Transistor Presentation
| Introduction to Transistors | ||
|---|---|---|
| A transistor is a semiconductor device that amplifies or switches electronic signals. It is a fundamental building block of modern electronic devices. Transistors are used in a wide range of applications such as radios, computers, and televisions. | ||
| 1 | ||
| Types of Transistors | ||
|---|---|---|
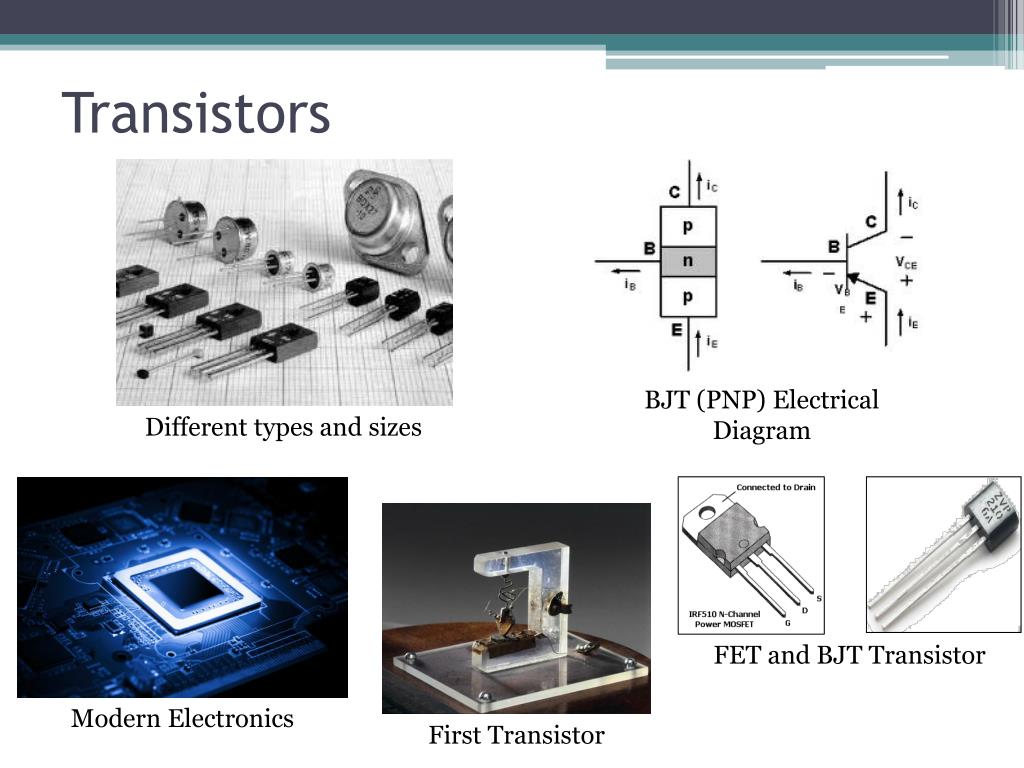
| There are two main types of transistors: bipolar junction transistors (BJTs) and field-effect transistors (FETs). BJTs use both electron and hole charge carriers, while FETs use only one type of charge carrier. FETs are further classified into junction FETs (JFETs) and metal-oxide-semiconductor FETs (MOSFETs). | ||
| 2 | ||
| How Transistors Work | ||
|---|---|---|
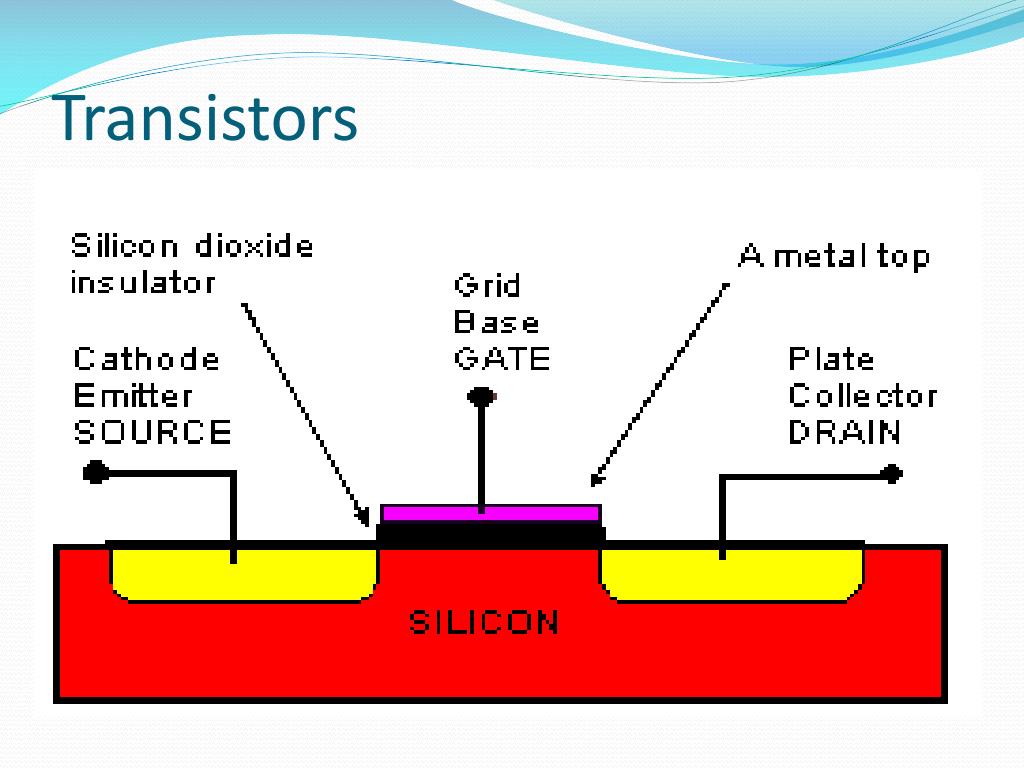
| A transistor consists of three layers of semiconductor material: the emitter, base, and collector. In a BJT, the emitter sends current into the base, controlling the current flowing from the collector to the emitter. FETs, on the other hand, use an electric field to control the current flow through a channel between the source and drain. | ||
| 3 | ||
| Amplification with Transistors | ||
|---|---|---|
| Transistors are primarily used for amplifying weak electronic signals. By applying a small input signal to the base or gate, a larger amplified signal is produced at the collector or drain. This amplification allows for the transmission of audio and video signals over long distances without significant loss. | ||
| 4 | ||
| Switching with Transistors | ||
|---|---|---|
