Vitamin A Presentation
| Introduction to Vitamin A | ||
|---|---|---|
| Vitamin A is a fat-soluble vitamin essential for various bodily functions. It plays a key role in maintaining healthy vision, promoting growth and development, and supporting the immune system. There are two main forms of vitamin A: retinol, found in animal-based foods, and beta-carotene, found in plant-based foods. | ||
| 1 | ||
| Benefits of Vitamin A | ||
|---|---|---|
| Supports vision health by helping to form visual pigments in the retina. Promotes healthy skin by supporting cell growth and repair. Strengthens the immune system by enhancing the function of white blood cells. | ||
| 2 | ||
| Food Sources of Vitamin A | ||
|---|---|---|
| Animal-based sources include liver, fish, eggs, and dairy products. Plant-based sources include carrots, sweet potatoes, spinach, and kale. Fortified foods, such as cereals and margarine, also provide vitamin A. | ||
| 3 | ||
| Vitamin A Deficiency | ||
|---|---|---|
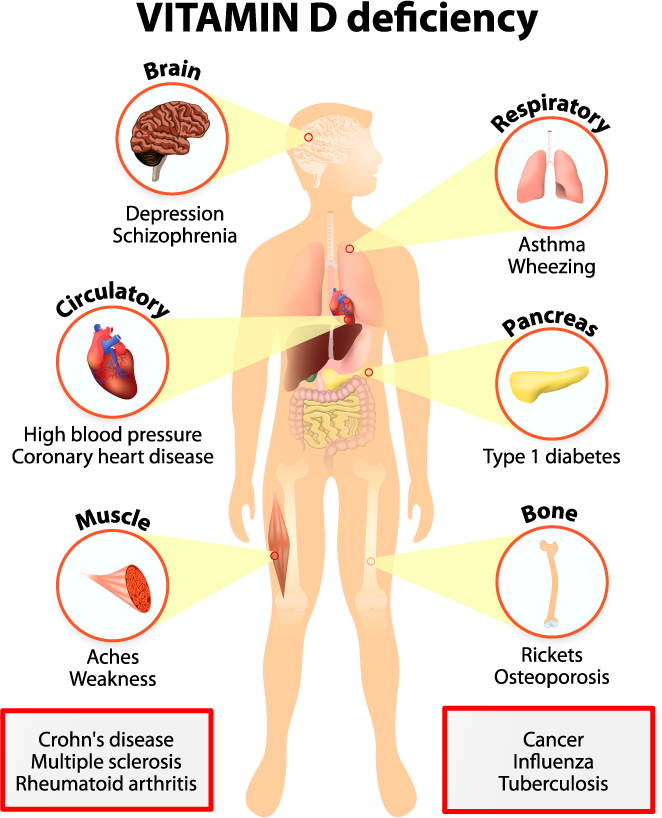
| Vitamin A deficiency is a major public health concern in many developing countries. It can lead to night blindness, increased susceptibility to infections, and impaired growth and development. Pregnant women with vitamin A deficiency are at higher risk of complications during childbirth. | ||
| 4 | ||
| Recommended Daily Intake | ||
|---|---|---|
| The recommended daily intake of vitamin A for adults is 900 micrograms for men and 700 micrograms for women. Pregnant and breastfeeding women have higher requirements. It is important to consume vitamin A within the recommended limits, as excessive intake can be toxic. | ||
| 5 | ||
| Vitamin A Supplementation | ||
|---|---|---|
