The Life Cycle Of Information Technology In Health Informatics Presentation
| Introduction to the Life Cycle of Information Technology in Health Informatics | ||
|---|---|---|
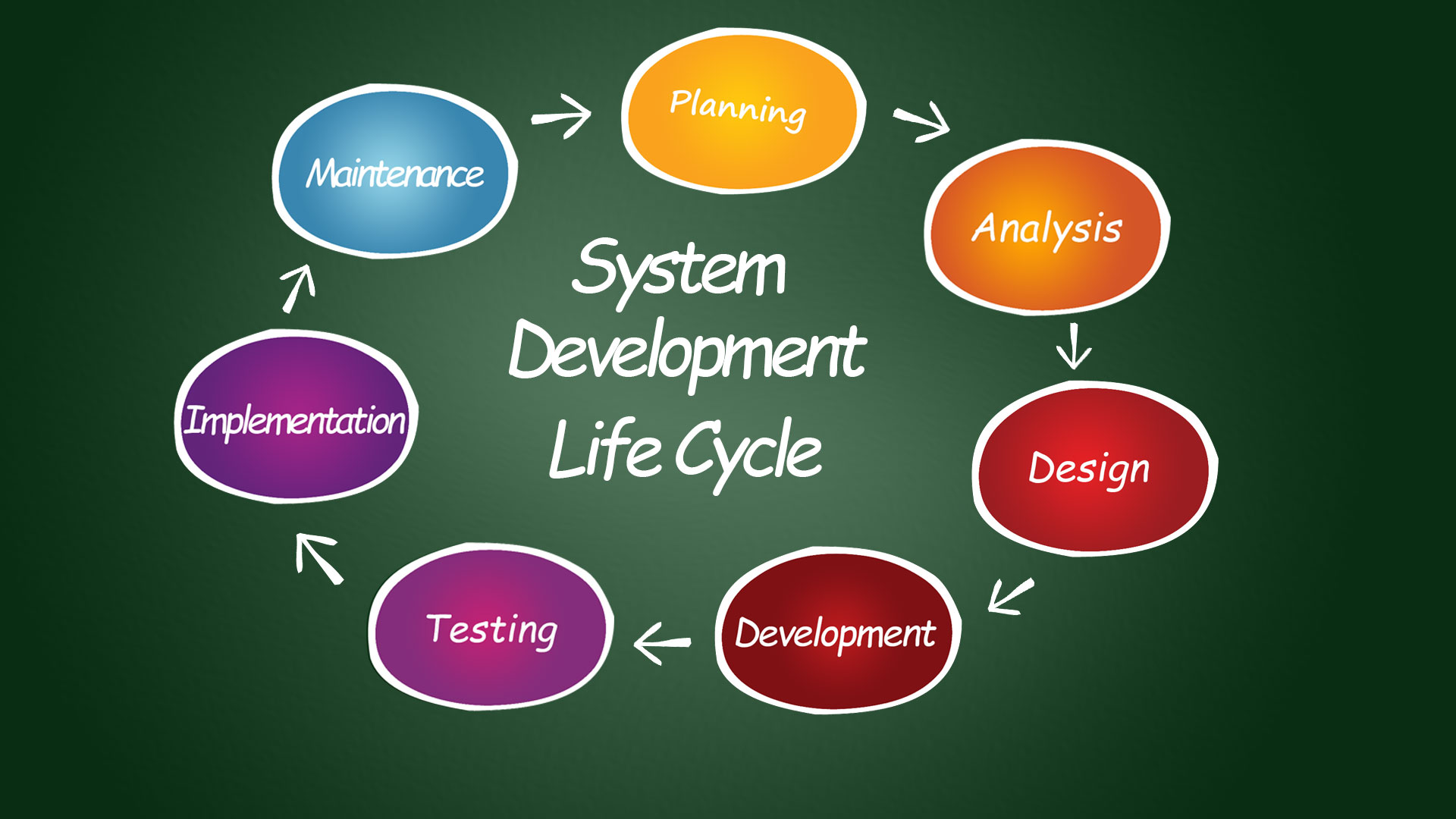
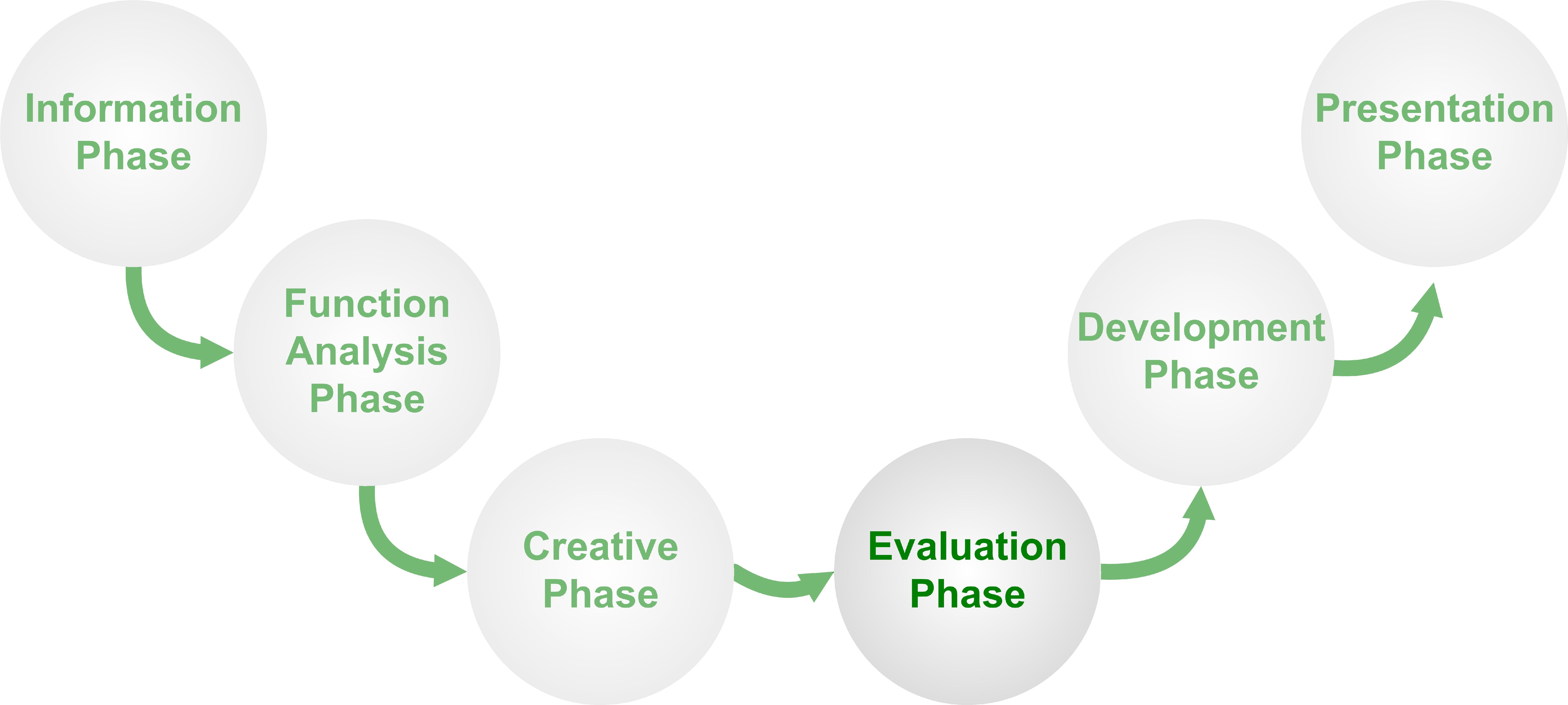
| The life cycle of IT in health informatics involves the development, implementation, and maintenance of technology solutions in healthcare settings. It encompasses various stages, including planning, analysis, design, implementation, and evaluation. Effective management of the life cycle ensures the successful integration of IT systems in healthcare organizations. | ||
| 1 | ||
| Planning Phase | ||
|---|---|---|
| During the planning phase, healthcare organizations identify their goals and objectives for implementing IT in health informatics. They assess their current IT infrastructure, identify gaps, and determine the required resources. Stakeholder engagement and collaboration are essential to ensure the alignment of IT initiatives with organizational strategies. | ||
