Ai Presentation
| Introduction to AI | ||
|---|---|---|
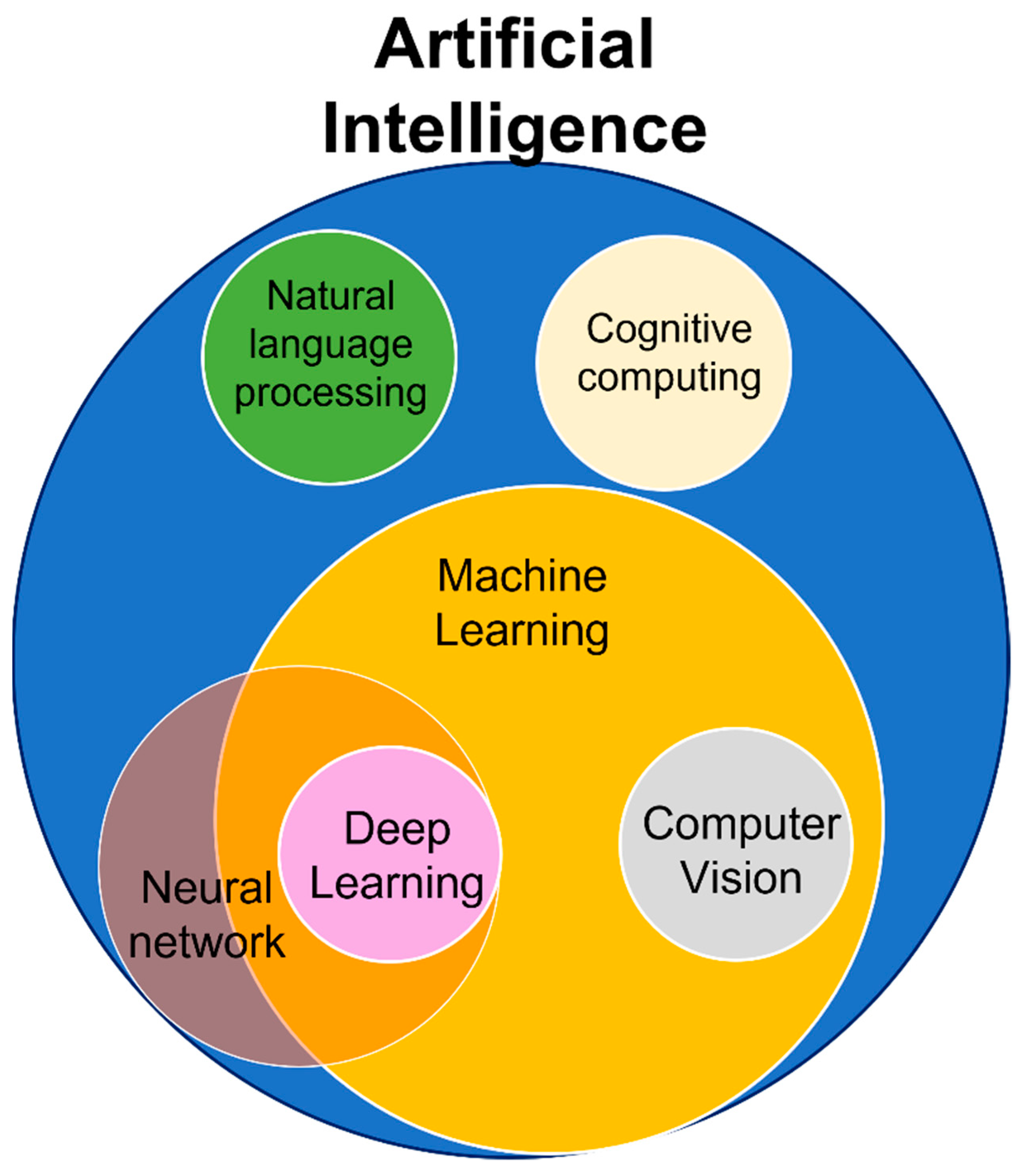
| Artificial Intelligence (AI) refers to the simulation of human intelligence in machines. AI enables computers to perform tasks that would typically require human intelligence. AI has the potential to revolutionize various industries, including healthcare, finance, and transportation. | ||
| 1 | ||
| Types of AI | ||
|---|---|---|
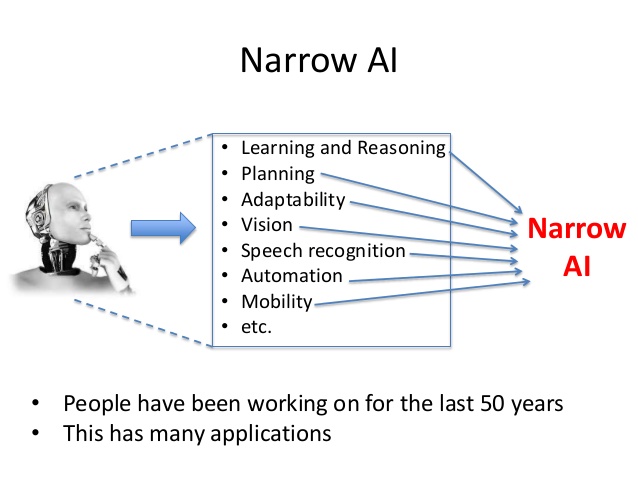
| Narrow AI, also known as Weak AI, is designed to perform specific tasks and lacks general human intelligence. General AI, also known as Strong AI, possesses human-like intelligence and can perform any intellectual task that a human being can do. Superintelligent AI surpasses human intelligence and is capable of outperforming humans in almost every task. | ||
| 2 | ||
| Machine Learning | ||
|---|---|---|
| Machine Learning is a subset of AI that enables computers to learn and improve from experience without being explicitly programmed. Supervised learning involves training a model with labeled data to make predictions or classifications. Unsupervised learning involves training a model with unlabeled data to find patterns and relationships. | ||
| 3 | ||
| Deep Learning | ||
|---|---|---|
