Swelling Presentation
| Introduction to Swelling | ||
|---|---|---|
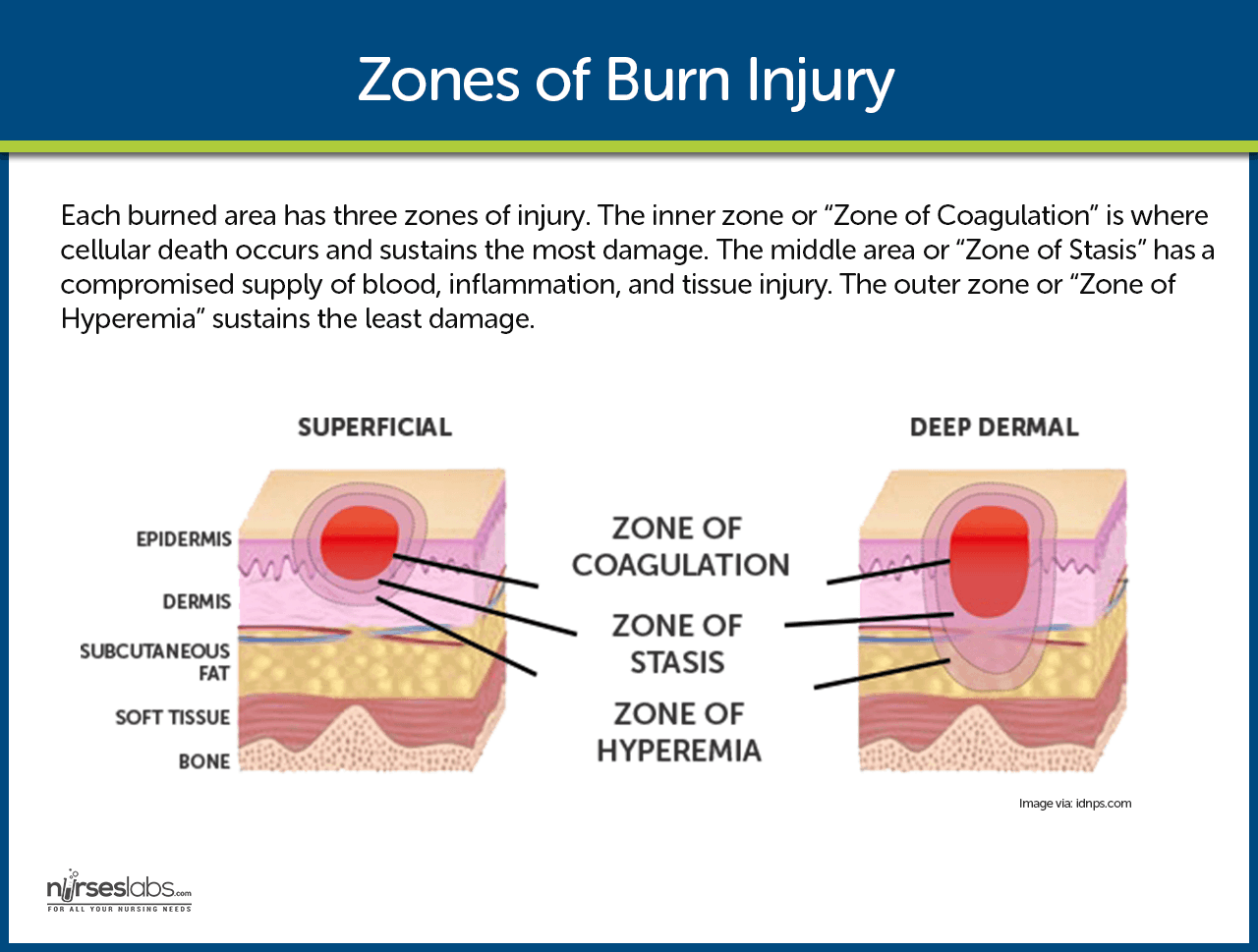
| Swelling, also known as edema, is the enlargement or puffiness of a body part due to an accumulation of fluid. It is a common symptom that can occur in various parts of the body. Swelling can be caused by various factors such as injury, inflammation, infection, or underlying medical conditions. | ||
| 1 | ||
| Types of Swelling | ||
|---|---|---|
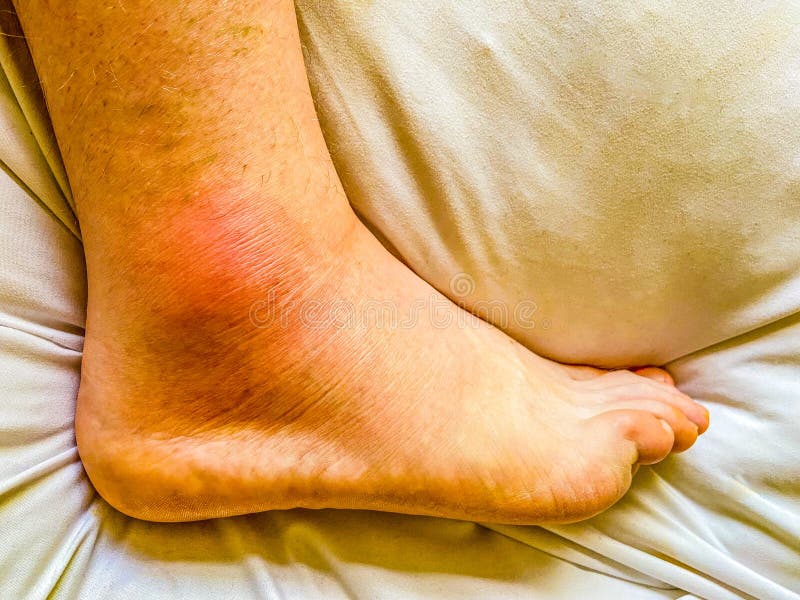
| Localized swelling: Limited to a specific area, such as an injury site or a joint affected by arthritis. Generalized swelling: Affects larger areas of the body, such as the legs, hands, or face. Pitting edema: When pressure applied to the swollen area leaves an indentation that slowly fills back in. | ||
| 2 | ||
| Causes of Swelling | ||
|---|---|---|
| Injury: Trauma or damage to tissues can lead to localized swelling. Inflammation: The body's response to injury or infection can cause swelling as part of the healing process. Infection: Swelling can occur as a result of an infection, such as cellulitis or abscess. | ||
| 3 | ||
| Symptoms Associated with Swelling | ||
|---|---|---|
| Redness and warmth: Swollen areas may appear red and feel warm to the touch. Pain or tenderness: Swelling can be accompanied by pain or tenderness, especially if caused by injury or inflammation. Limited range of motion: Swelling in joints can restrict movement and cause stiffness. | ||
| 4 | ||
| When to Seek Medical Attention | ||
|---|---|---|
| Severe or sudden swelling without an apparent cause. Swelling accompanied by severe pain or inability to move the affected area. Swelling that persists or worsens over time. | ||
| 5 | ||
| Treatment Options for Swelling | ||
|---|---|---|