| 2 | ||
| Analysis Phase | ||
|---|---|---|
| In the analysis phase, healthcare organizations evaluate their workflows, processes, and information needs. They conduct a comprehensive assessment of their current systems, identifying areas for improvement and potential integration with new technologies. Data security, privacy, and regulatory compliance considerations are crucial during this phase. | ||
| 3 | ||
| Design Phase | ||
|---|---|---|
| During the design phase, healthcare organizations develop a detailed plan for implementing IT solutions. They create system specifications, select appropriate hardware and software, and design user interfaces. Interoperability, usability, and scalability are key factors considered in the design of IT systems. | ||
| 4 | ||
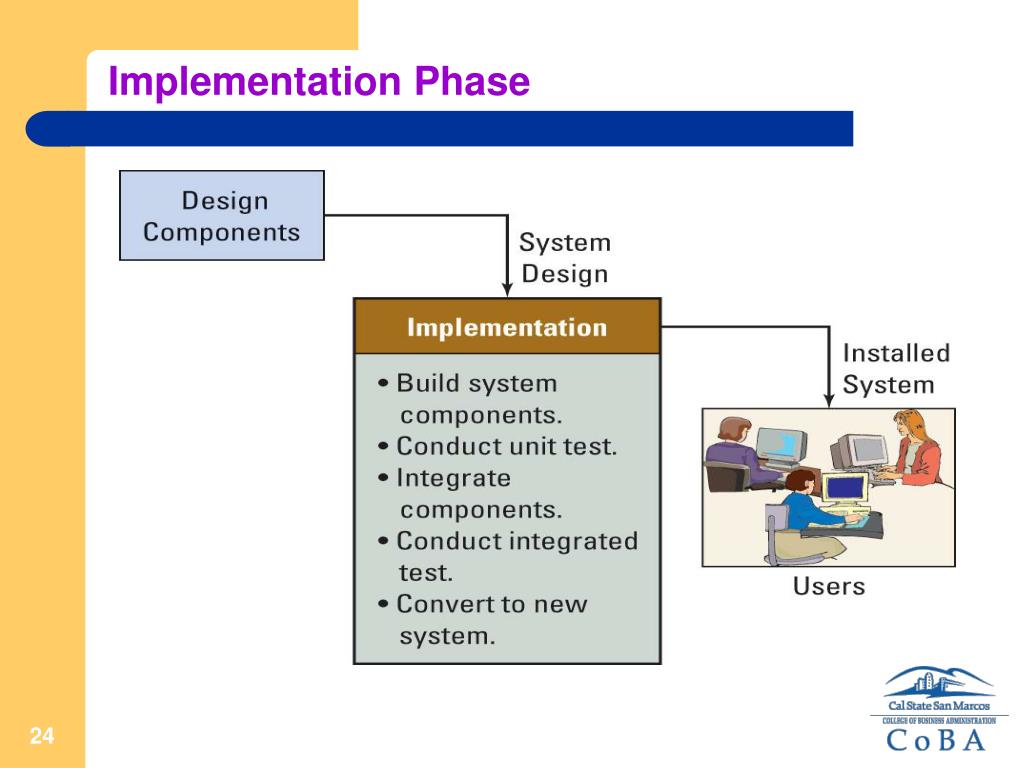
| Implementation Phase | ||
|---|---|---|
| The implementation phase involves the actual deployment of IT solutions in healthcare settings. It includes activities such as installation, configuration, data migration, and training of end-users. Effective change management strategies and user support are critical to ensure a smooth transition to the new IT systems. | ||
