The World Of Blockchain Presentation
| Introduction to Blockchain | ||
|---|---|---|
| Blockchain is a decentralized technology that enables secure and transparent transactions. It is a digital ledger that records all transactions across multiple computers. Blockchain eliminates the need for intermediaries, making transactions faster and more efficient. | ||
| 1 | ||
| Key Components of Blockchain | ||
|---|---|---|
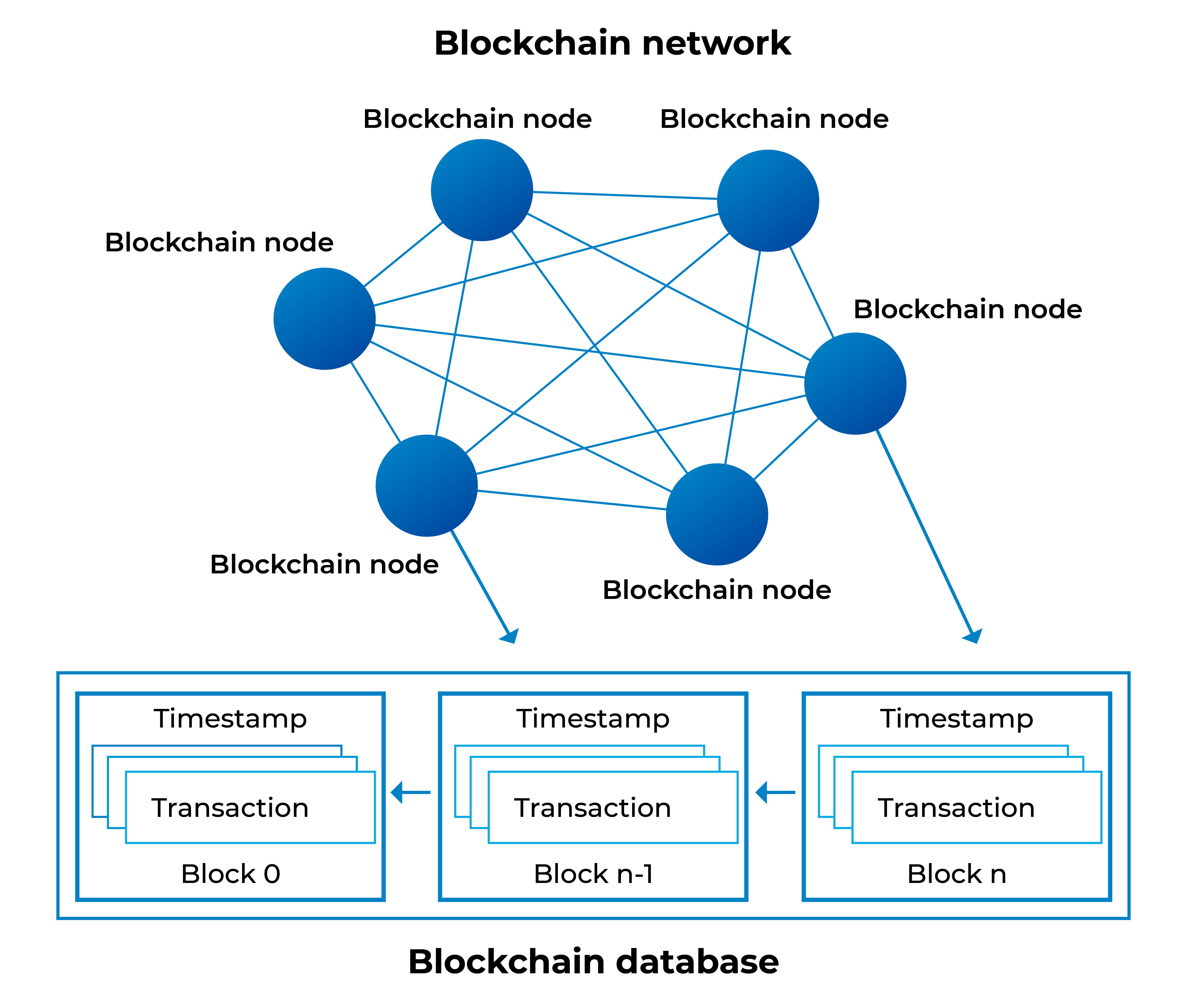
| Blocks: Information is stored in blocks, which contain transaction data and a unique identifier. Nodes: Computers participating in the blockchain network, validating and verifying transactions. Cryptography: Ensures the security of transactions by using encryption algorithms. | ||
| 2 | ||
| How Blockchain Works | ||
|---|---|---|
| Transactions are grouped into blocks and added to the blockchain in a chronological order. Each block contains a hash, a unique identifier, and a reference to the previous block. Consensus mechanisms, such as Proof of Work or Proof of Stake, are used to validate transactions. | ||
| 3 | ||
| Benefits of Blockchain | ||
|---|---|---|
| Transparency: All participants have access to the same information, reducing fraud and corruption. Security: Blockchain is tamper-proof due to cryptographic algorithms and distributed network. Efficiency: Removing intermediaries speeds up transactions and reduces costs. | ||
| 4 | ||
| Use Cases of Blockchain | ||
|---|---|---|
| Cryptocurrencies: Blockchain is the underlying technology behind digital currencies like Bitcoin and Ethereum. Supply Chain Management: Blockchain can trace and verify the origin and authenticity of products. Identity Management: Blockchain can provide secure and decentralized identity verification. | ||
| 5 | ||
| Challenges of Blockchain | ||
|---|---|---|
| Scalability: Blockchain networks can struggle with processing large volumes of transactions. Energy Consumption: Proof of Work consensus mechanism requires significant computational power. Regulatory Concerns: Legal frameworks and regulations around blockchain are still evolving. | ||
| 6 | ||
| Public vs. Private Blockchains | ||
|---|---|---|
| Public Blockchains: Open to anyone, transparent, and decentralized, like Bitcoin and Ethereum. Private Blockchains: Restricted access, controlled by a single organization or consortium. Hybrid Blockchains: Combination of public and private blockchains, offering flexibility and privacy. | ||
| 7 | ||
| Future Trends in Blockchain | ||
|---|---|---|
| Interoperability: Connecting different blockchain networks to enable seamless data exchange. Tokenization: Representing real-world assets as digital tokens on the blockchain. Decentralized Finance (DeFi): Blockchain-based financial services without intermediaries. | ||
| 8 | ||
| Industries Disrupted by Blockchain | ||
|---|---|---|
| Finance: Blockchain has the potential to revolutionize banking, payments, and remittances. Healthcare: Blockchain can securely store and share patient records, improving data accuracy. Supply Chain: Blockchain can enhance transparency and traceability in global supply chains. | ||
| 9 | ||
| Conclusion | ||
|---|---|---|
| Blockchain technology has the potential to transform various industries and improve efficiency. As the technology continues to evolve, it is crucial to address its challenges and embrace its opportunities. The world of blockchain is a promising and exciting space for innovation and disruption. | ||
| 10 | ||