Underwater Welding Presentation
| Introduction to Underwater Welding | ||
|---|---|---|
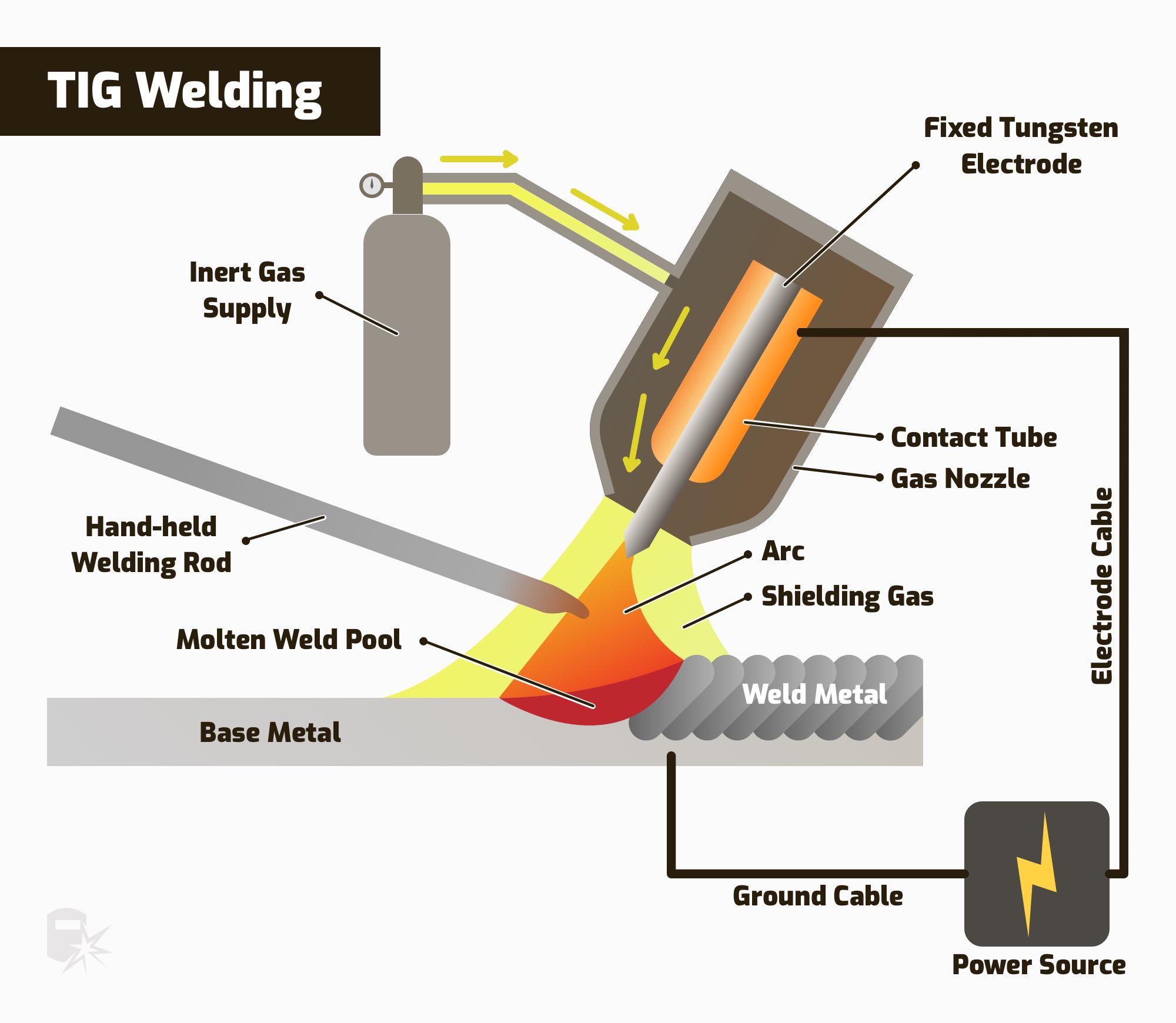
| Underwater welding is a specialized welding technique used to join metals underwater. It plays a crucial role in various industries such as offshore oil and gas, marine construction, and underwater infrastructure maintenance. The process requires highly skilled and certified welders who are trained to work in challenging underwater conditions. | ||
| 1 | ||
| Types of Underwater Welding | ||
|---|---|---|
| There are two main types of underwater welding: wet welding and dry welding. Wet welding is performed directly in the water using a waterproof electrode. Dry welding involves creating a dry environment around the welding area using a chamber or habitat. | ||
| 2 | ||
| Wet Welding Process | ||
|---|---|---|
| Wet welding utilizes a special waterproof electrode that generates a protective gas shield around the weld pool. The welder wears a diving suit and uses specially designed equipment to maintain a stable arc and complete the weld. Wet welding is suitable for relatively shallow depths and is commonly used for emergency repairs or quick fixes. | ||
| 3 | ||
| Dry Welding Process | ||
|---|---|---|
| Dry welding involves creating a dry environment around the weld area using a habitat or chamber. The welder enters the habitat and performs the welding operation in a controlled environment. Dry welding allows for better control of welding parameters and is preferred for critical or complex welding projects at greater depths. | ||
| 4 | ||
| Equipment Used in Underwater Welding | ||
|---|---|---|
| Underwater welding requires specialized equipment such as welding machines, electrodes, and diving gear. Welding machines used underwater are specially designed to withstand water pressure and provide stable power supply. Diving gear includes diving suits, helmets, umbilical cords, and other safety equipment to protect the welder from underwater hazards. | ||
| 5 | ||
| Safety Considerations | ||
|---|---|---|
| Underwater welding poses several safety risks including electric shock, explosion, and decompression sickness. Welders must undergo rigorous training and certification to ensure their competence in handling these risks. Strict safety protocols and procedures must be followed to minimize the potential hazards associated with underwater welding. | ||
| 6 | ||
| Applications of Underwater Welding | ||
|---|---|---|
| Underwater welding is used in various industries such as oil and gas, shipbuilding, bridge construction, and underwater infrastructure maintenance. It is commonly used for repairing offshore structures, pipelines, and underwater cables. The technique is also utilized in salvage operations, underwater cutting, and inspection of underwater structures. | ||
| 7 | ||
| Advantages of Underwater Welding | ||
|---|---|---|
| Underwater welding allows for repairs and maintenance to be carried out without the need for expensive and time-consuming dry-docking. It enables quick response to emergency situations, reducing downtime and minimizing potential losses. The technique provides cost-effective solutions for underwater repairs and construction projects. | ||
| 8 | ||
| Challenges in Underwater Welding | ||
|---|---|---|
| Underwater welding poses several challenges, including limited visibility, cold temperatures, and hydrostatic pressure. Maintaining a stable arc and ensuring proper shielding gas coverage can be challenging in the underwater environment. Welders must be highly skilled and experienced to overcome these challenges and produce high-quality welds. | ||
| 9 | ||
| Conclusion | ||
|---|---|---|
| Underwater welding is a specialized technique that plays a crucial role in various industries. It requires skilled and certified welders who can work under challenging underwater conditions. With proper training, equipment, and safety measures, underwater welding offers efficient and cost-effective solutions for underwater repairs and construction projects. | ||
| 10 | ||
| References (download PPTX file for details) | ||
|---|---|---|
| American Welding Society. (2021). Underwater ... Diver Welder. (n.d.). Underwater Welding Guid... Your third bullet... |  | |
| 11 | ||