Volume By Triple Integration And Centre Of Gravity Presentation
| Introduction to Volume by Triple Integration and Centre of Gravity | ||
|---|---|---|
| Volume by triple integration is a mathematical technique used to calculate the volume of three-dimensional objects. It involves integrating a function over a given region in three-dimensional space. Centre of gravity is a point where the weight of an object can be considered to act, and it is used to find the equilibrium of an object. | ||
| 1 | ||
| Understanding Triple Integration | ||
|---|---|---|
| Triple integration involves integrating a function over a three-dimensional region. It is represented as ∭f(x, y, z) dV, where f(x, y, z) is the function and dV represents an infinitesimally small volume element. The limits of integration for each variable determine the region over which the integration is performed. | ||
| 2 | ||
| Calculating Volume Using Triple Integration | ||
|---|---|---|
| To calculate volume using triple integration, we integrate the constant function 1 over the desired region. The integral represents the sum of infinitesimally small volumes within the region, resulting in the total volume. The region can be defined using inequalities or geometric shapes such as spheres, cylinders, or cones. | ||
| 3 | ||
| Centre of Gravity Concept | ||
|---|---|---|
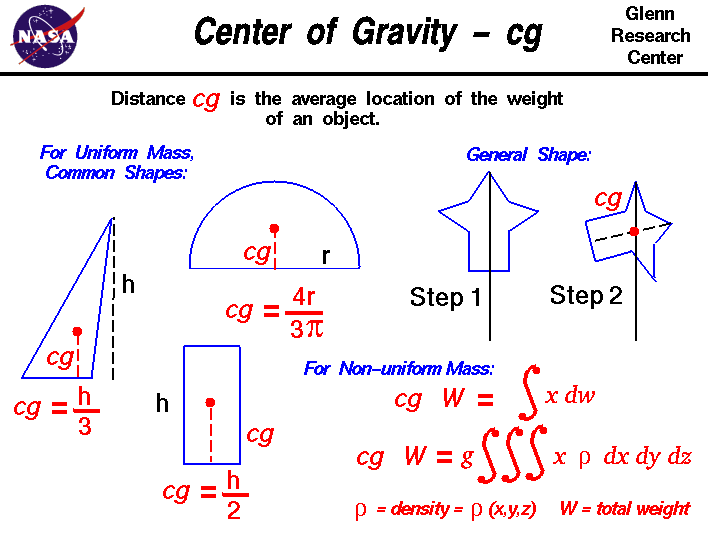
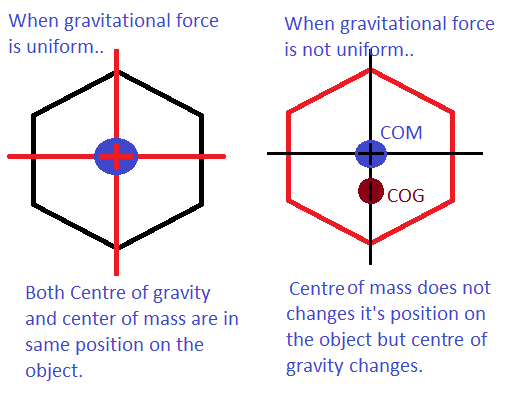
| Centre of gravity is the average position of all parts of an object, weighted according to their masses. It is often denoted as (x̄, ȳ, z̄), where x̄, ȳ, and z̄ represent the average positions in each coordinate direction. Centre of gravity is used to analyze the stability and equilibrium of objects. | ||
| 4 | ||
| Calculating Centre of Gravity | ||
|---|---|---|
| To calculate the centre of gravity, we need to determine the position of each infinitesimally small mass element within the object. We then integrate the product of the position vector and the mass density function over the entire object. Dividing the resulting integral by the total mass of the object gives us the coordinates of the centre of gravity. | ||
| 5 | ||
| Centre of Gravity for Homogeneous Objects | ||
|---|---|---|
| For homogeneous objects with uniform mass density, the centre of gravity is located at the geometric centre. In such cases, the mass density function is constant, simplifying the integration process. The coordinates of the centre of gravity can be found by taking the average of the maximum and minimum values for each coordinate direction. | ||
| 6 | ||
| Centre of Gravity for Irregular Objects | ||
|---|---|---|
| For irregular objects with non-uniform mass distribution, the centre of gravity may not coincide with the geometric centre. The mass density function varies throughout the object, requiring a more complex integration process. Numerical methods or computer simulations can be used to approximate the centre of gravity in such cases. | ||
| 7 | ||
| Application of Centre of Gravity | ||
|---|---|---|
| Centre of gravity is widely used in engineering, architecture, and physics. It helps determine the stability and balance of structures, vehicles, and machinery. In biomechanics, it is used to analyze human movement and posture. | ||
| 8 | ||
| Summary | ||
|---|---|---|
| Volume by triple integration is a technique to calculate the volume of three-dimensional objects. Centre of gravity is the average position of all parts of an object, used to find equilibrium. Calculating the centre of gravity involves integrating the position vector and mass density function. | ||
| 9 | ||
| References (download PPTX file for details) | ||
|---|---|---|
| [Insert reference 1]... [Insert reference 2]... [Insert reference 3]... |  | |
| 10 | ||
| References (download PPTX file for details) | ||
|---|---|---|
| Your first bullet... Your second bullet... Your third bullet... |  | |
| 11 | ||