| Deep Learning is a subfield of Machine Learning that utilizes artificial neural networks to process and understand complex patterns and data. Deep Learning models are inspired by the structure and function of the human brain. Deep Learning has achieved breakthroughs in image recognition, natural language processing, and speech recognition. | ||
| 4 | ||
| Applications of AI in Healthcare | ||
|---|---|---|
| AI can assist in diagnosing diseases by analyzing medical images, such as X-rays and MRIs. AI-powered chatbots can provide basic medical advice and support to patients. AI can help in drug discovery and development by analyzing vast amounts of data. | ||
| 5 | ||
| Applications of AI in Finance | ||
|---|---|---|
| AI algorithms can analyze financial data and predict market trends, enabling more accurate investment decisions. AI-powered chatbots can provide customer support in banking and insurance sectors. AI can automate routine financial tasks, such as fraud detection and risk assessment. | ||
| 6 | ||
| Applications of AI in Transportation | ||
|---|---|---|
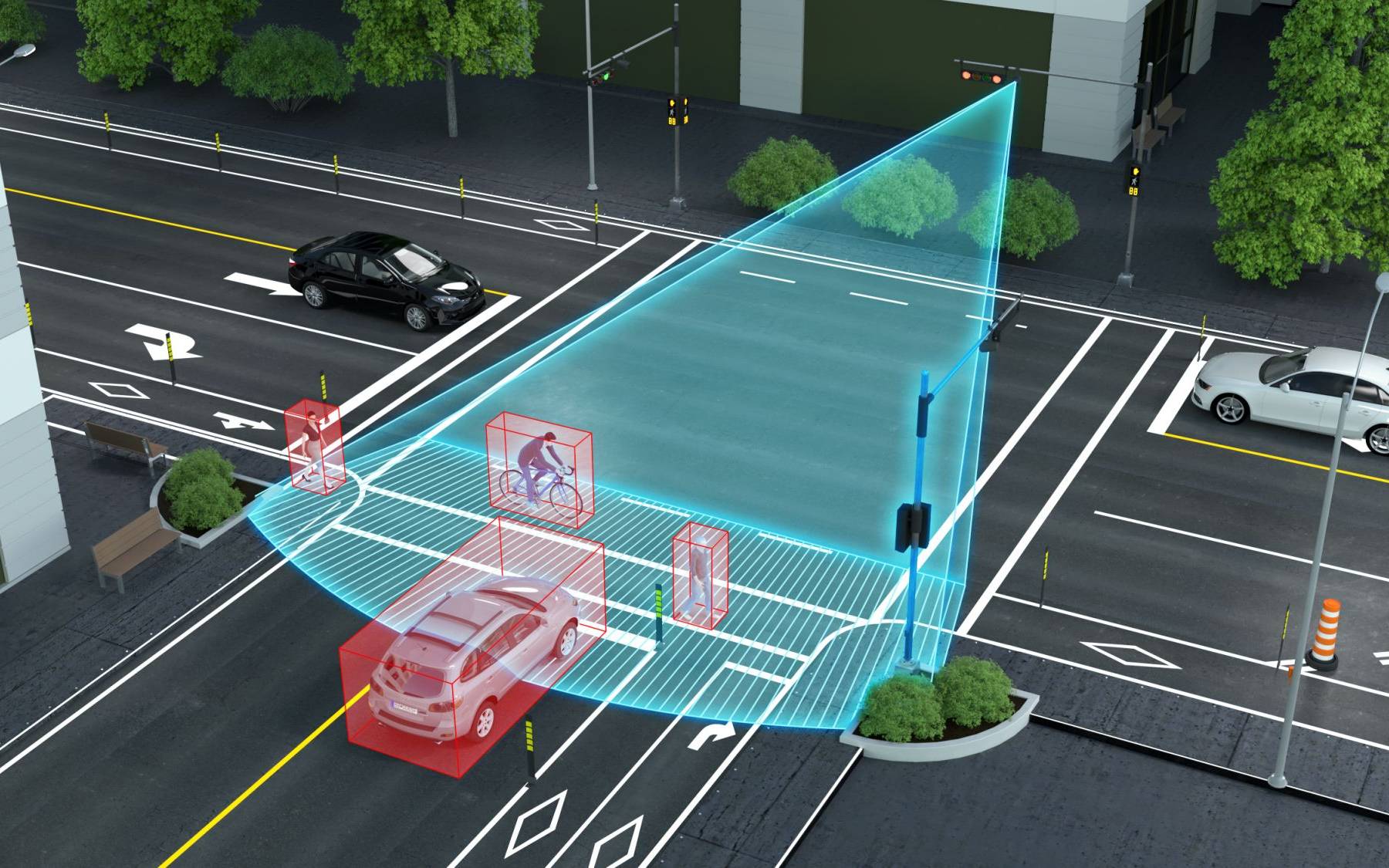
| AI can optimize traffic flow and reduce congestion by analyzing real-time data from traffic sensors. AI can enhance autonomous vehicles, enabling them to navigate complex environments and make real-time decisions. AI-powered algorithms can optimize logistics and supply chain management, improving efficiency and reducing costs. | ||
| 7 | ||
| Ethical Considerations | ||
|---|---|---|
| AI raises ethical concerns regarding privacy, data security, and potential bias in decision-making algorithms. Ethical frameworks and guidelines are being developed to ensure responsible AI development and usage. Collaboration between policymakers, researchers, and industries is crucial to address ethical challenges associated with AI. | ||
| 8 | ||
| Future of AI | ||
|---|---|---|
| AI is expected to continue advancing rapidly, leading to even more sophisticated applications and capabilities. AI may transform various industries, creating new job opportunities and changing the nature of work. Continued research and development are essential to harness the potential of AI while addressing its challenges. | ||
| 9 | ||
| Conclusion | ||
|---|---|---|
| AI has the potential to revolutionize various industries, improving efficiency, accuracy, and decision-making. However, ethical considerations and responsible development are crucial to ensure the benefits of AI outweigh its risks. AI is an exciting field with vast potential, and its continued progress will shape the future of technology and society. | ||
| 10 | ||
| References (download PPTX file for details) | ||
|---|---|---|
| Russell, S. J., & Norvig, P. (2016). Artifici... Goodfellow, I., Bengio, Y., & Courville, A. (... Topol, E. J. (2019). Deep Medicine: How Artif... |  | |
| 11 | ||