Thyroid Dysfunction Presentation
| Introduction to Thyroid Dysfunction | ||
|---|---|---|
| Thyroid dysfunction refers to any condition that affects the normal functioning of the thyroid gland. The thyroid gland is a small, butterfly-shaped gland located in the neck, responsible for producing hormones that regulate metabolism. Thyroid dysfunction can lead to either an overactive thyroid (hyperthyroidism) or an underactive thyroid (hypothyroidism). | ||
| 1 | ||
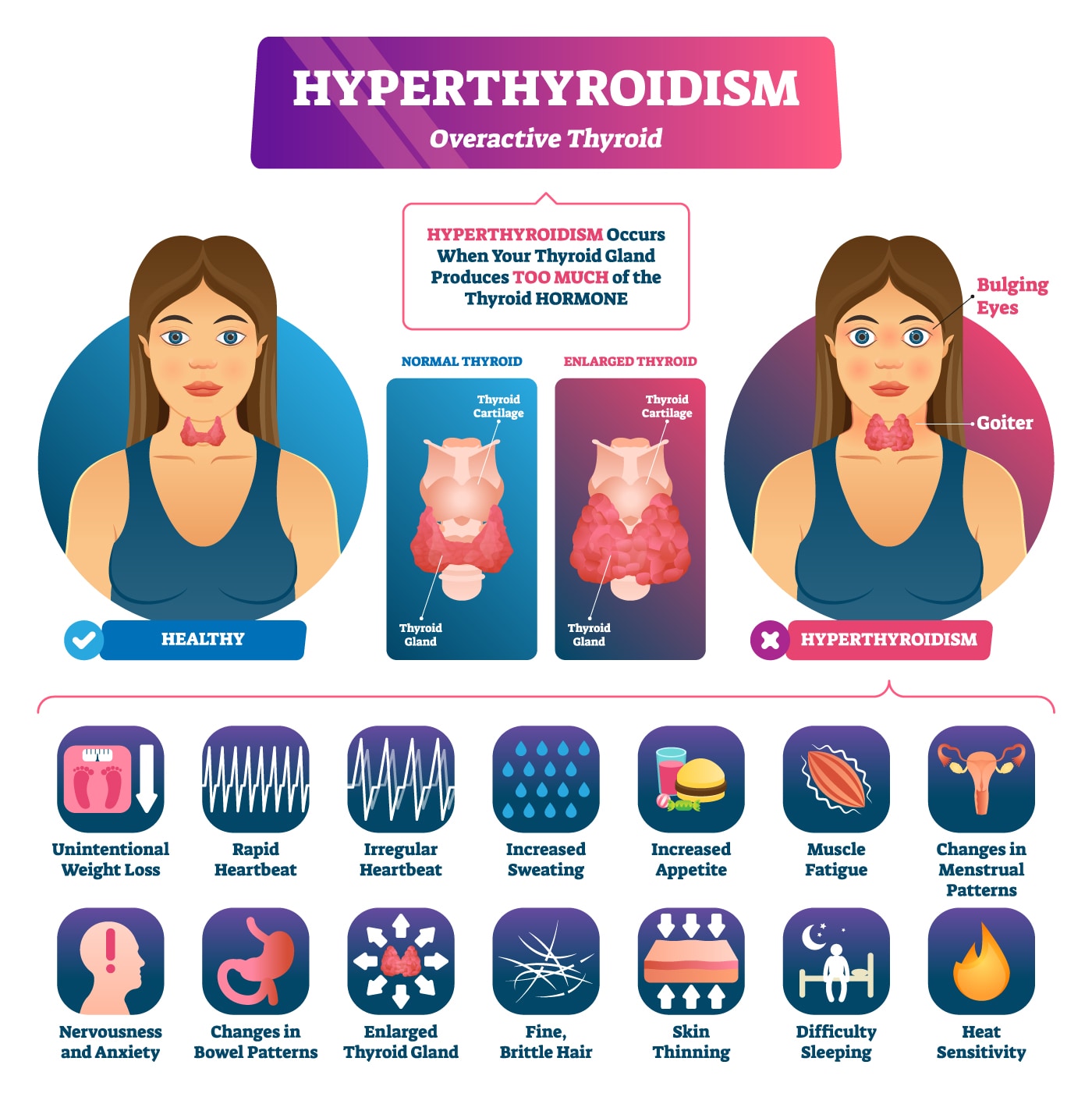
| Symptoms of Hyperthyroidism | ||
|---|---|---|
| Hyperthyroidism is characterized by an overactive thyroid gland, leading to an excessive production of thyroid hormones. Common symptoms include weight loss, increased appetite, restlessness, anxiety, rapid heartbeat, and tremors. Other symptoms may include heat intolerance, sweating, fatigue, and changes in menstrual patterns. | ||
| 2 | ||
| Causes of Hyperthyroidism | ||
|---|---|---|
| The most common cause of hyperthyroidism is an autoimmune condition called Graves' disease. Other causes include toxic nodular goiter, thyroiditis, and excessive intake of thyroid hormone medication. Hyperthyroidism can also be triggered by certain medications, such as amiodarone or lithium. | ||
| 3 | ||
| Treatment Options for Hyperthyroidism | ||
|---|---|---|
| Antithyroid medications, such as methimazole or propylthiouracil, can help to reduce the production of thyroid hormones. Radioactive iodine therapy is another treatment option, which destroys the overactive thyroid cells. In some cases, surgery may be required to remove a portion or all of the thyroid gland. | ||
| 4 | ||
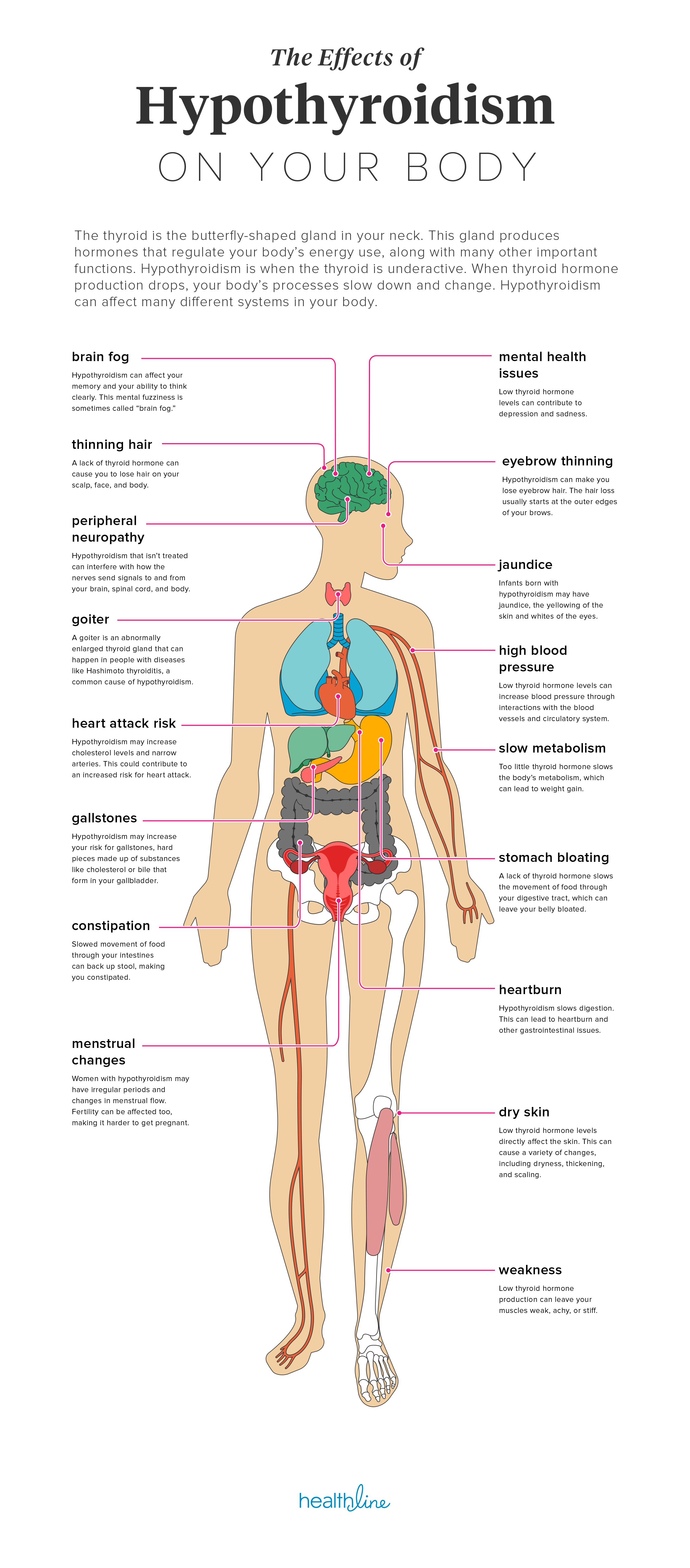
| Symptoms of Hypothyroidism | ||
|---|---|---|
| Hypothyroidism is characterized by an underactive thyroid gland, leading to a decreased production of thyroid hormones. Common symptoms include fatigue, weight gain, cold intolerance, constipation, dry skin, and thinning hair. Other symptoms may include depression, memory problems, muscle weakness, and heavy or irregular menstrual periods. | ||
