Calculation Systems C++ Presentation
| Introduction to Calculation Systems in C++ | ||
|---|---|---|
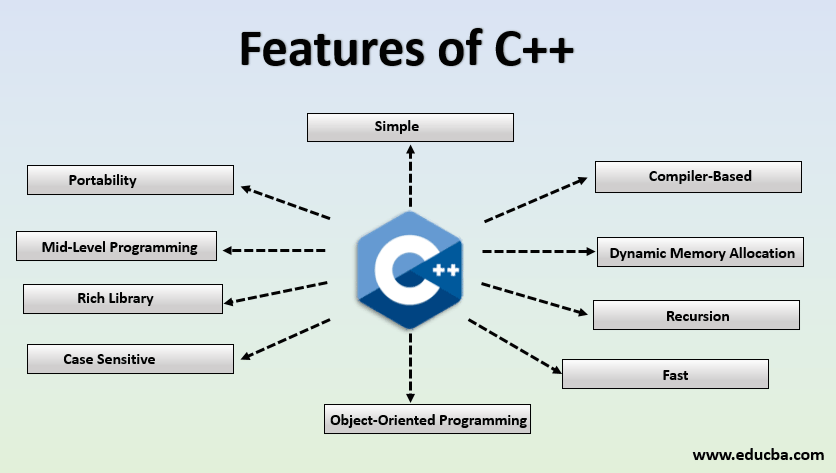
| Calculation systems in C++ are powerful tools used for performing various mathematical calculations. C++ provides a wide range of functions and operators that can be used to implement different calculation systems. These calculation systems enable programmers to solve complex mathematical problems efficiently. | ||
| 1 | ||
| Basic Arithmetic Operators | ||
|---|---|---|
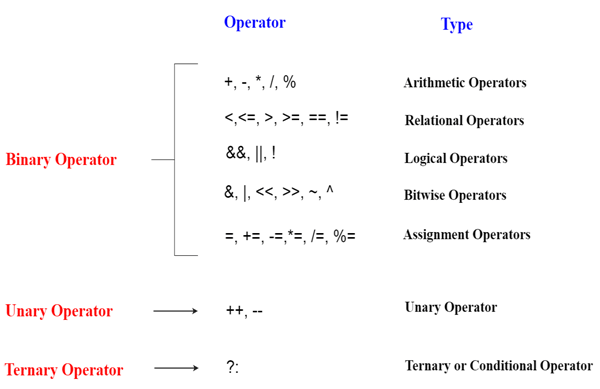
| C++ supports basic arithmetic operators such as addition (+), subtraction (-), multiplication ( ), and division (/ ). These operators are used to perform basic arithmetic calculations in C++. | ||
| 2 | ||
| Mathematical Functions | ||
|---|---|---|
| C++ provides a library of mathematical functions that can be used for advanced calculations. These functions include trigonometric functions (sin, cos, tan), exponential functions (pow, exp), and logarithmic functions (log, log10). Example: double sineValue = sin(0.5); // returns the sine value of 0.5 radians. | ||
| 3 | ||
| Precedence and Associativity | ||
