Fuels Cells Presentation
| Introduction to Fuel Cells | ||
|---|---|---|
| Fuel cells are electrochemical devices that convert chemical energy from a fuel into electrical energy. They are highly efficient and produce minimal greenhouse gas emissions. Fuel cells have a wide range of applications, including transportation, stationary power generation, and portable devices. | 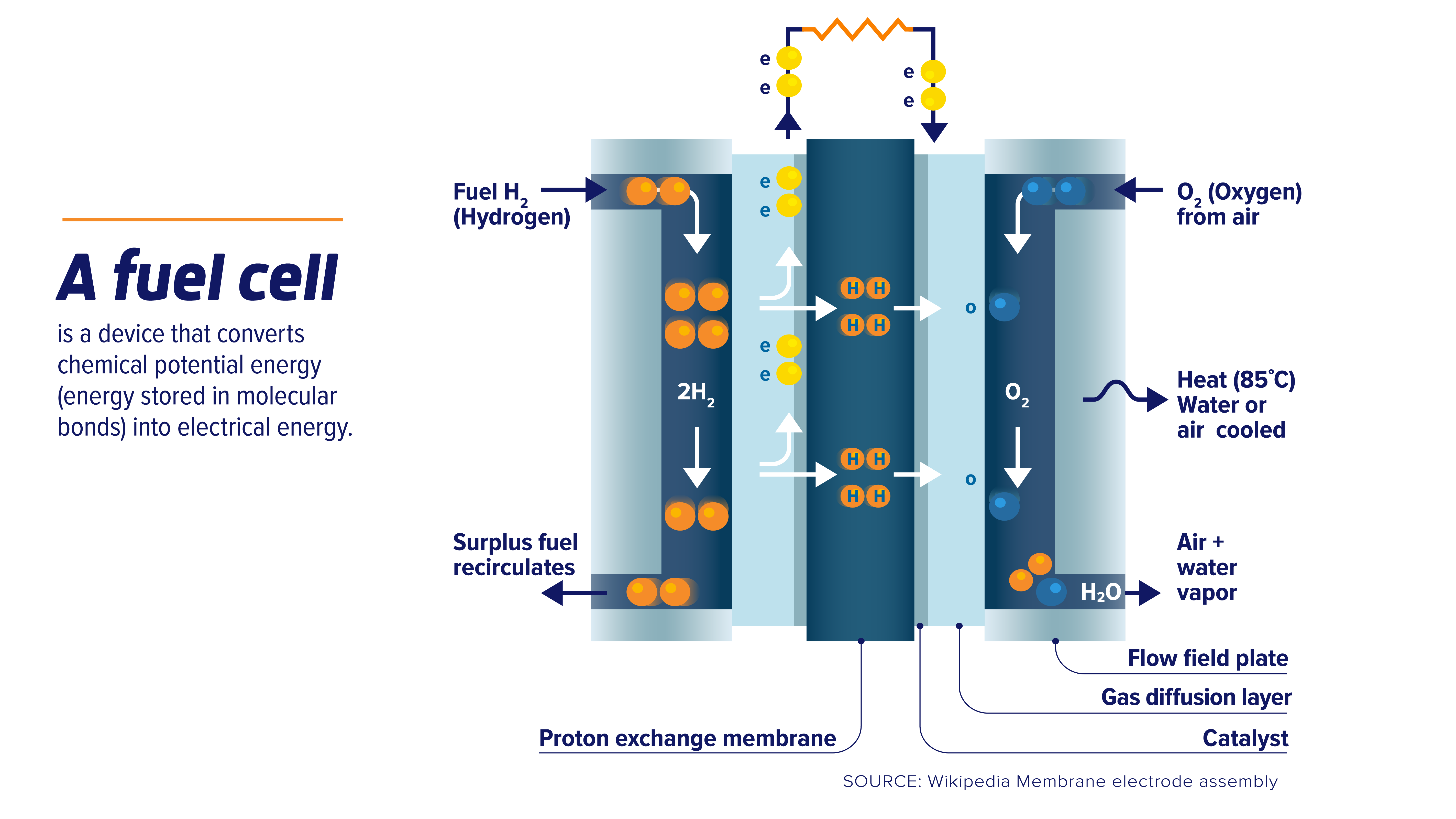 | |
| 1 | ||
| How Fuel Cells Work | ||
|---|---|---|
| Fuel cells consist of an anode, cathode, and electrolyte. Hydrogen fuel is supplied to the anode, while oxygen or air is supplied to the cathode. The fuel undergoes oxidation at the anode, releasing electrons that travel through an external circuit, producing electricity. | ||
| 2 | ||
| Types of Fuel Cells | ||
|---|---|---|
| Proton Exchange Membrane Fuel Cells (PEMFCs) are commonly used in vehicles and portable applications. Solid Oxide Fuel Cells (SOFCs) operate at high temperatures and are suitable for stationary power generation. Molten Carbonate Fuel Cells (MCFCs) and Phosphoric Acid Fuel Cells (PAFCs) are used in large-scale stationary applications. | 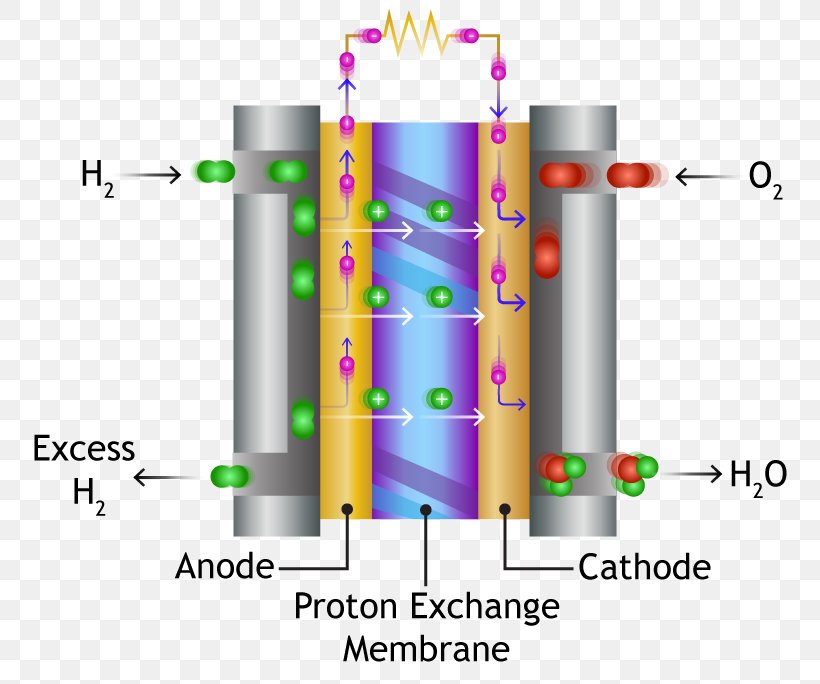 | |
| 3 | ||
| Advantages of Fuel Cells | ||
|---|---|---|
| High efficiency: Fuel cells can achieve up to 60% efficiency in converting fuel into electricity. Reduced emissions: Fuel cells produce lower emissions compared to traditional combustion-based power generation. Versatility: Fuel cells can use a variety of fuels, including hydrogen, natural gas, methanol, and ethanol. |  | |
| 4 | ||
| Challenges of Fuel Cells | ||
|---|---|---|
