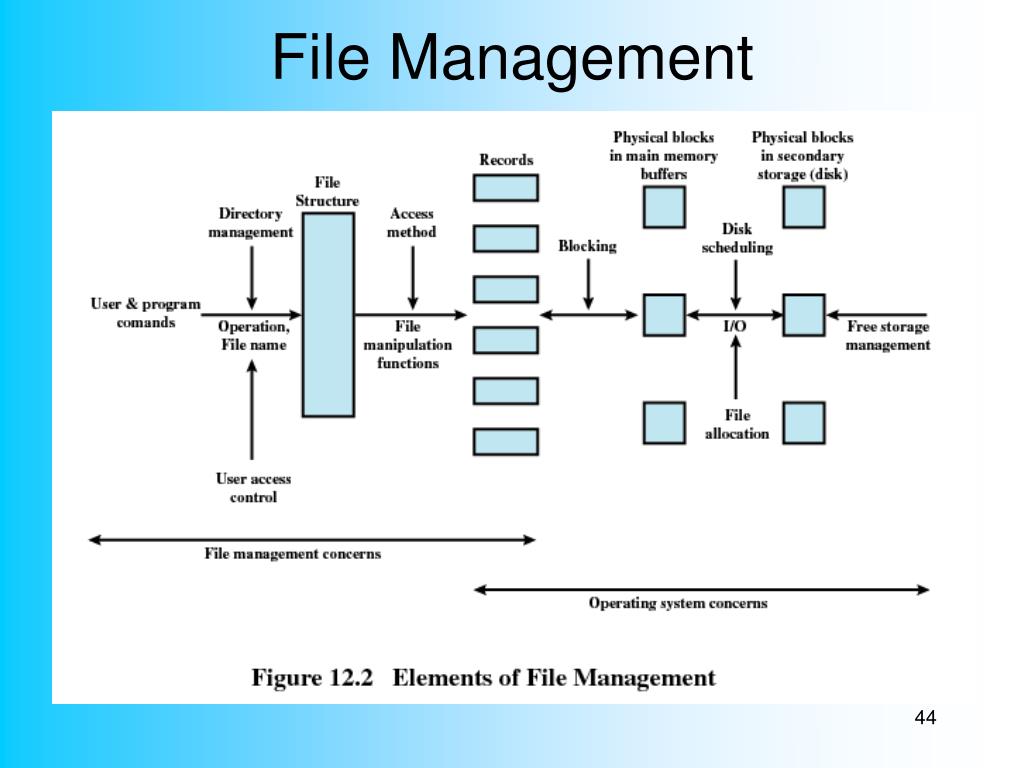
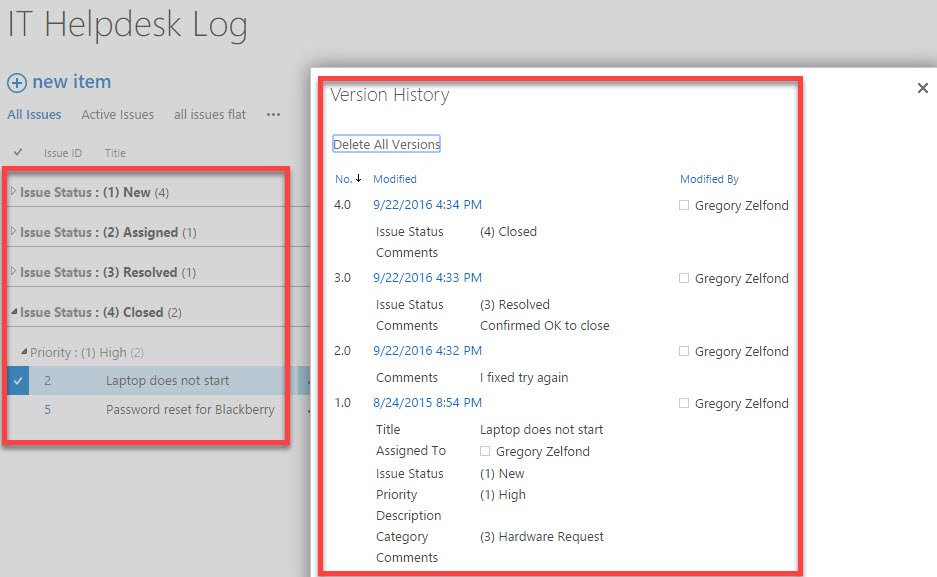
File Management Presentation
| Introduction to File Management | ||
|---|---|---|
| File management refers to the process of organizing, storing, and retrieving digital files efficiently. Effective file management is crucial for maximizing productivity and ensuring data security. Proper file management helps in avoiding clutter, saving time, and maintaining a structured work environment. | ||
| 1 | ||
| Benefits of File Management | ||
|---|---|---|
| Improved organization: File management allows for systematic arrangement of files, making it easier to locate and access information. Enhanced productivity: With efficient file management, users can quickly retrieve and work on files, leading to increased productivity. Data protection: Proper file management includes backup and recovery strategies, minimizing the risk of data loss due to hardware failure or human error. | ||
| 2 | ||
| File Organization Techniques | ||
|---|---|---|
| Hierarchical structure: Organize files in a tree-like structure with main folders, subfolders, and files, creating a logical hierarchy. Descriptive file naming: Use clear and concise names for files, including relevant keywords to facilitate quick search and identification. Categorization: Group files into categories based on their content, purpose, or project, making it easier to locate related files. | ||
| 3 | ||
| Folder Structures | ||
|---|---|---|
| Alphabetical: Arrange folders in alphabetical order to simplify navigation and make it easier to find specific folders. Chronological: Organize folders based on the date or time of creation, useful for projects or files with time-sensitive information. Functional: Group folders based on their function, such as "Finance," "Marketing," or "Human Resources," to streamline file access and collaboration. | ||
| 4 | ||
| File Naming Conventions | ||
|---|---|---|
| Consistency: Establish and follow a standardized naming convention to ensure uniformity across files and folders. Use of metadata: Include relevant metadata in file names, such as document type, date, version, or project name, to provide additional context. Avoid special characters: Use alphanumeric characters and underscores to prevent compatibility issues or file system limitations. | ||
| 5 | ||
| File Storage Options | ||