|---|---|---|
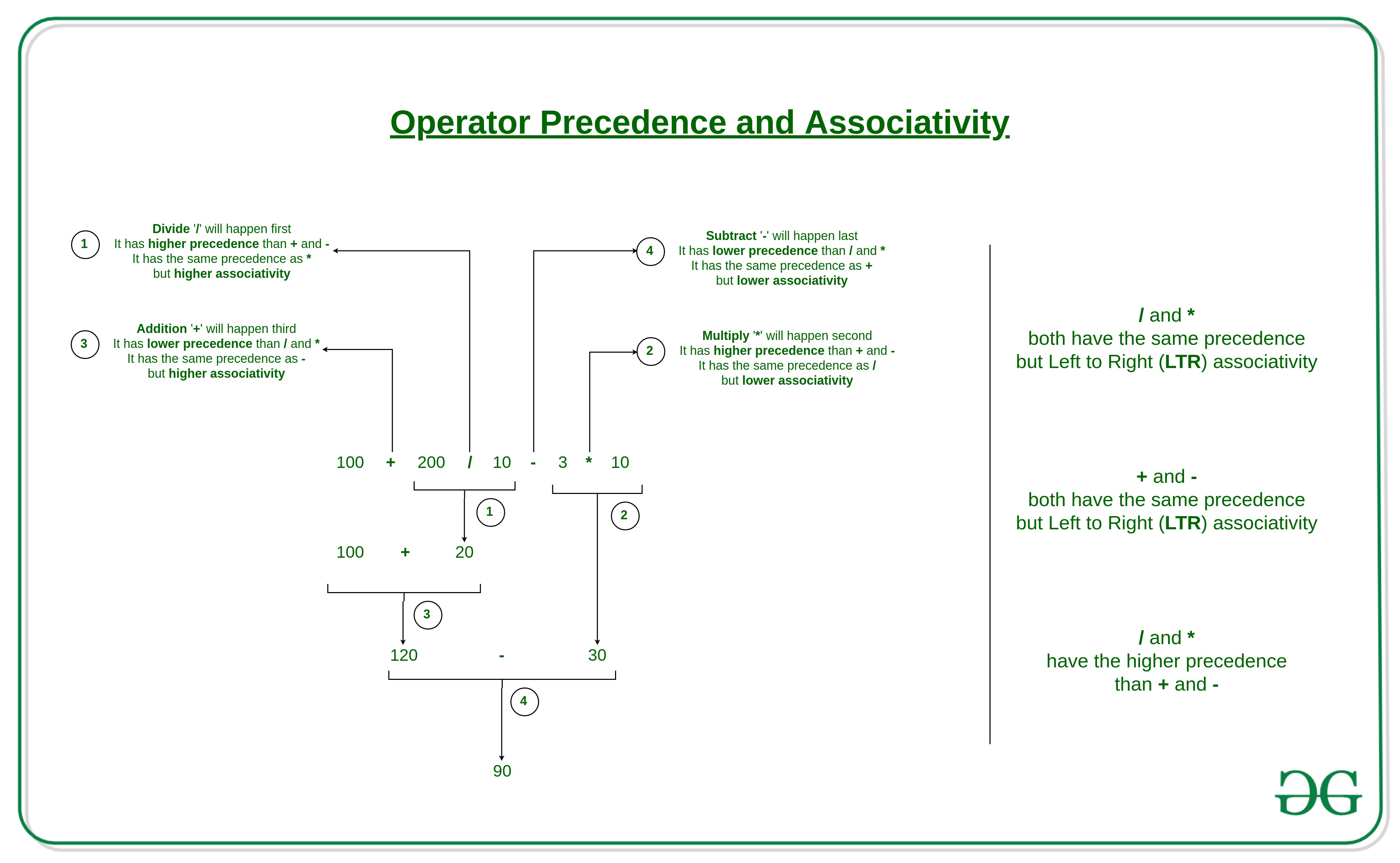
| C++ follows a set of rules called operator precedence and associativity to determine the order of evaluation in expressions. Operators with higher precedence are evaluated first. Example: int result = 10 + 5 | ||
| 4 | ||
| Increment and Decrement Operators | ||
|---|---|---|
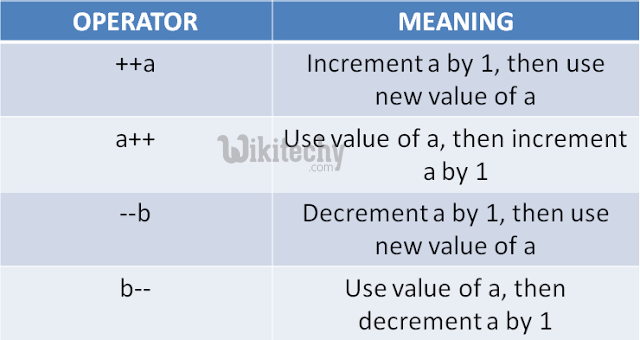
| C++ provides increment (++) and decrement (--) operators to increase or decrease the value of variables by 1. These operators can be used in calculations or loops. Example: int count = 5; count++; // count will be 6. | ||
| 5 | ||
| Assignment Operators | ||
|---|---|---|
| C++ provides various assignment operators such as =, +=, -=, =, and / =. These operators are used to assign values to variables and perform arithmetic calculations simultaneously. | ||
| 6 | ||
| Bitwise Operators | ||
|---|---|---|
| C++ supports bitwise operators such as AND (&), OR (|), XOR (^), left shift (<<), and right shift (>>). These operators perform bit-level operations on integers. Example: int result = 5 & 3; // result will be 1. |  | |
| 7 | ||
| Conditional Operators | ||
