Plant Hormones Presentation
| Introduction to Plant Hormones | ||
|---|---|---|
| Plant hormones are naturally occurring substances that regulate various physiological processes in plants. These hormones play a crucial role in plant growth, development, and response to environmental stimuli. There are five major types of plant hormones: auxins, gibberellins, cytokinins, abscisic acid, and ethylene. | ||
| 1 | ||
| Auxins | ||
|---|---|---|
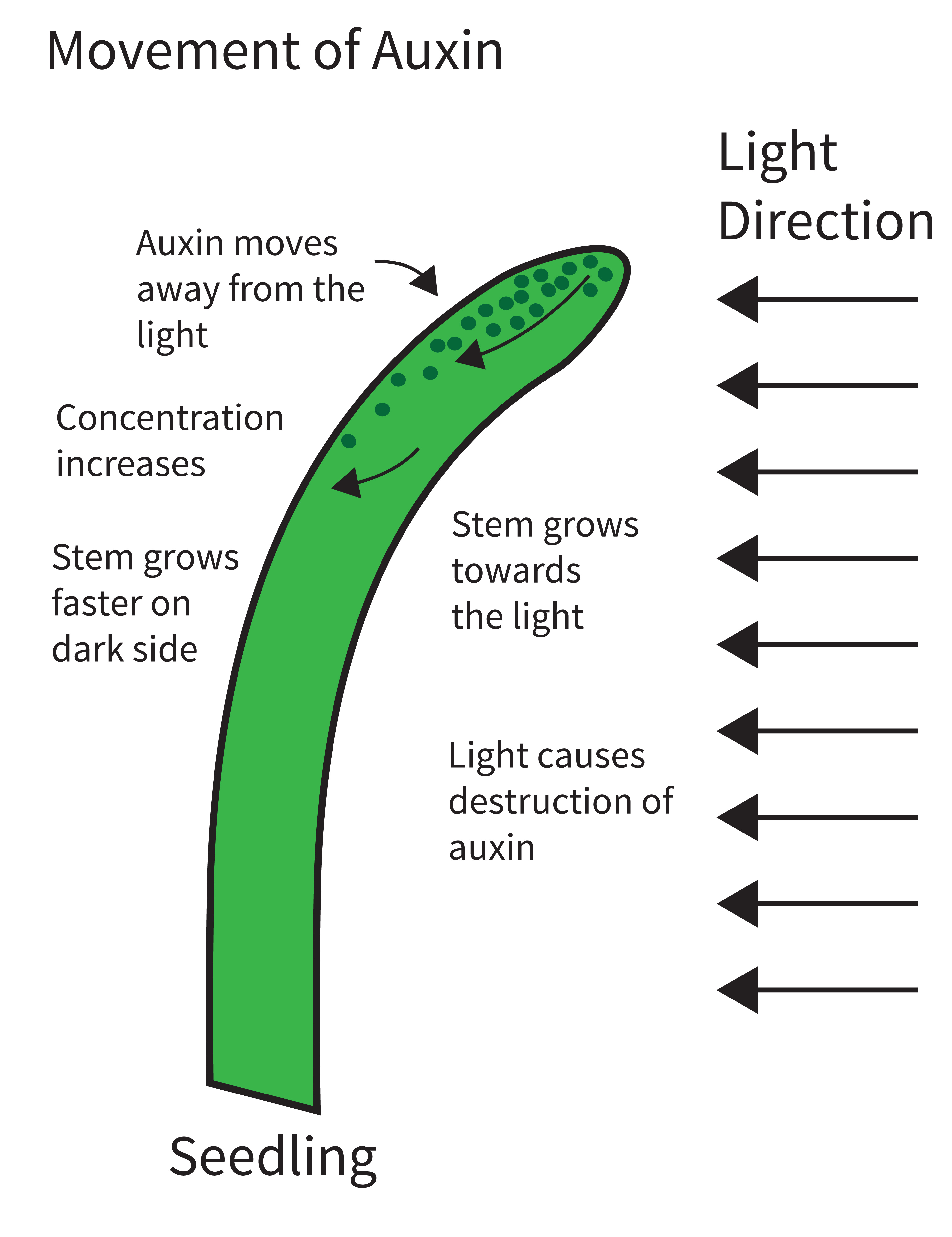
| Auxins are primarily responsible for cell elongation and growth in plants. They promote apical dominance, inhibiting the growth of lateral buds. Auxins also play a role in tropisms, such as phototropism (growth towards light) and gravitropism (growth in response to gravity). | ||
| 2 | ||
| Gibberellins | ||
|---|---|---|
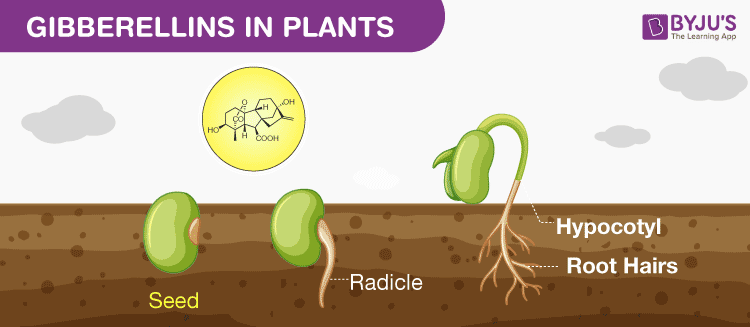
| Gibberellins are involved in stem elongation and cell division in plants. They promote seed germination and flowering. Gibberellins also play a role in fruit development and ripening. | ||
| 3 | ||
| Cytokinins | ||
|---|---|---|
| Cytokinins promote cell division, differentiation, and shoot formation in plants. They delay aging and senescence in plant tissues. Cytokinins also regulate nutrient mobilization and root growth. | ||
| 4 | ||
| Abscisic Acid | ||
|---|---|---|
| Abscisic acid is primarily involved in plant stress responses. It regulates seed dormancy and inhibits seed germination. Abscisic acid also controls stomatal closure in response to drought and other environmental stresses. | ||
| 5 | ||
| Ethylene | ||
|---|---|---|
| Ethylene is a gaseous hormone involved in various physiological processes in plants. It promotes fruit ripening and senescence. Ethylene also plays a role in leaf abscission, root growth inhibition, and response to mechanical stress. | ||
| 6 | ||
| Conclusion | ||
|---|---|---|
| Plant hormones are essential for the growth, development, and survival of plants. They regulate various physiological processes, including cell elongation, division, differentiation, and response to environmental stimuli. Understanding plant hormones is crucial for optimizing agricultural practices, improving crop yield, and managing plant stress. | ||
| 7 | ||