Zener Diode - Characteristics And Zener Diode As Voltage Regulator Presentation
| Introduction to Zener Diode | ||
|---|---|---|
| Zener diode is a type of diode that operates in reverse-biased condition. It is designed to work in the breakdown region, where it exhibits the Zener effect. The Zener effect allows the diode to maintain a constant voltage across its terminals, regardless of the current flowing through it. | ||
| 1 | ||
| Zener Diode Construction | ||
|---|---|---|
| Zener diodes are made from heavily doped p-n junctions. The p-side is heavily doped with impurities of a trivalent material (e.g., boron), while the n-side is doped with impurities of a pentavalent material (e.g., phosphorus). This creates a narrow depletion region where the Zener effect occurs. | ||
| 2 | ||
| Zener Diode Characteristics | ||
|---|---|---|
| Zener diodes have a specific breakdown voltage, called the Zener voltage (VZ). When the reverse voltage across the diode exceeds the Zener voltage, a significant current starts flowing through it. The Zener voltage can range from a few volts to several hundred volts. | ||
| 3 | ||
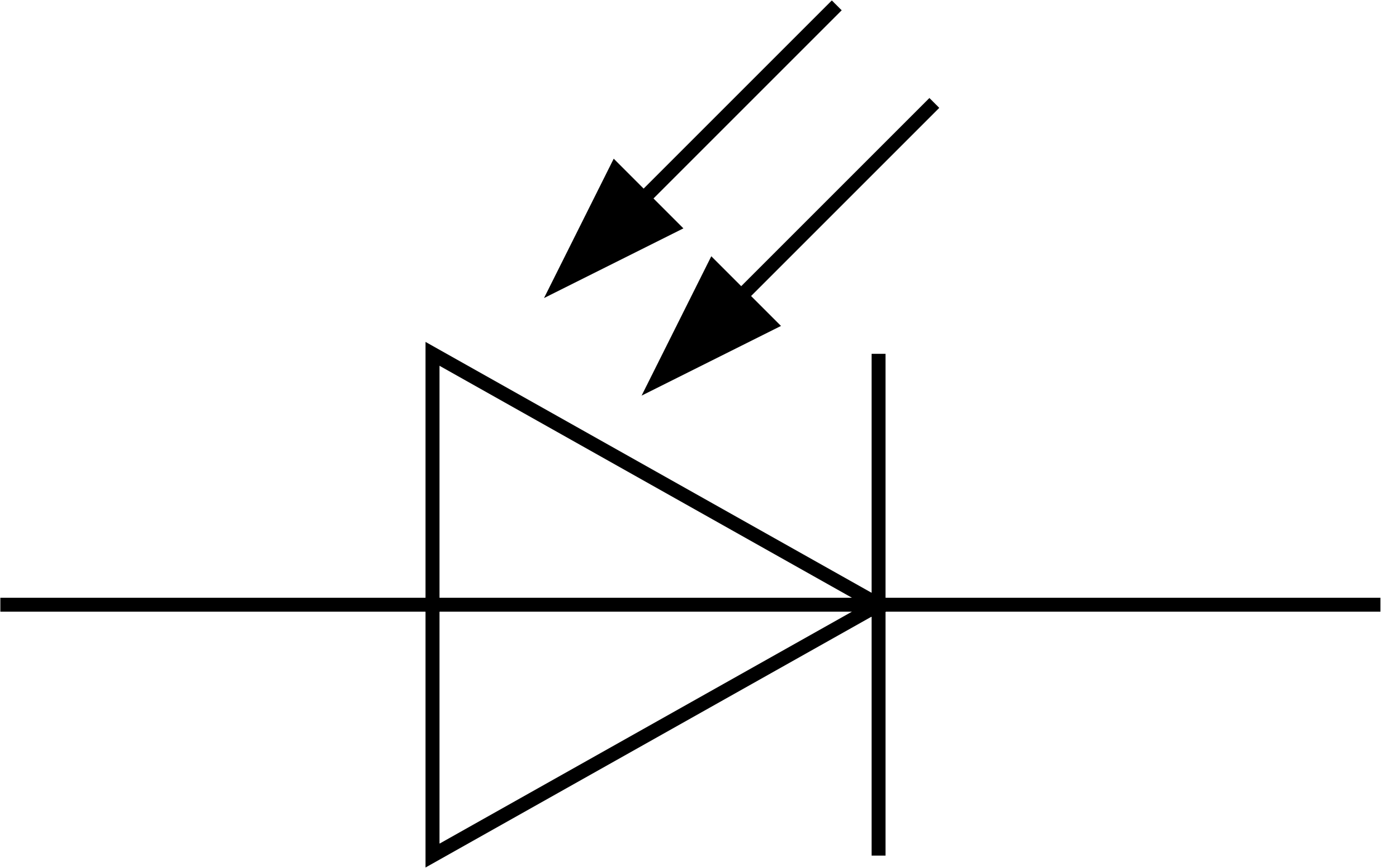
| Zener Diode Symbol and Notation | ||
|---|---|---|
| Zener diodes are represented by a symbol that resembles a regular diode, but with two diagonal lines within the arrowhead. The Zener voltage is usually mentioned next to the symbol, e.g., Zener diode 1N4733A with a Zener voltage of 5.1V. Your third bullet | ||
| 4 | ||
| Zener Diode as Voltage Regulator | ||
|---|---|---|
| Zener diodes are commonly used as voltage regulators in electronic circuits. By placing a Zener diode in parallel with a load, it can provide a constant voltage across the load. This is useful in applications where a stable voltage is required, such as in power supplies. | ||
| 5 | ||
| Zener Diode Voltage Regulation Mechanism | ||
|---|---|---|
| When the input voltage exceeds the Zener voltage, the excess voltage is dropped across the Zener diode. The Zener diode acts as a voltage shunt, diverting the excess voltage away from the load. This ensures that the load receives a constant voltage, even if the input voltage varies. | ||
| 6 | ||
| Zener Diode Voltage Regulation Formula | ||
|---|---|---|
| The voltage across the load can be calculated using the formula: Vload = VZ - VZK, where VZK is the Zener knee voltage. The Zener knee voltage is the voltage at which the Zener diode starts conducting significant current. By selecting an appropriate Zener diode with a specific Zener voltage, the desired output voltage can be achieved. | ||
| 7 | ||
| Zener Diode Voltage Regulation Limitations | ||
|---|---|---|
| Zener diodes have a maximum power dissipation rating, which should not be exceeded. The maximum current that can flow through the Zener diode should also be considered. If the input voltage drops below the Zener voltage, the Zener diode cannot regulate the voltage effectively. | ||
| 8 | ||
| Applications of Zener Diodes | ||
|---|---|---|
| Zener diodes are used in voltage regulators, voltage references, and surge protection circuits. They are also used in analog-to-digital converters to provide a stable reference voltage. Zener diodes can be found in various electronic devices, such as power supplies, televisions, and automotive electronics. | ||
| 9 | ||
| Summary and Conclusion | ||
|---|---|---|
| Zener diodes are specialized diodes that work in the breakdown region, providing a constant voltage across their terminals. They are commonly used as voltage regulators to ensure a stable voltage across a load. Understanding the characteristics and applications of Zener diodes is crucial for designing reliable electronic circuits. | ||
| 10 | ||