|---|---|---|
| Local storage: Storing files on a computer's hard drive or an external storage device provides quick access but may limit collaboration and backup options. Cloud storage: Utilizing cloud-based platforms like Google Drive or Dropbox allows for remote access, collaboration, and automatic backups. Network drives: Storing files on a shared network drive facilitates centralized access, collaboration, and backup within an organization. | ||
| 6 | ||
| File Versioning | ||
|---|---|---|
| Version control: Maintain different versions of a file to track changes, facilitate collaboration, and ensure data integrity. Document history: Keep a record of file modifications, including who made the changes and when, to easily revert to previous versions if needed. Collaboration tools: Utilize collaboration platforms like Microsoft SharePoint or Google Docs that offer built-in version control and document tracking. | ||
| 7 | ||
| Backup and Recovery | ||
|---|---|---|
| Regular backups: Create a backup schedule to ensure critical files are regularly copied to a separate storage location, minimizing the risk of data loss. Redundancy: Maintain multiple copies of important files in different storage devices or locations to safeguard against hardware failure or disasters. Test backups: Periodically restore files from backups to verify their integrity and ensure successful recovery when needed. | ||
| 8 | ||
| Security Considerations | ||
|---|---|---|
| Access control: Implement user permissions and restrictions to limit file access to authorized individuals and protect sensitive information. Encryption: Secure files with encryption to prevent unauthorized access, providing an additional layer of protection for sensitive data. Antivirus software: Regularly scan files for malware or viruses to mitigate the risk of compromising file integrity or spreading malicious software. | ||
| 9 | ||
| Conclusion | ||
|---|---|---|
| Effective file management is essential for productivity, organization, and data security. By organizing files, establishing naming conventions, utilizing storage options, and implementing backup strategies, users can optimize their file management practices. Prioritizing file management leads to time savings, reduced stress, and improved efficiency in both personal and professional settings. | ||
| 10 | ||