|---|---|---|
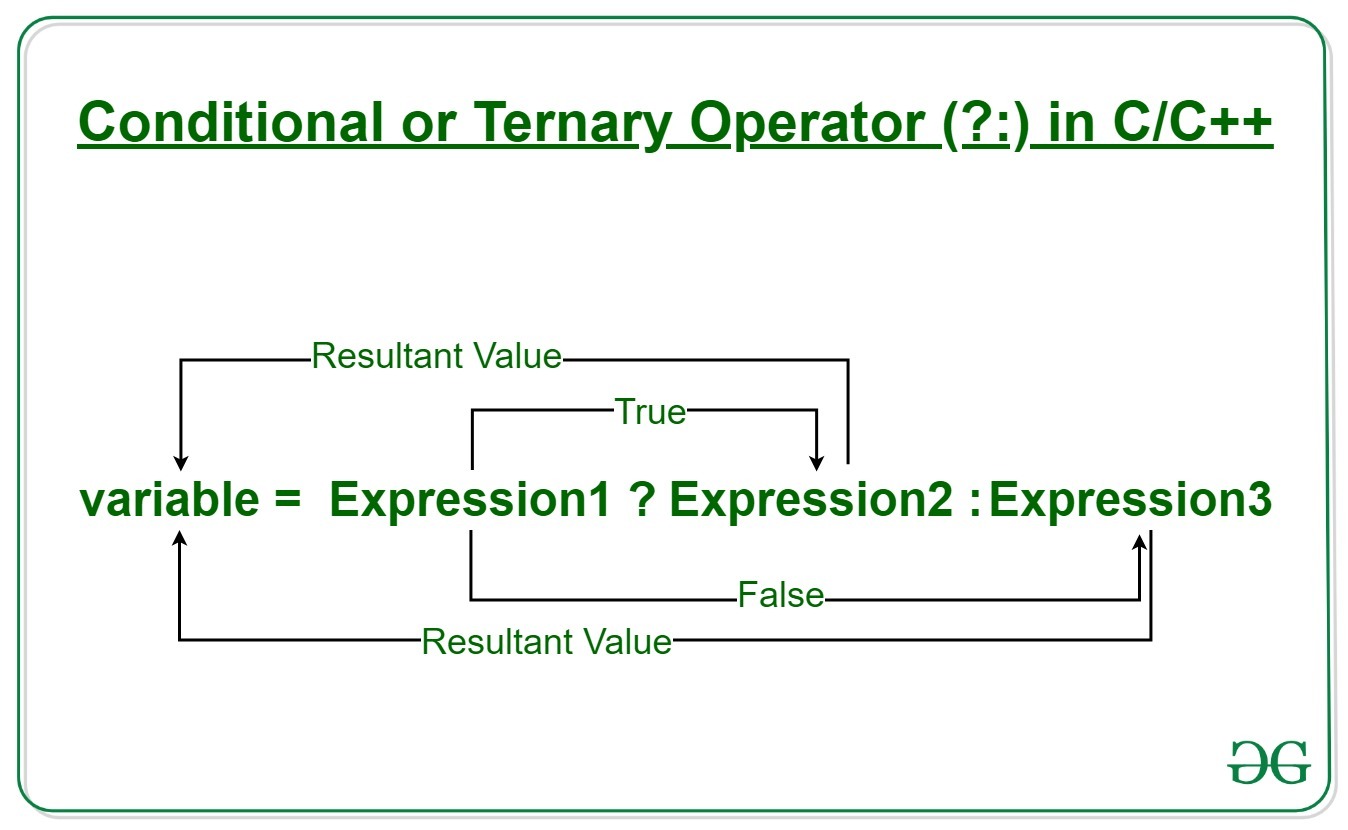
| C++ provides conditional operators such as ternary operator (? :) to perform conditional calculations. These operators evaluate a condition and return one of two values based on the result. Example: int x = 5, y = 10; int result = (x > y) ? x : y; // result will be 10. | ||
| 8 | ||
| Mathematical Constants | ||
|---|---|---|
| C++ provides predefined mathematical constants such as M_PI for the value of pi and M_E for the value of Euler's number. These constants can be used in calculations without explicitly defining their values. Example: double circleArea = M_PI | ||
| 9 | ||
| Error Handling | ||
|---|---|---|
| Error handling is an important aspect of calculation systems in C++. Proper error handling techniques such as exception handling should be implemented to handle unexpected errors during calculations. Example: try { // code that may throw an exception } catch (exceptionType e) { / / code to handle the exception } Note: This is a general overview of calculation systems in C++. More advanced topics and specific calculation systems can be explored in detail. | ||
| 10 | ||