Fullwave And Halfwave Presentation
| Introduction | ||
|---|---|---|
| Fullwave and halfwave are rectification techniques used in electrical circuits. These techniques are used to convert AC (alternating current) to DC (direct current). Rectifiers play a crucial role in various electronic devices and power supplies. | ||
| 1 | ||
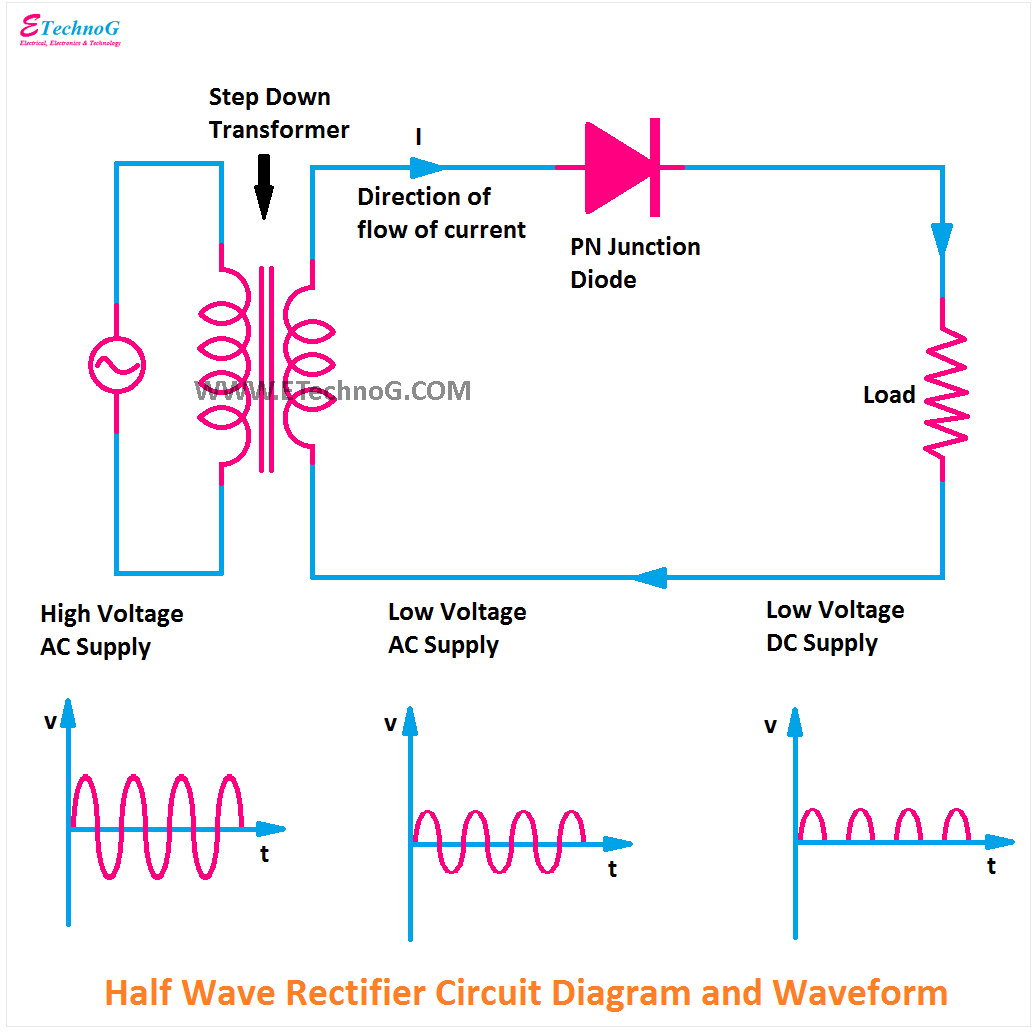
| Halfwave Rectification | ||
|---|---|---|
| Halfwave rectification allows only one half of the AC waveform to pass through. During the positive half-cycle, the diode conducts and allows current flow. During the negative half-cycle, the diode blocks current flow. | ||
| 2 | ||
| Halfwave Rectification Advantages | ||
|---|---|---|
| Simple and cost-effective solution for low-power applications. Requires fewer components compared to fullwave rectification. Suitable for applications where a lower average output voltage is acceptable. | ||
| 3 | ||
| Halfwave Rectification Disadvantages | ||
|---|---|---|
| Generates a considerable amount of ripple voltage. Low efficiency due to only utilizing half of the AC waveform. Not suitable for applications requiring a stable and smooth DC output. | ||
| 4 | ||
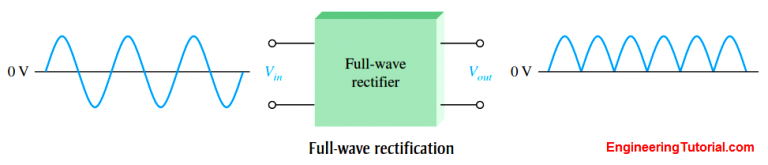
| Fullwave Rectification | ||
|---|---|---|
| Fullwave rectification allows both halves of the AC waveform to be utilized. Utilizes two diodes in a bridge configuration to rectify the AC signal. Provides a more efficient and smoother DC output compared to halfwave rectification. | ||
| 5 | ||
| Fullwave Rectification Advantages | ||
|---|---|---|
| Provides a higher average output voltage compared to halfwave rectification. Produces a lower amount of ripple voltage, resulting in a more stable DC output. Suitable for applications requiring a higher efficiency and smoother DC supply. | ||
| 6 | ||
| Fullwave Rectification Disadvantages | ||
|---|---|---|
| Requires additional components compared to halfwave rectification. More complex circuitry and higher cost compared to halfwave rectification. More components mean increased chances of failure or malfunctions. | ||
| 7 | ||
| Comparison - Halfwave vs Fullwave | ||
|---|---|---|
| Halfwave rectification is simpler and cost-effective, while fullwave rectification provides a more efficient and stable output. Halfwave rectification is suitable for low-power applications, while fullwave rectification is preferred for high-power applications. Halfwave rectification generates more ripple voltage, while fullwave rectification produces smoother and more stable DC output. | ||
| 8 | ||
| Applications | ||
|---|---|---|
| Halfwave rectification is commonly used in low-cost power supplies, battery chargers, and small electronic devices. Fullwave rectification is widely used in power electronics, high-power supplies, and industrial applications. Your third bullet | ||
| 9 | ||
| Conclusion | ||
|---|---|---|
| Fullwave and halfwave rectification techniques are essential for converting AC to DC in various electrical and electronic applications. The choice between halfwave and fullwave rectification depends on factors such as cost, efficiency, ripple voltage requirements, and power output. Your third bullet | ||
| 10 | ||
| References (download PPTX file for details) | ||
|---|---|---|
| [Insert reference 1]... [Insert reference 2]... [Insert reference 3]... |  | |
| 11 | ||