| Rest and elevation: Elevating the affected area above heart level can help reduce swelling. Applying cold compress: Using ice packs or cold compresses can help reduce inflammation and swelling. Medications: In some cases, over-the-counter anti-inflammatory drugs or prescribed medications may be necessary. | ||
| 6 | ||
| Prevention and Self-Care | ||
|---|---|---|
| Avoiding prolonged periods of inactivity or sitting can help prevent swelling in the legs and feet. Wearing compression garments, such as stockings, can improve circulation and reduce swelling. Maintaining a healthy diet and weight can help prevent swelling associated with fluid retention. | ||
| 7 | ||
| Complications of Swelling | ||
|---|---|---|
| Impaired circulation: Severe or prolonged swelling can impede blood flow, leading to tissue damage or other complications. Infection: Swollen areas are more susceptible to infection, especially if the skin is broken or compromised. Chronic swelling: Some medical conditions can cause long-term or recurring swelling, requiring ongoing management. | ||
| 8 | ||
| When to Follow Up with a Healthcare Provider | ||
|---|---|---|
| Swelling that does not improve with self-care measures. Swelling accompanied by other concerning symptoms, such as fever or unexplained weight loss. Swelling that affects daily activities or quality of life. | ||
| 9 | ||
| Conclusion | ||
|---|---|---|
| Swelling is a common symptom that can occur due to various reasons. Prompt evaluation and appropriate treatment can help alleviate symptoms and prevent complications. If you have concerns about swelling, it is important to consult with a healthcare provider for an accurate diagnosis and proper management. | ||
| 10 | ||







/common-causes-of-foot-and-ankle-swelling-1337777_final-b2d7802a1c594b9f8cbea3301755a4ef.png)