The Life Cycle Of Information Technology (IT) Presentation
| Introduction to the Life Cycle of Information Technology (IT) | ||
|---|---|---|
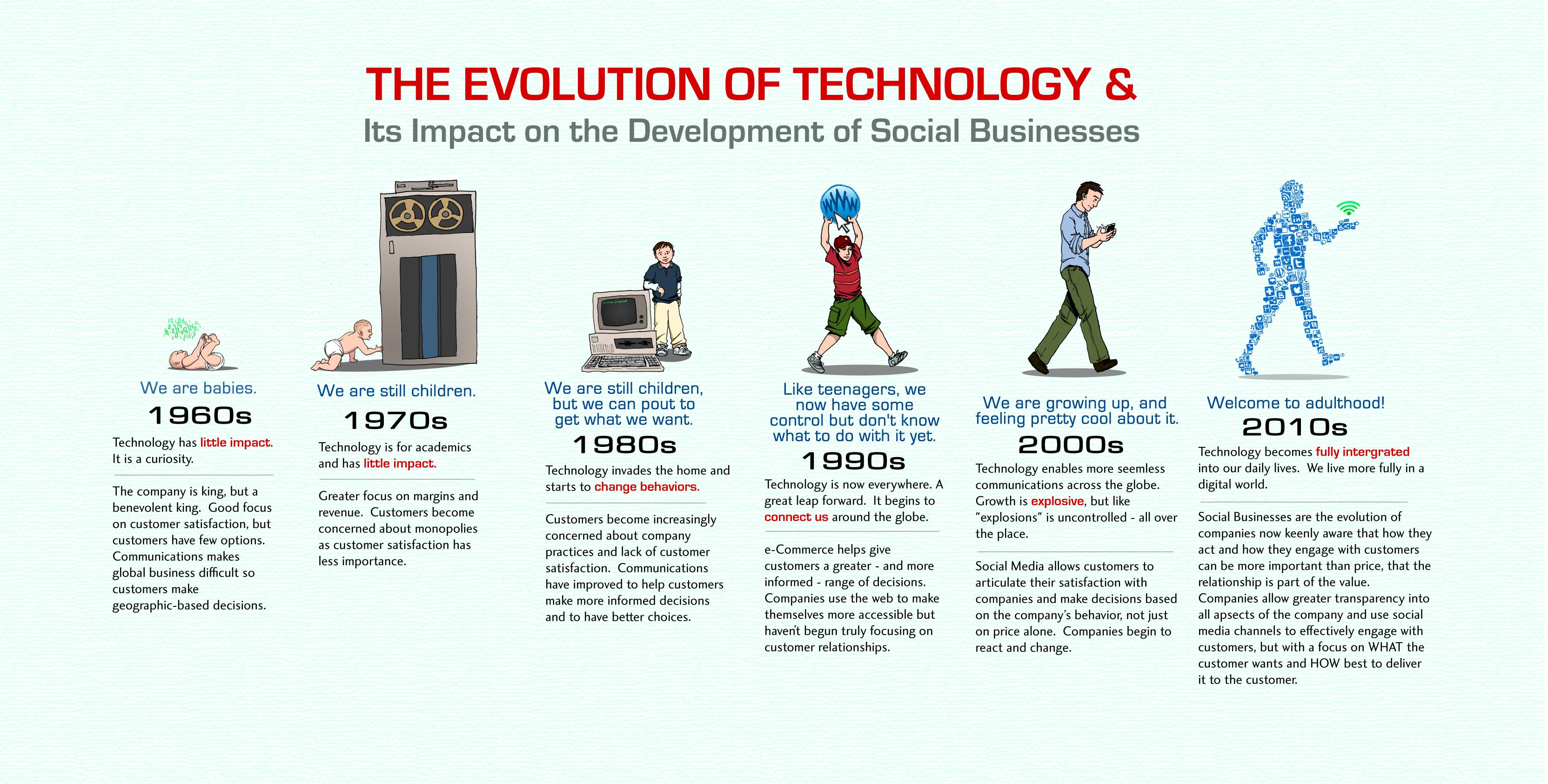
| The life cycle of IT refers to the stages through which technology evolves and becomes obsolete. It encompasses the development, deployment, maintenance, and retirement of IT systems. Understanding this life cycle is crucial for organizations to effectively manage their IT investments. | ||
| 1 | ||
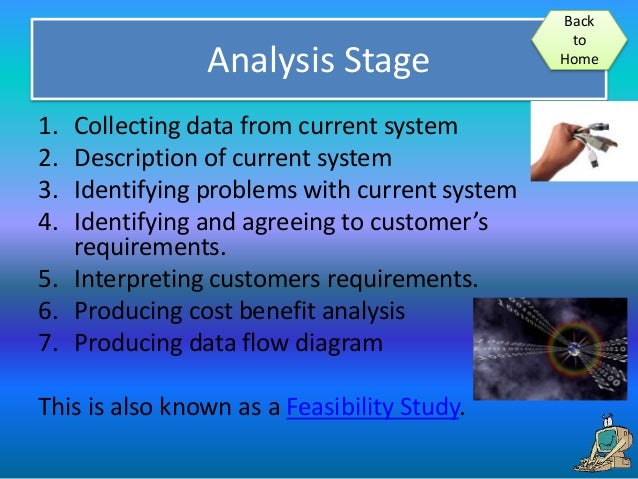
| Stage 1 - Planning and Analysis | ||
|---|---|---|
| In this stage, organizations identify their IT needs and goals. They conduct a thorough analysis of existing systems and determine the requirements for new technology. The planning and analysis stage sets the foundation for successful IT implementation. | ||
| 2 | ||
| Stage 2 - Design and Development | ||
|---|---|---|
| During this stage, IT professionals design the architecture and infrastructure of the system. They develop software and hardware components based on the identified requirements. Design and development involve iterative processes to ensure the system meets user expectations. | ||
| 3 | ||
| Stage 3 - Implementation and Deployment | ||
|---|---|---|
