Incident Management Presentation
| Introduction to Incident Management | ||
|---|---|---|
| Incident management is a structured approach to handling and resolving incidents in an organization. It involves identifying, analyzing, and responding to incidents in a timely and effective manner. The goal of incident management is to minimize the impact of incidents on business operations and ensure a quick recovery. | ||
| 1 | ||
| Key Components of Incident Management | ||
|---|---|---|
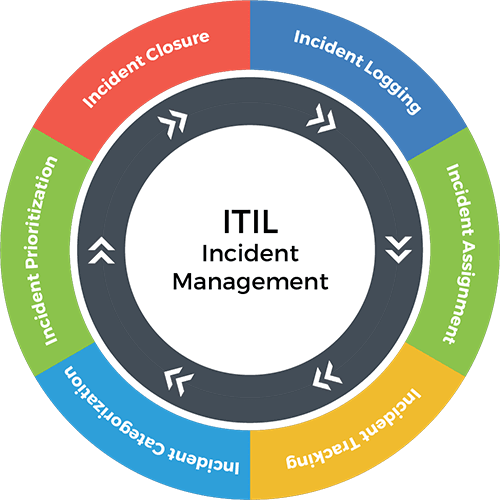
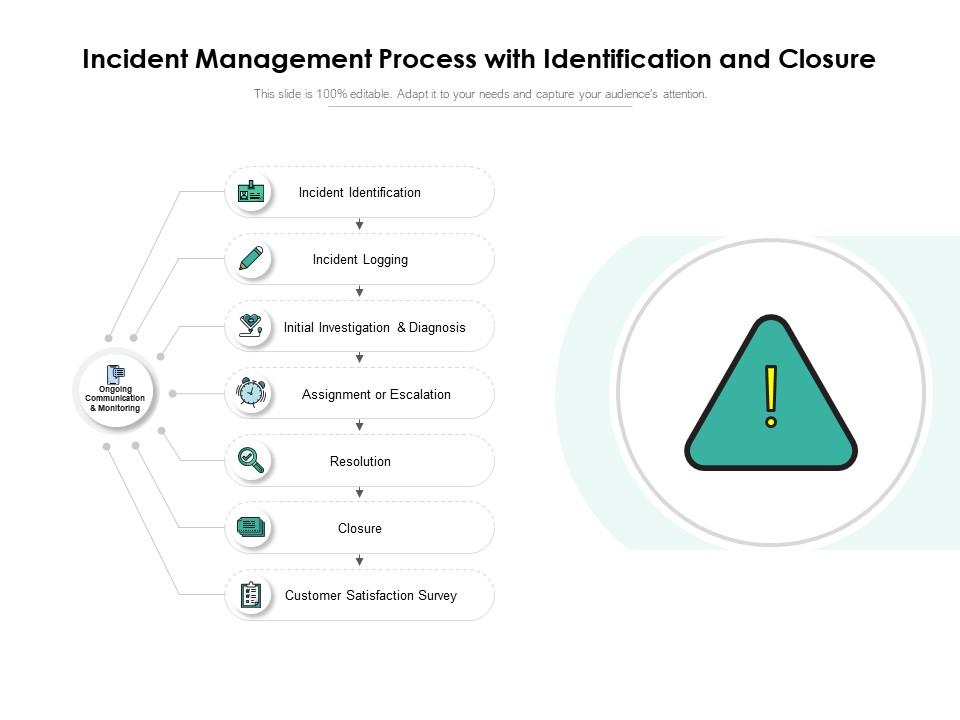
| Incident Identification: The process of detecting and recognizing incidents, often through monitoring systems and user reports. Incident Logging: Capturing detailed information about incidents, including date, time, description, and initial impact assessment. Incident Categorization: Classifying incidents based on their nature, urgency, and impact to prioritize response and resolution efforts. | ||
| 2 | ||
| Incident Response and Escalation | ||
|---|---|---|
| Incident Triage: Assessing the severity and urgency of incidents to determine the appropriate response and resources needed. Incident Investigation: Conducting a thorough analysis to identify the root cause and contributing factors of the incident. Incident Escalation: The process of involving higher-level support or management when incidents cannot be resolved within established timeframes. | ||
| 3 | ||
| Incident Resolution and Closure | ||
|---|---|---|
| Incident Resolution: Taking necessary actions to resolve incidents, including implementing workarounds or permanent fixes. Incident Communication: Keeping stakeholders informed about incident status, progress, and resolution through regular updates. Incident Closure: Declaring an incident as resolved when the impact is mitigated, and documenting the actions taken for future reference. | ||
| 4 | ||
| Importance of Incident Management | ||
|---|---|---|
| Minimizes Downtime: Effective incident management reduces the duration and impact of service disruptions, minimizing downtime for users. Improves Customer Satisfaction: Prompt and efficient incident resolution enhances customer satisfaction and maintains trust in the organization. Enhances Organizational Resilience: By learning from incidents and implementing preventive measures, organizations become more resilient to future disruptions. | ||
| 5 | ||
| Best Practices in Incident Management | ||
|---|---|---|
| Establishing Clear Incident Management Processes and Policies: Defining roles, responsibilities, and workflows to ensure a consistent and standardized approach. Implementing Incident Management Tools: Utilizing specialized software and tools to automate incident logging, tracking, and reporting. Conducting Regular Incident Management Reviews: Evaluating incident response performance, identifying areas for improvement, and implementing corrective actions. [Note: This is a basic outline for a 6-slide presentation on incident management. Additional slides and more detailed content can be added based on specific requirements and audience.] |  | |
| 6 | ||