| 5 | ||
| Evaluation Phase | ||
|---|---|---|
| The evaluation phase focuses on assessing the effectiveness and efficiency of implemented IT solutions. Healthcare organizations monitor key performance indicators, collect user feedback, and evaluate system usability. Continuous improvement and optimization efforts are undertaken based on the evaluation results. | ||
| 6 | ||
| Maintenance and Support | ||
|---|---|---|
| Maintenance and support are ongoing activities throughout the life cycle of IT in health informatics. Regular system updates, bug fixes, and security patches are applied to ensure system reliability. Helpdesk services and user training are provided to address user issues and promote system adoption. | ||
| 7 | ||
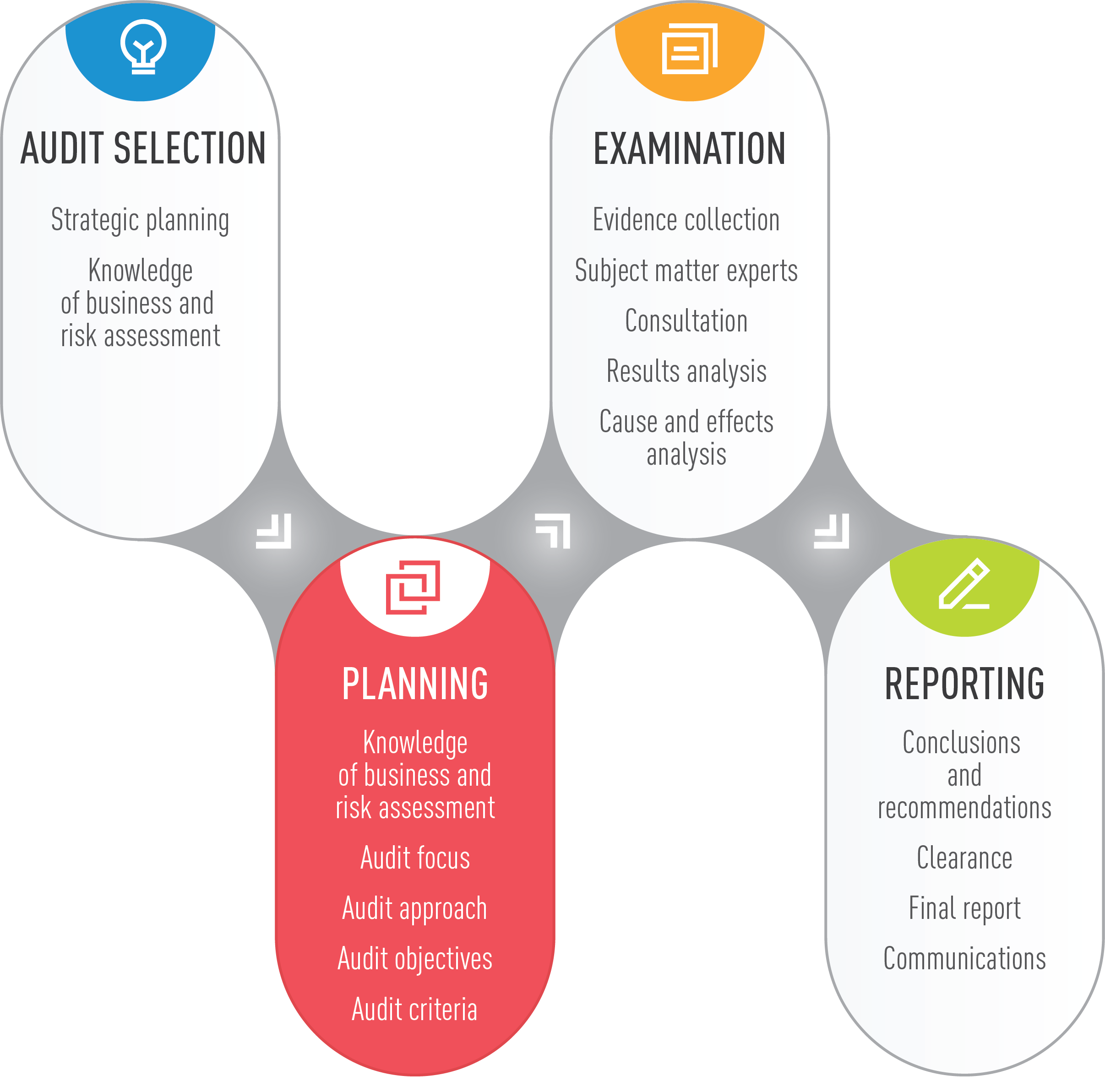
| Challenges and Considerations | ||
|---|---|---|
| Integration of IT systems with existing legacy systems can be complex and challenging. Ensuring data security and privacy while maintaining interoperability is a major concern. Adequate budget allocation and resource management are critical for the successful implementation and maintenance of IT solutions. | ||
| 8 | ||
| Benefits of IT in Health Informatics | ||
|---|---|---|
| Improved clinical decision-making through access to accurate and timely patient information. Enhanced patient care coordination and continuity across healthcare settings. Increased efficiency and productivity through automation of administrative tasks. | ||
| 9 | ||
| Conclusion | ||
|---|---|---|
| The life cycle of IT in health informatics involves planning, analysis, design, implementation, evaluation, and ongoing maintenance and support. Effective management of this life cycle ensures successful integration and utilization of IT systems in healthcare organizations. IT in health informatics brings numerous benefits, including improved clinical outcomes, enhanced patient care, and increased operational efficiency. | ||
| 10 | ||