Staphylococcus Presentation
| Introduction to Staphylococcus | ||
|---|---|---|
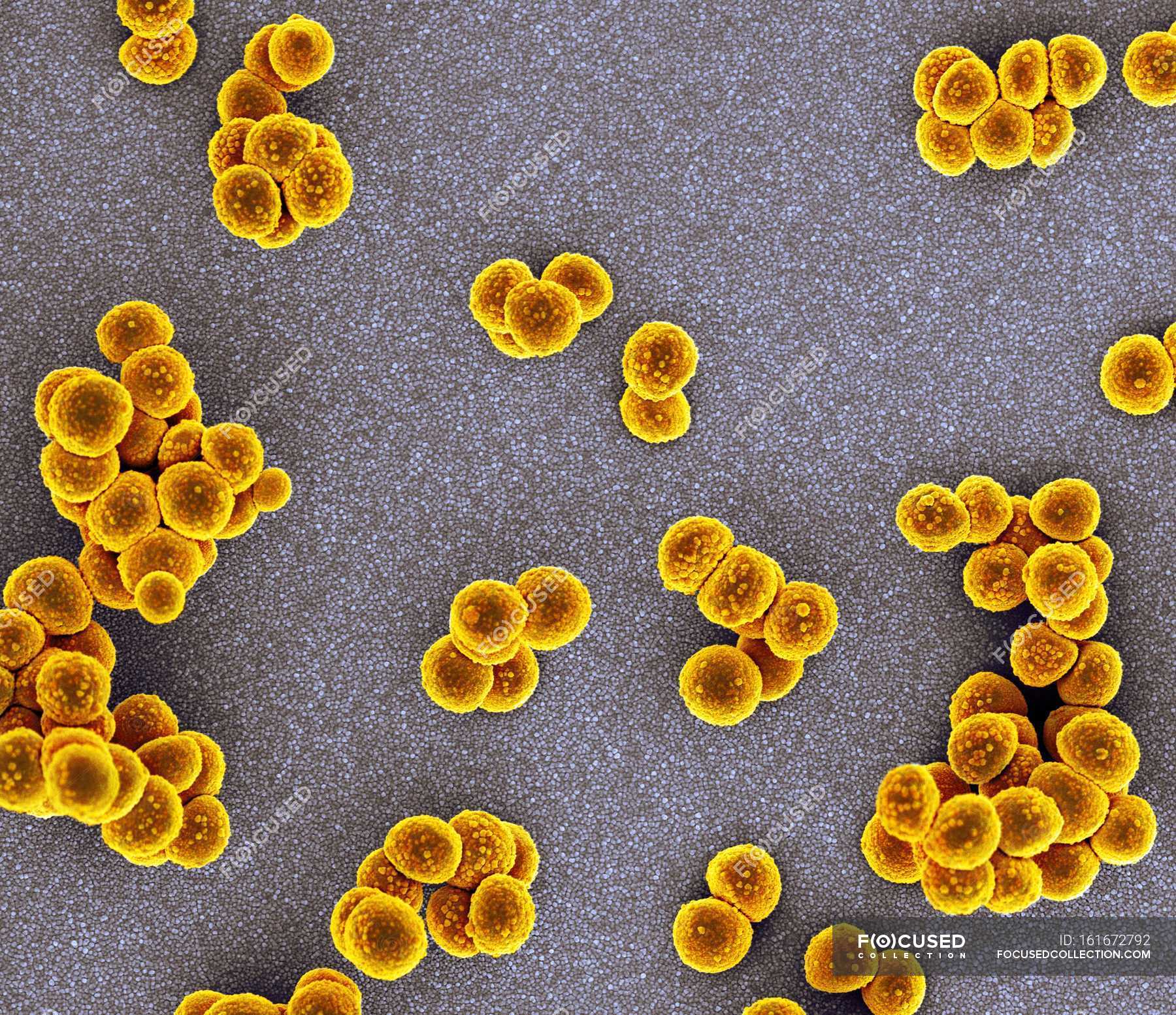
| Staphylococcus is a genus of bacteria that belongs to the family Staphylococcaceae. It is commonly found on the skin and mucous membranes of humans and animals. Staphylococcus can cause a range of infections, from minor skin infections to severe and life-threatening diseases. | ||
| 1 | ||
| Types of Staphylococcus | ||
|---|---|---|
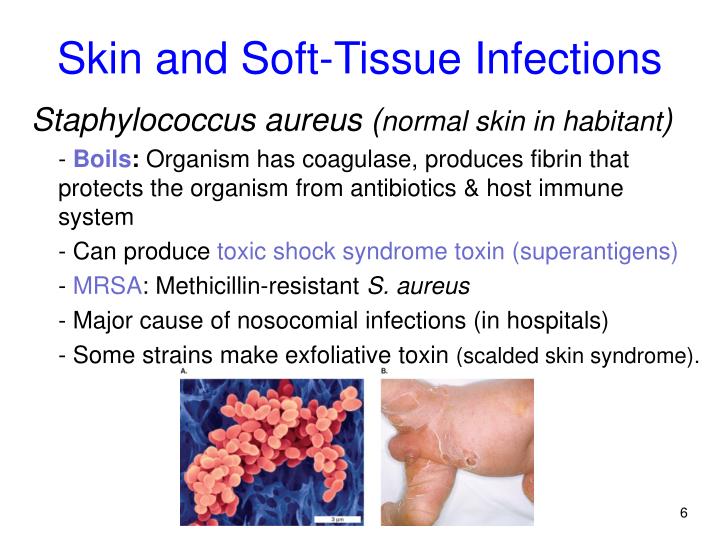
| Staphylococcus aureus is the most common and well-known species of Staphylococcus. Other species include Staphylococcus epidermidis, Staphylococcus saprophyticus, and Staphylococcus haemolyticus. Each species of Staphylococcus has different virulence factors and characteristics. | ||
| 2 | ||
| Staphylococcus Infections | ||
|---|---|---|
| Staphylococcus infections can manifest as skin and soft tissue infections, such as boils and impetigo. Invasive infections can occur, including pneumonia, bloodstream infections, and endocarditis. Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) is a major concern due to its resistance to many antibiotics. | ||
| 3 | ||
| Transmission of Staphylococcus | ||