| In certain cases, vitamin A supplementation may be necessary, especially in areas with high deficiency rates. Supplementation programs are often targeted towards children and pregnant women. Supplementation should be done under medical supervision to avoid toxicity risks. | ||
| 6 | ||
| Health Conditions and Vitamin A | ||
|---|---|---|
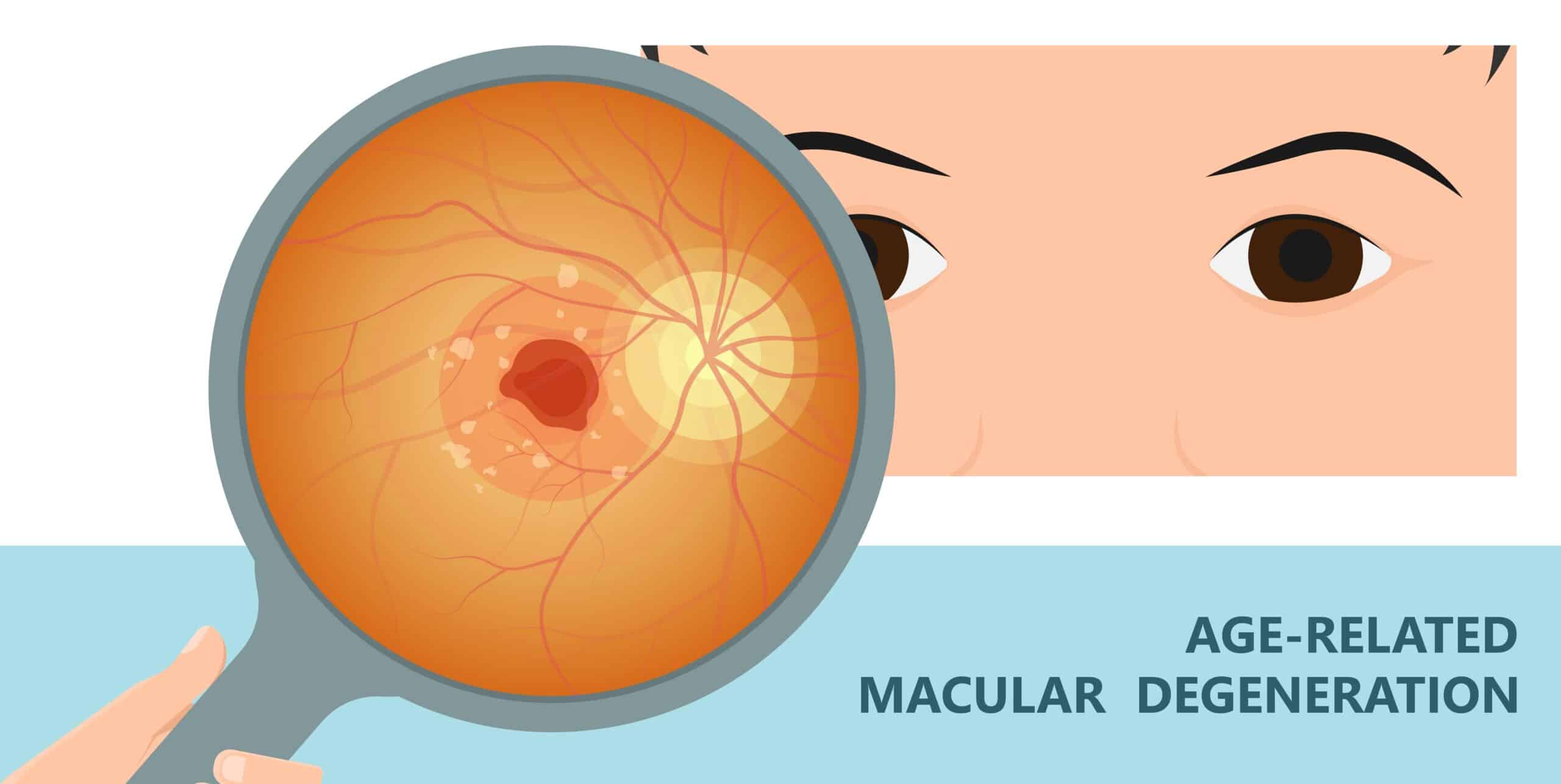
| Vitamin A has been linked to a reduced risk of age-related macular degeneration, a leading cause of vision loss in older adults. It may also play a role in reducing the risk of certain cancers, such as lung and prostate cancer. However, more research is needed to fully understand these potential benefits. | ||
| 7 | ||
| Cooking and Vitamin A | ||
|---|---|---|
| Cooking methods can affect the vitamin A content of foods. Boiling or steaming vegetables can lead to some loss of vitamin A. To maximize vitamin A retention, it is recommended to consume vegetables raw or lightly cooked. | ||
| 8 | ||
| Interactions and Supplements | ||
|---|---|---|
| Vitamin A supplements can interact with certain medications, such as cholesterol-lowering drugs and acne medications. It is important to inform your healthcare provider about any supplements you are taking. Taking vitamin A supplements should be done under professional guidance to avoid adverse effects. | ||
| 9 | ||
| Conclusion | ||
|---|---|---|
| Vitamin A is a vital nutrient that plays a crucial role in vision, growth, and immune function. It can be obtained from a variety of animal and plant-based sources. Consuming a balanced diet and meeting the recommended daily intake is key to maintaining optimal vitamin A levels. | ||
| 10 | ||






/Lipitor-56d2ef9e3df78cfb37d0f1f0.jpg)