| Cost: Fuel cells are currently more expensive than traditional power generation technologies. Infrastructure: The lack of hydrogen refueling stations poses a challenge for the widespread adoption of fuel cell vehicles. Durability: The longevity and reliability of fuel cell systems still need improvement. |  | |
| 5 | ||
| Applications of Fuel Cells | ||
|---|---|---|
| Transportation: Fuel cell vehicles offer zero-emission transportation, with longer driving ranges and shorter refueling times compared to electric vehicles. Stationary Power Generation: Fuel cells can provide clean and reliable power for homes, buildings, and remote areas. Portable Devices: Fuel cells can be used as portable power sources for electronic devices, such as laptops and smartphones. | ||
| 6 | ||
| Current Developments | ||
|---|---|---|
| Research is focused on improving fuel cell performance, durability, and reducing costs. Development of hydrogen production methods from renewable sources. Integration of fuel cells with energy storage systems to enhance reliability and grid stability. |  | |
| 7 | ||
| Future Outlook | ||
|---|---|---|
| Fuel cells have the potential to play a significant role in the transition to a low-carbon energy future. Advancements in materials and manufacturing processes will drive down costs and increase accessibility. Increased investments and government support will accelerate the deployment of fuel cell technologies. |  | |
| 8 | ||
| References (download PPTX file for details) | ||
|---|---|---|
| U.S. Department of Energy. (2021). Fuel Cells... Fuel Cell and Hydrogen Energy Association. (n... Retrieved from https:// www.fchea.org/ fuel-c... |  | |
| 9 | ||
