Nature Of Personality, Theories Of Personality, Determinants Pf Personality And Its Traits Presentation
| Introduction to Personality | ||
|---|---|---|
| Personality refers to the unique set of characteristics, behaviors, and patterns of thinking that define an individual. It shapes how we perceive and interact with the world, influencing our thoughts, emotions, and actions. Understanding personality is crucial for various fields, including psychology, sociology, and even business. | ||
| 1 | ||
| The Nature of Personality | ||
|---|---|---|
| Personality is a combination of genetic and environmental factors. It is relatively stable over time but can also be influenced by life experiences and personal growth. Personality traits can be categorized into different dimensions, such as introversion vs. extraversion, openness, conscientiousness, agreeableness, and neuroticism. | ||
| 2 | ||
| Theories of Personality - Psychodynamic Theory | ||
|---|---|---|
| The psychodynamic theory, proposed by Sigmund Freud, suggests that personality is influenced by unconscious processes and childhood experiences. According to Freud, personality consists of three components: the id (basic instincts and desires), the ego (mediator between the id and superego), and the superego (moral conscience). Freud also introduced defense mechanisms, such as repression and displacement, which help individuals cope with anxiety and conflicts. |  | |
| 3 | ||
| Theories of Personality - Trait Theory | ||
|---|---|---|
| Trait theory focuses on identifying and measuring specific traits that contribute to personality. The Big Five model is one of the most widely accepted trait theories, consisting of five dimensions: openness, conscientiousness, extraversion, agreeableness, and neuroticism. Trait theory suggests that individuals possess varying degrees of each trait, influencing their behavior and attitudes. | ||
| 4 | ||
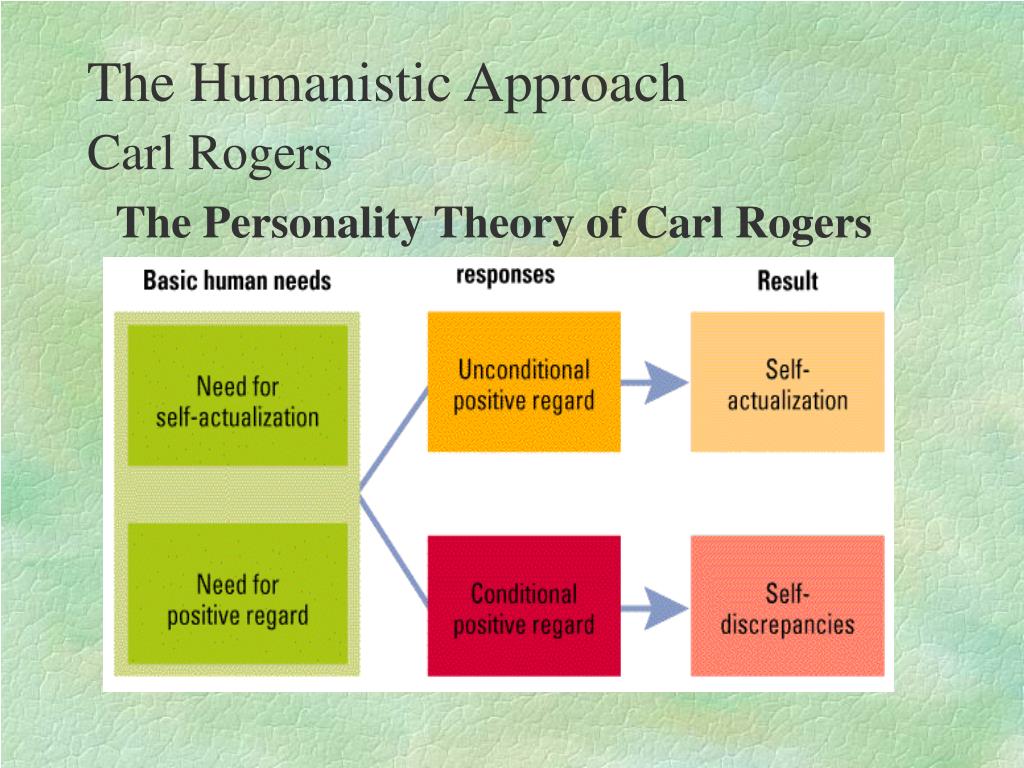
| Theories of Personality - Humanistic Theory | ||
|---|---|---|
| Humanistic theory emphasizes individual potential for personal growth and self-actualization. Carl Rogers proposed a humanistic approach known as person-centered therapy, emphasizing empathy, unconditional positive regard, and genuineness. Humanistic theory suggests that individuals strive to fulfill their innate needs for self-esteem, love, and self-actualization. | ||
