Working And Construction Of A Bjt Presentation
| Introduction to the BJT | ||
|---|---|---|
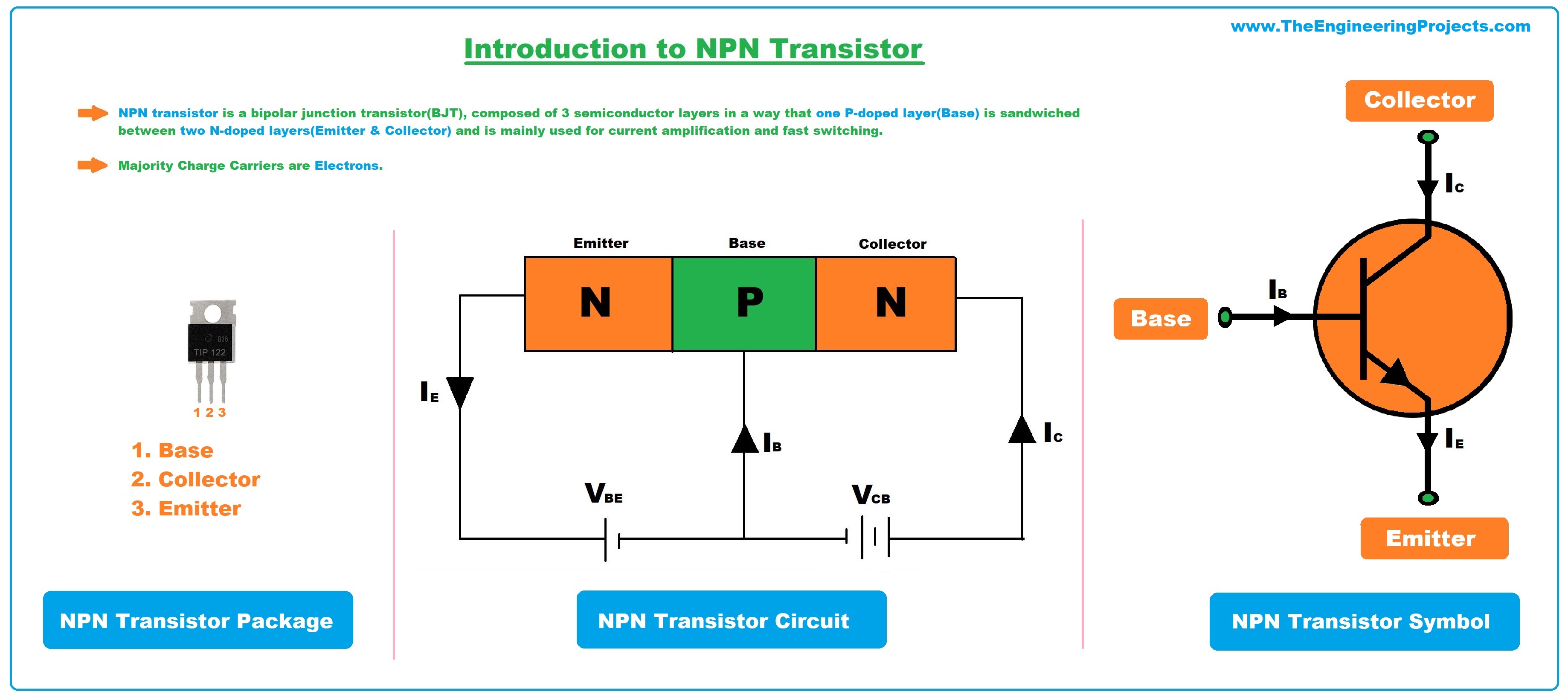
| The BJT (Bipolar Junction Transistor) is a three-layer semiconductor device. It consists of two p-n junctions formed by two differently doped semiconductor regions. The three layers are the emitter, base, and collector. | ||
| 1 | ||
| Construction of a BJT | ||
|---|---|---|
| The BJT is constructed using either NPN or PNP configurations. In an NPN transistor, the emitter is made of N-type material, the base is P-type, and the collector is N-type. In a PNP transistor, the emitter is made of P-type material, the base is N-type, and the collector is P-type. | ||
| 2 | ||
| Working Principle - NPN Transistor | ||
|---|---|---|
| When a positive voltage is applied to the base-emitter junction, it forward biases the junction. This causes majority carriers (electrons) to flow from the emitter to the base. The base-emitter current controls the flow of majority carriers from the collector to the emitter. | ||
| 3 | ||
| Working Principle - PNP Transistor | ||
|---|---|---|
| When a negative voltage is applied to the base-emitter junction, it forward biases the junction. This causes majority carriers (holes) to flow from the base to the emitter. The base-emitter current controls the flow of majority carriers from the emitter to the collector. | ||
| 4 | ||
| BJT Amplification | ||
|---|---|---|
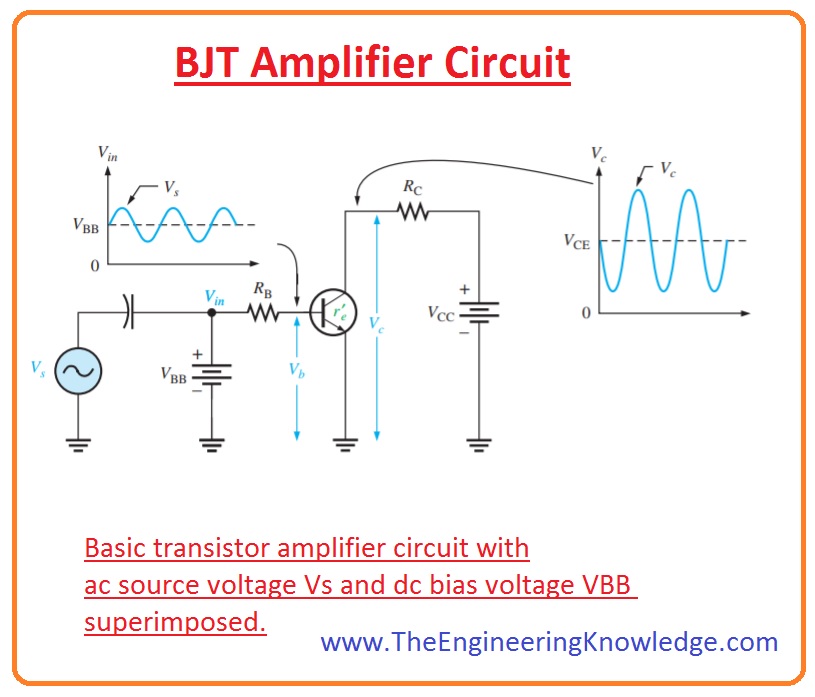