| 5 | ||
| Causes of Hypothyroidism | ||
|---|---|---|
| The most common cause of hypothyroidism is an autoimmune condition called Hashimoto's thyroiditis. Other causes include thyroid surgery, radiation therapy, certain medications (e.g., lithium), and congenital hypothyroidism. Iodine deficiency, although rare in developed countries, can also lead to hypothyroidism. | ||
| 6 | ||
| Treatment Options for Hypothyroidism | ||
|---|---|---|
| Hypothyroidism is typically managed with synthetic thyroid hormone replacement therapy, such as levothyroxine. The medication helps to restore the proper levels of thyroid hormones in the body. Regular monitoring of thyroid hormone levels through blood tests is necessary to ensure the correct dosage of medication. | ||
| 7 | ||
| Complications of Untreated Thyroid Dysfunction | ||
|---|---|---|
| Untreated hyperthyroidism can lead to complications such as atrial fibrillation, osteoporosis, and thyroid storm (life-threatening condition). Untreated hypothyroidism can result in complications like heart disease, infertility, and myxedema coma (severe hypothyroidism). Your third bullet | ||
| 8 | ||
| Prevention and Lifestyle Tips | ||
|---|---|---|
| It is not always possible to prevent thyroid dysfunction, but some lifestyle factors can help support thyroid health. These include maintaining a balanced diet rich in iodine, selenium, and other essential nutrients. Regular exercise, stress management, and avoiding smoking are also beneficial for overall thyroid health. | ||
| 9 | ||
| Conclusion | ||
|---|---|---|
| Thyroid dysfunction is a common condition that can significantly impact a person's overall health and well-being. Recognizing the symptoms, seeking appropriate medical care, and following the prescribed treatment plan are crucial for managing thyroid dysfunction effectively. With proper management, individuals with thyroid dysfunction can lead a healthy and fulfilling life. | ||
| 10 | ||