| 5 | ||
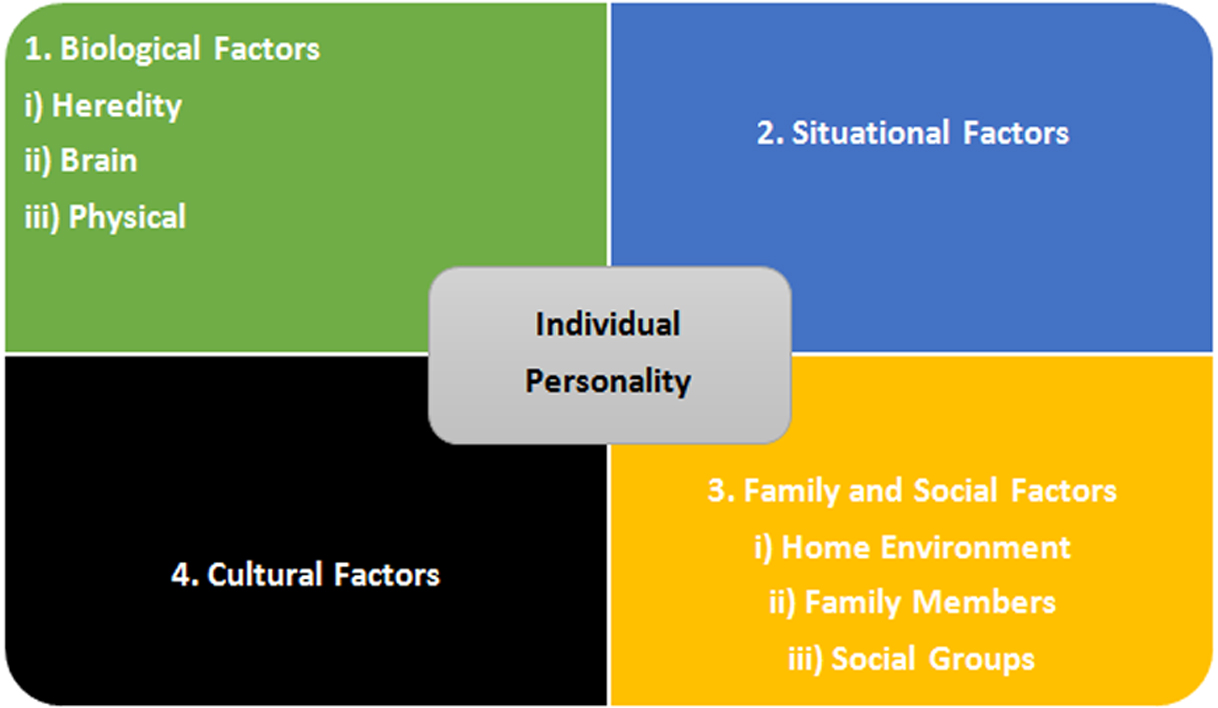
| Determinants of Personality - Genetic Factors | ||
|---|---|---|
| Genetic factors play a significant role in shaping personality traits. Twin and adoption studies provide evidence for the heritability of personality traits. Specific genes and variations, such as the DRD4 gene, have been associated with certain personality traits like novelty-seeking. | ||
| 6 | ||
| Determinants of Personality - Environmental Factors | ||
|---|---|---|
| Environmental factors, including family, culture, and social experiences, also influence personality development. Parenting styles, peer influences, and cultural norms shape an individual's personality. Life events and experiences, such as trauma or success, can impact personality and lead to significant changes. | ||
| 7 | ||
| Determinants of Personality - Cognitive Factors | ||
|---|---|---|
| Cognitive factors, such as beliefs, thoughts, and interpretations, contribute to personality formation. Albert Bandura's social cognitive theory emphasizes the role of observational learning in shaping personality. Cognitive processes, such as self-efficacy and locus of control, influence how individuals perceive and respond to the world. | ||
| 8 | ||
| Personality Traits | ||
|---|---|---|
| Personality traits are enduring patterns of thoughts, feelings, and behaviors. Commonly studied traits include extraversion, agreeableness, conscientiousness, emotional stability, and openness. Traits can be assessed using self-report questionnaires, behavioral observations, and projective tests. | ||
| 9 | ||
| Conclusion | ||
|---|---|---|
| Personality is a complex and multifaceted concept that is influenced by various factors. Different theories, such as psychodynamic, trait, and humanistic theories, provide different perspectives on personality. Genetic, environmental, and cognitive factors all contribute to the development of an individual's unique personality traits. Note: This is just a sample presentation outline. You can expand on each sub-bullet and add relevant images or examples to make it more engaging. | ||
| 10 | ||

/2795392-article-what-is-nature-versus-nurture-5a971887eb97de0036685ad3.png)




:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/personality-perspectives-2795950_FINAL-5be9973046e0fb0026c89ca5.png)