| The BJT can be used as an amplifier by biasing it in the active region. In the active region, small changes in base current result in larger changes in collector current. This allows for amplification of voltage or current signals. | ||
| 5 | ||
| BJT Applications | ||
|---|---|---|
| BJTs are extensively used in electronic devices such as amplifiers, switches, and oscillators. They are commonly found in audio systems, televisions, computers, and telecommunications equipment. The BJT's ability to amplify and switch signals makes it a versatile component in modern electronics. | ||
| 6 | ||
| BJT Advantages | ||
|---|---|---|
| BJTs have high current gains, making them suitable for amplification purposes. They can handle high power levels and have low noise characteristics. BJTs are relatively inexpensive and widely available in various sizes and packages. | ||
| 7 | ||
| BJT Limitations | ||
|---|---|---|
| BJTs are more power-consuming compared to other transistor types. They have lower switching speeds compared to MOSFETs. BJTs are more susceptible to temperature variations, requiring careful thermal management. Conclusion: In summary, the BJT is a three-layer semiconductor device constructed using NPN or PNP configurations. It operates by controlling the flow of majority carriers through the base-emitter junction. The BJT's ability to amplify signals and its various applications make it an integral component in modern electronics. However, it also has limitations such as power consumption and slower switching speeds. Overall, the BJT remains a fundamental building block in electronic circuits. |  | |
| 8 | ||