Transistor Biasing And Stabilization Techniques Presentation
| Introduction to Transistor Biasing and Stabilization Techniques. | ||
|---|---|---|
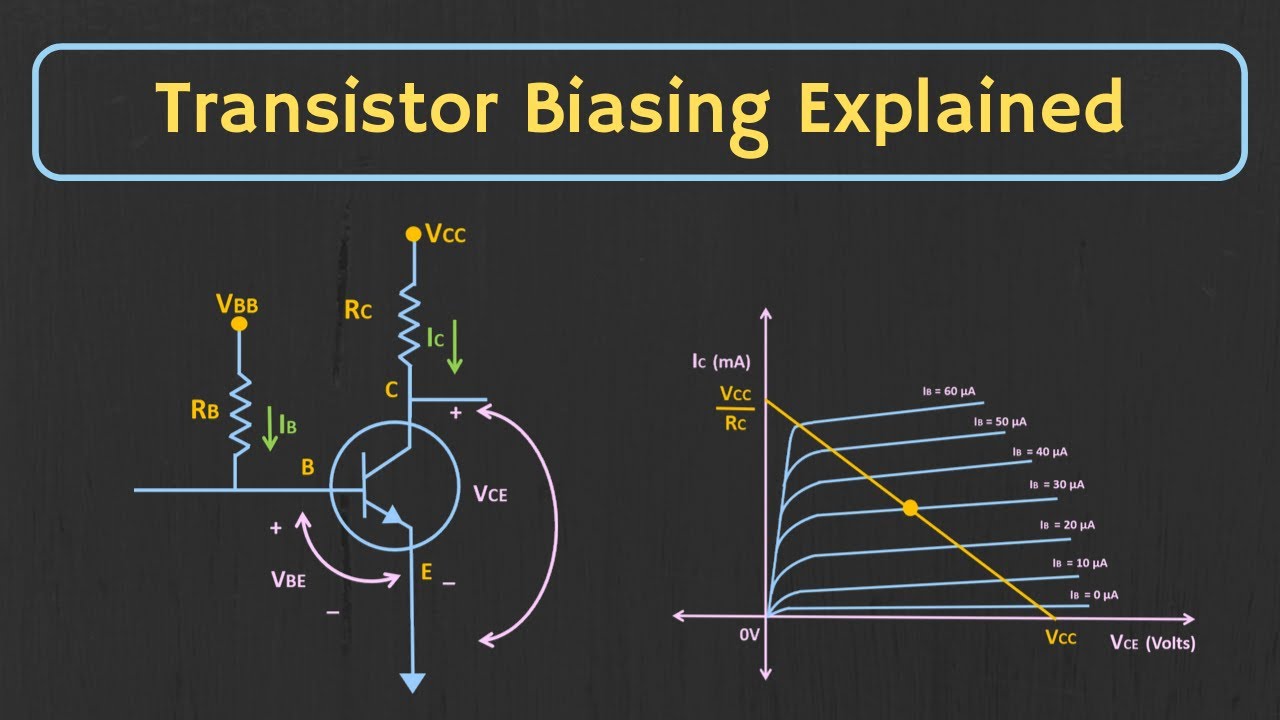
| Transistor biasing is the process of establishing a suitable operating point for the transistor. Proper biasing ensures that the transistor operates in its active region. Stabilization techniques are used to maintain the operating point despite variations in temperature, transistor parameters, or power supply. | ||
| 1 | ||
| Common Emitter Biasing Technique. | ||
|---|---|---|
| The common emitter configuration is widely used in transistor amplifiers. A voltage divider network is used to provide the required bias voltage at the base. A coupling capacitor is used to block DC voltage, allowing only the AC signal to pass. | ||
| 2 | ||
| Base Biasing Technique. | ||
|---|---|---|
| In base biasing, a single resistor is used to provide the required bias voltage at the base. The resistor is connected between the base and the power supply. This technique is simple but less stable compared to other biasing methods. | ||
| 3 | ||
| Collector Feedback Biasing Technique. | ||
|---|---|---|
| Collector feedback biasing uses a resistor and a capacitor in parallel connected between the collector and the base. This technique provides better stability and compensates for variations in temperature. The resistor-capacitor combination sets the DC operating point and the AC signal gain. | ||
| 4 | ||
| Emitter Biasing Technique. | ||
|---|---|---|
| Emitter biasing is commonly used in amplifiers and provides good stability and temperature compensation. A resistor is connected between the emitter and the power supply. This technique provides negative feedback, which helps stabilize the operating point. | ||
| 5 | ||
| Voltage Divider Biasing Technique. | ||
|---|---|---|
| Voltage divider biasing uses a resistive network to provide the required bias voltage at the base. The resistive network typically includes two resistors connected in series. This technique provides stability and compensates for variations in transistor parameters. | ||
| 6 | ||
| Thermal Stabilization Techniques. | ||
|---|---|---|
| Thermal stabilization techniques are used to compensate for variations in temperature. The use of temperature-sensitive resistors or diodes helps maintain a constant bias voltage. Thermal coupling between components can also be used to stabilize the transistor. | ||
| 7 | ||
| Current Mirror Biasing Technique. | ||
|---|---|---|
| Current mirror biasing is used to provide a stable bias current. It uses a reference current source and a transistor mirror to generate a stable bias current. This technique is widely used in integrated circuits for precise biasing. | ||
| 8 | ||
| Summary. | ||
|---|---|---|
| Transistor biasing is essential for proper operation and amplification. Various biasing techniques such as common emitter, base biasing, collector feedback, emitter biasing, voltage divider, and current mirror can be used. Stabilization techniques, including thermal stabilization, help maintain the operating point despite variations. | ||
| 9 | ||
| References (download PPTX file for details) | ||
|---|---|---|
| Include a list of references used in the pres... Your second bullet... Your third bullet... |  | |
| 10 | ||