Transduction Presentation
| Introduction to Transduction | ||
|---|---|---|
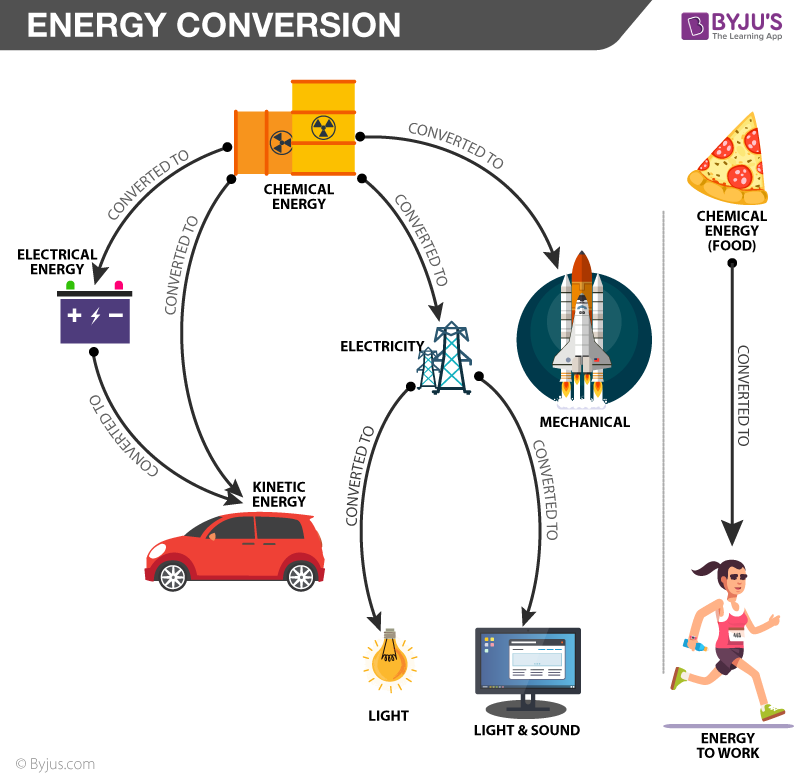
| Transduction is a process of converting one form of energy into another form of energy. It is a fundamental concept in various fields, including biology, physics, and engineering. Transduction plays a crucial role in signal processing and communication systems. | ||
| 1 | ||
| Types of Transduction | ||
|---|---|---|
| Mechanical Transduction: Conversion of mechanical energy into electrical signals, such as in microphones or speakers. Optical Transduction: Conversion of light energy into electrical signals, as seen in photovoltaic cells or digital cameras. Chemical Transduction: Conversion of chemical signals into electrical or mechanical signals, like in chemical sensors or taste receptors. | ||
| 2 | ||
| Biological Transduction | ||
|---|---|---|
| In biology, transduction refers to the conversion of physical stimuli into electrical signals in sensory organs. Example: In the human eye, light energy is transduced by photoreceptor cells into electrical signals that can be interpreted by the brain. Biological transduction allows organisms to perceive and respond to their environment. | ||
| 3 | ||
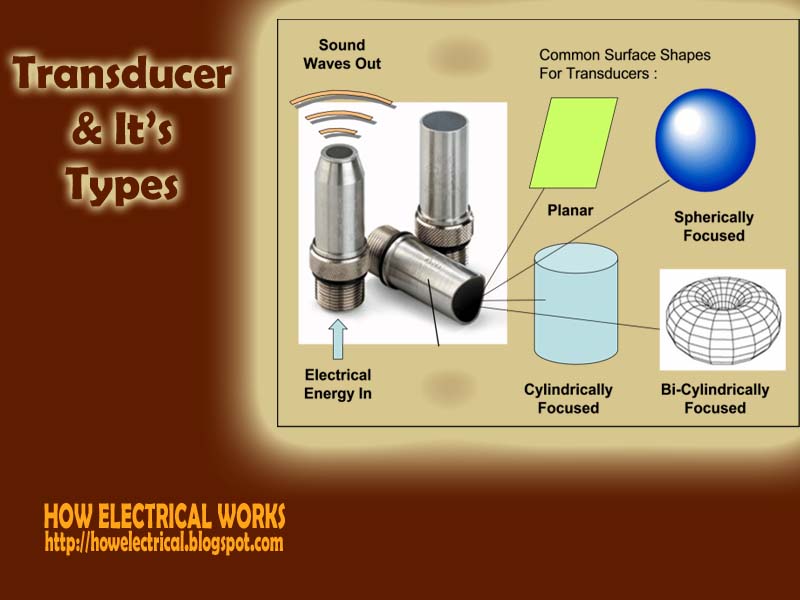
| Transducers in Electronics | ||
|---|---|---|
| Transducers are devices that convert one form of energy into another. Examples of transducers include microphones, speakers, and sensors. Transducers are essential components in various electronic systems, such as audio devices, medical equipment, and automotive systems. | ||
| 4 | ||
| Transduction in Communication Systems | ||
|---|---|---|
| In communication systems, transduction is used to convert information signals into electrical or electromagnetic signals. Transduction enables the transmission and reception of information through different mediums, such as wires, optical fibers, or radio waves. Examples of transduction in communication systems include modems, antennas, and transceivers. | ||
| 5 | ||
| Principles of Transduction | ||
|---|---|---|
| Transduction is based on the principles of energy conversion and signal processing. It involves the use of transducers that can sense and convert specific types of energy. The transduction process often includes amplification, filtering, and modulation to optimize signal quality. | ||
| 6 | ||
| Challenges and Advances in Transduction | ||
|---|---|---|
| Designing transducers with high sensitivity, accuracy, and reliability poses challenges in various applications. Advances in materials science, nanotechnology, and signal processing have led to significant improvements in transduction technologies. Emerging technologies, such as biosensors and quantum transducers, offer promising solutions for future transduction applications. | ||
| 7 | ||
| Applications of Transduction | ||
|---|---|---|
| Transduction is utilized in a wide range of applications, including healthcare, environmental monitoring, and consumer electronics. Examples include medical imaging devices, environmental sensors, touchscreens, and virtual reality systems. Transduction enables the measurement, control, and manipulation of physical and biological phenomena. | ||
| 8 | ||
| Conclusion | ||
|---|---|---|
| Transduction is a fundamental process of energy conversion that plays a critical role in various fields. It enables the conversion of one form of energy into another, facilitating communication and information processing. Advances in transduction technologies continue to drive innovation in multiple industries, leading to new applications and improved functionalities. | ||
| 9 | ||
| References (download PPTX file for details) | ||
|---|---|---|
| Smith, L. (2019). Transduction: Energy conver... Ramanathan, K. (Ed.). (2017). Transduction in... Varadan, V. K., & Jha, C. K. (Eds.). (2017). ... |  | |
| 10 | ||