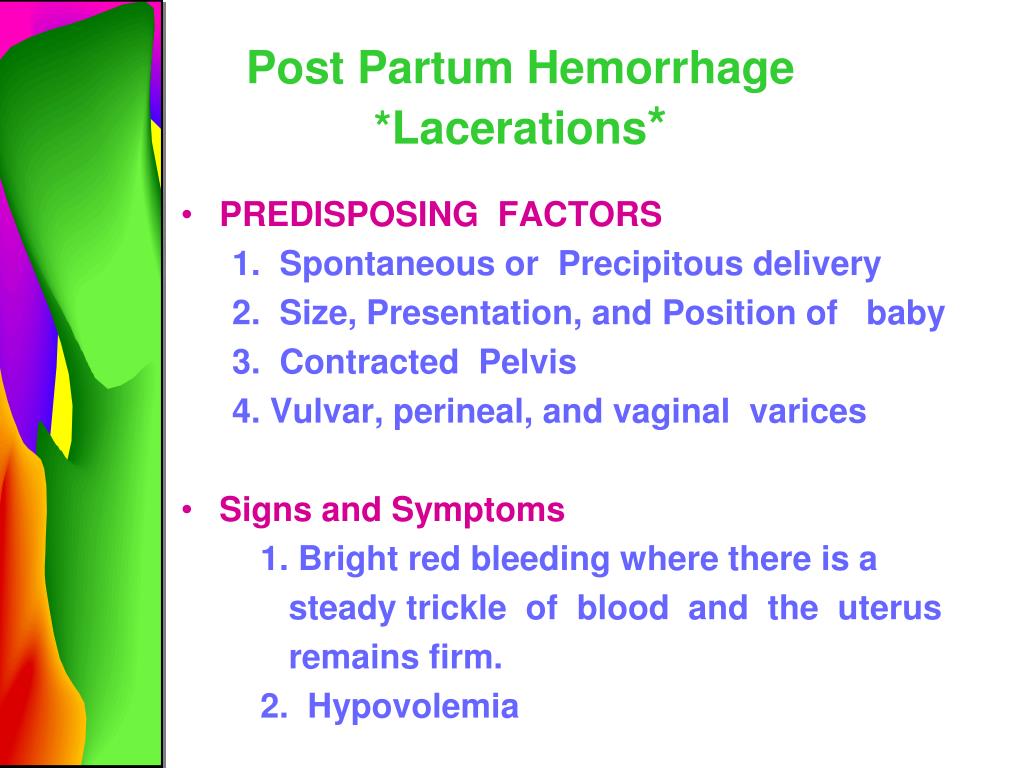
| Uterine atony, or failure of the uterus to contract after birth, is the most common cause of PPH. Other risk factors include previous PPH, multiple pregnancies, prolonged labor, and obesity. Medical conditions such as high blood pressure and coagulation disorders also increase the risk. | ||
| 2 | ||
| Signs and Symptoms of Postpartum Haemorrhage | ||
|---|---|---|
| Excessive or prolonged bleeding from the vagina is the primary sign of PPH. Other symptoms may include a rapid heart rate, low blood pressure, and pale skin. The presence of blood clots or tissue passage may also indicate PPH. | ||
| 3 | ||
| Management of Postpartum Haemorrhage | ||
|---|---|---|
| Immediate management involves uterine massage, administration of uterotonic drugs, and fluid resuscitation. If conservative measures fail, surgical interventions like uterine artery ligation or hysterectomy may be necessary. Timely blood transfusion and correction of coagulation abnormalities are crucial for managing PPH. | ||
| 4 | ||
| Prevention of Postpartum Haemorrhage | ||
|---|---|---|
| Active management of the third stage of labor, including the use of uterotonic drugs and controlled cord traction, can reduce the risk of PPH. Adequate prenatal care and identification of high-risk pregnancies are essential in preventing PPH. Prompt recognition and management of risk factors during labor and delivery can also help prevent PPH. | ||
| 5 | ||
| Complications of Postpartum Haemorrhage | ||
|---|---|---|
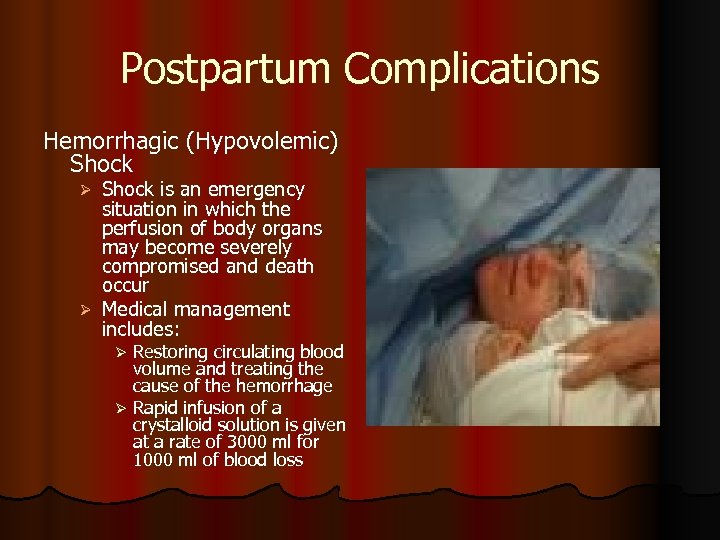
| Severe PPH can lead to hypovolemic shock, organ failure, and maternal death. Blood transfusions may be required to replace lost blood and restore hemoglobin levels. PPH can also increase the risk of postpartum depression and delayed bonding with the newborn. | ||
| 6 | ||
| Global Impact of Postpartum Haemorrhage | ||
|---|---|---|
| PPH is a major contributor to maternal mortality worldwide, especially in low-income countries with limited access to healthcare. Efforts are being made to improve access to skilled birth attendants, essential drugs, and blood transfusion services in these regions. Raising awareness about PPH and its prevention is crucial to reducing maternal mortality rates. | ||
| 7 | ||
| Research and Innovations in Postpartum Haemorrhage | ||
|---|---|---|
| Ongoing research focuses on developing new uterotonic drugs and interventions to control bleeding. Innovations like the use of tranexamic acid and balloon tamponade have shown promising results in managing PPH. Collaboration between healthcare providers, researchers, and policymakers is essential to drive advancements in PPH management. | ||
| 8 | ||
| Impact of COVID-19 on Postpartum Haemorrhage | ||
|---|---|---|
| The COVID-19 pandemic has disrupted healthcare systems and posed challenges in managing PPH. Limited access to healthcare facilities, reduced antenatal care, and delays in emergency obstetric care have increased the risk of PPH. Efforts are being made to adapt services and ensure continuity of care for pregnant individuals during the pandemic. | ||
| 9 | ||
| References (download PPTX file for details) | ||
|---|---|---|
| World Health Organization. (2019). WHO recomm... American College of Obstetricians and Gynecol... Sentilhes, L., Vayssière, C., Deneux-Tharaux,... |  | |
| 10 | ||
| References (download PPTX file for details) | ||
|---|---|---|
| World Health Organization. (2019). WHO recomm... American College of Obstetricians and Gynecol... Sentilhes, L., Vayssière, C., Deneux-Tharaux,... |  | |
| 11 | ||