| The implementation stage involves installing and configuring the IT system in the organization's environment. IT professionals test the system to ensure functionality and compatibility with existing infrastructure. Once the system is deemed ready, it is deployed and made available to users. | ||
| 4 | ||
| Stage 4 - Operation and Maintenance | ||
|---|---|---|
| After deployment, the system enters the operation and maintenance stage. IT personnel monitor and manage the system to ensure its smooth operation. Regular updates, patches, and troubleshooting are performed to address any issues that arise. | ||
| 5 | ||
| Stage 5 - Upgrades and Enhancements | ||
|---|---|---|
| IT systems require periodic upgrades to incorporate new features and technologies. Enhancements may include improving performance, adding functionality, or addressing security vulnerabilities. Upgrades and enhancements are essential to keep the system up-to-date and aligned with evolving needs. | ||
| 6 | ||
| Stage 6 - Retirement and Replacement | ||
|---|---|---|
| Eventually, IT systems become outdated or no longer meet organizational needs. The retirement stage involves retiring or decommissioning the system. Organizations must plan for the replacement of the retired system to ensure continuity of operations. | ||
| 7 | ||
| Challenges in the IT Life Cycle | ||
|---|---|---|
| One of the challenges is the rapid pace of technological advancements, which can lead to systems quickly becoming obsolete. Budget constraints may limit the ability to invest in necessary upgrades or replacements. Ensuring the security and privacy of data throughout the life cycle is another significant challenge. | ||
| 8 | ||
| Best Practices for Managing the IT Life Cycle | ||
|---|---|---|
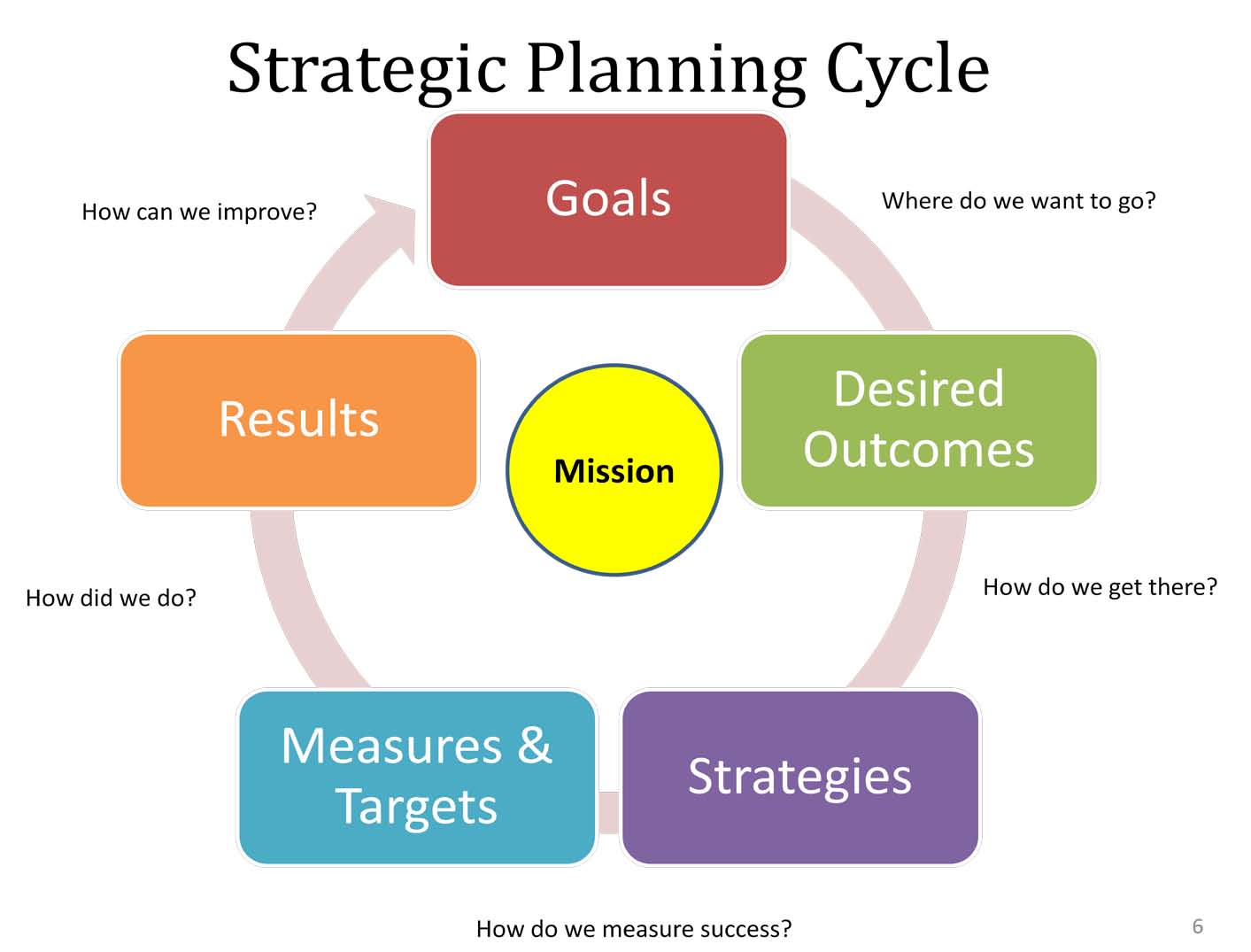
| Adopt a strategic approach that aligns IT investments with organizational goals. Regularly assess and update IT policies and procedures to adapt to changing technology and security requirements. Establish a comprehensive asset management system to track and manage the life cycle of IT resources. | ||
| 9 | ||
| Conclusion | ||
|---|---|---|
| The life cycle of IT encompasses planning, analysis, design, implementation, operation, upgrades, and retirement. Effective management of the IT life cycle is crucial for organizations to maximize their IT investments. By understanding the stages and challenges of the life cycle, organizations can make informed decisions and ensure their IT systems support their overall objectives. | ||
| 10 | ||





.png)