| Transistors can also be used as electronic switches in digital circuits. By applying a small control signal to the base or gate, the transistor can be turned on or off, allowing or blocking current flow. This property enables the binary representation of data in computers and other digital devices. | ||
| 5 | ||
| Advantages of Transistors | ||
|---|---|---|
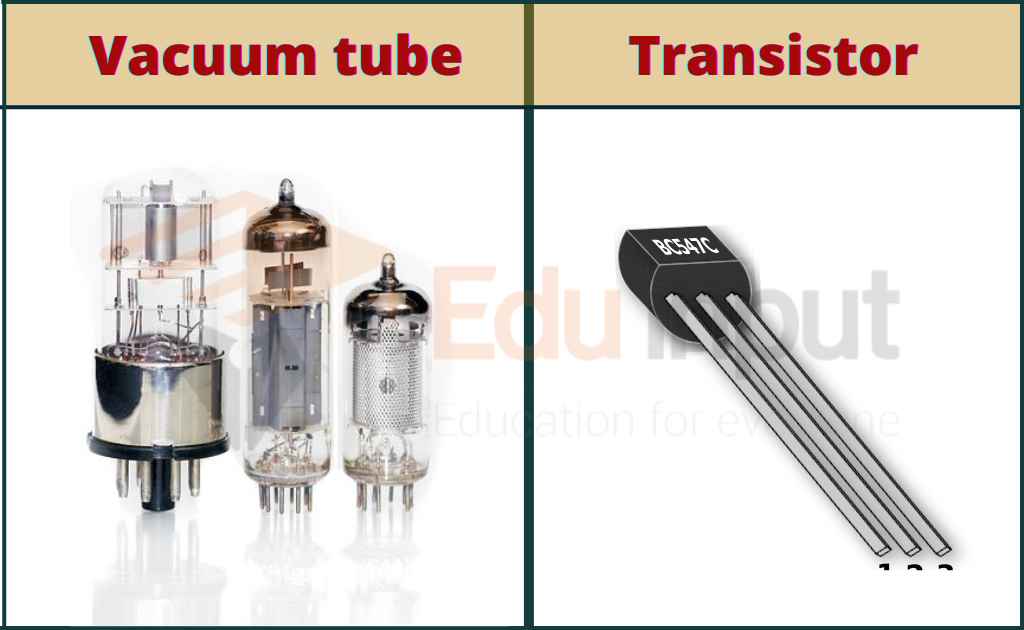
| Compared to vacuum tubes, transistors are smaller, more reliable, and consume less power. They have a longer lifespan and do not require warm-up time like vacuum tubes. Transistors also generate less heat and are less prone to failure due to mechanical shocks. | ||
| 6 | ||
| Applications of Transistors | ||
|---|---|---|
| Transistors are essential components in audio amplifiers, radio receivers, and televisions. They are used in computer processors, memory chips, and other digital circuitry. Transistors are crucial in power electronics, controlling the flow of electricity in devices like power supplies and motor drives. | ||
| 7 | ||
| Transistor Scaling | ||
|---|---|---|
| Moore's Law states that the number of transistors on integrated circuits doubles approximately every two years. This scaling has led to the development of smaller, more powerful, and energy-efficient electronic devices. Advances in transistor technology have revolutionized the field of electronics and enabled the rapid growth of the digital age. | ||
| 8 | ||
| Conclusion | ||
|---|---|---|
| Transistors are key components in modern electronics, enabling amplification and switching of electronic signals. Their small size, reliability, and efficiency make them indispensable in various applications. Continued advancements in transistor technology will continue to drive innovation in the field of electronics. | ||
| 9 | ||