|---|---|---|
| Staphylococcus can be transmitted through direct contact with infected individuals or contaminated surfaces. Poor hygiene practices, crowded living conditions, and compromised immune systems increase the risk of transmission. Healthcare settings, such as hospitals, are common sites for Staphylococcus outbreaks. | ||
| 4 | ||
| Diagnosis of Staphylococcus Infections | ||
|---|---|---|
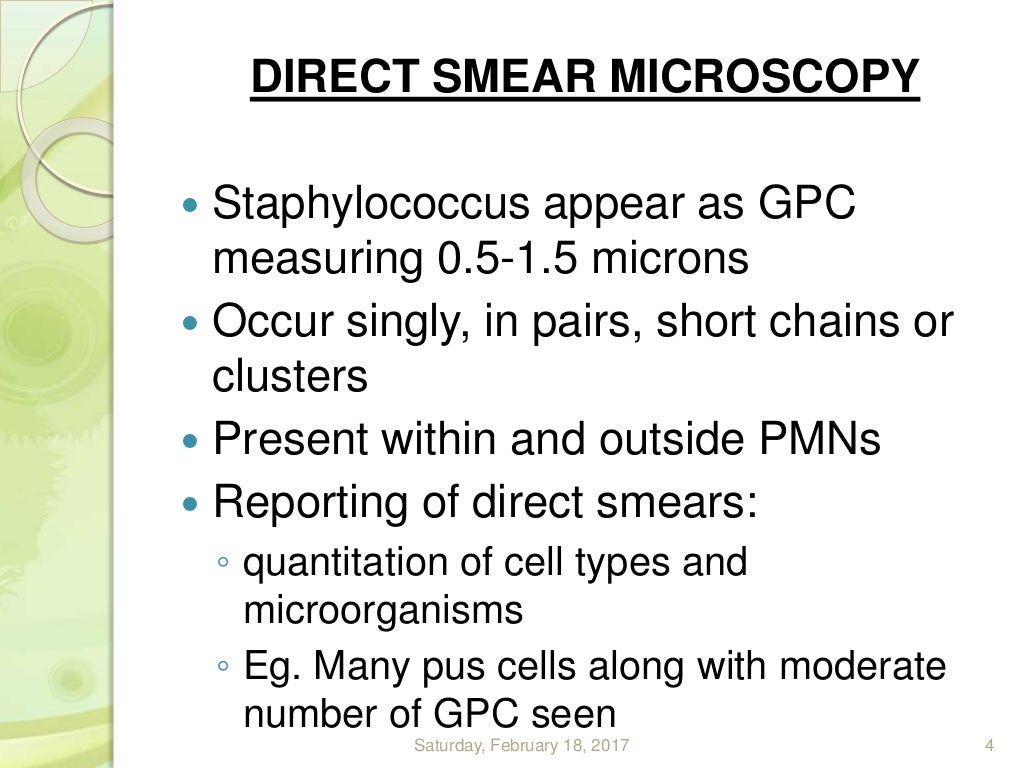
| Laboratory tests, such as blood cultures and swab cultures, are used to identify Staphylococcus infections. The antibiotic susceptibility of the bacteria is determined through antimicrobial susceptibility testing. Rapid diagnostic tests, such as PCR, can provide quick results for certain Staphylococcus infections. | ||
| 5 | ||
| Treatment of Staphylococcus Infections | ||
|---|---|---|
| Antibiotics are the mainstay of treatment for Staphylococcus infections. The choice of antibiotics depends on the susceptibility profile of the bacteria. In severe cases, surgical intervention may be required to drain abscesses or remove infected tissues. | ||
| 6 | ||
| Prevention and Control of Staphylococcus Infections | ||
|---|---|---|
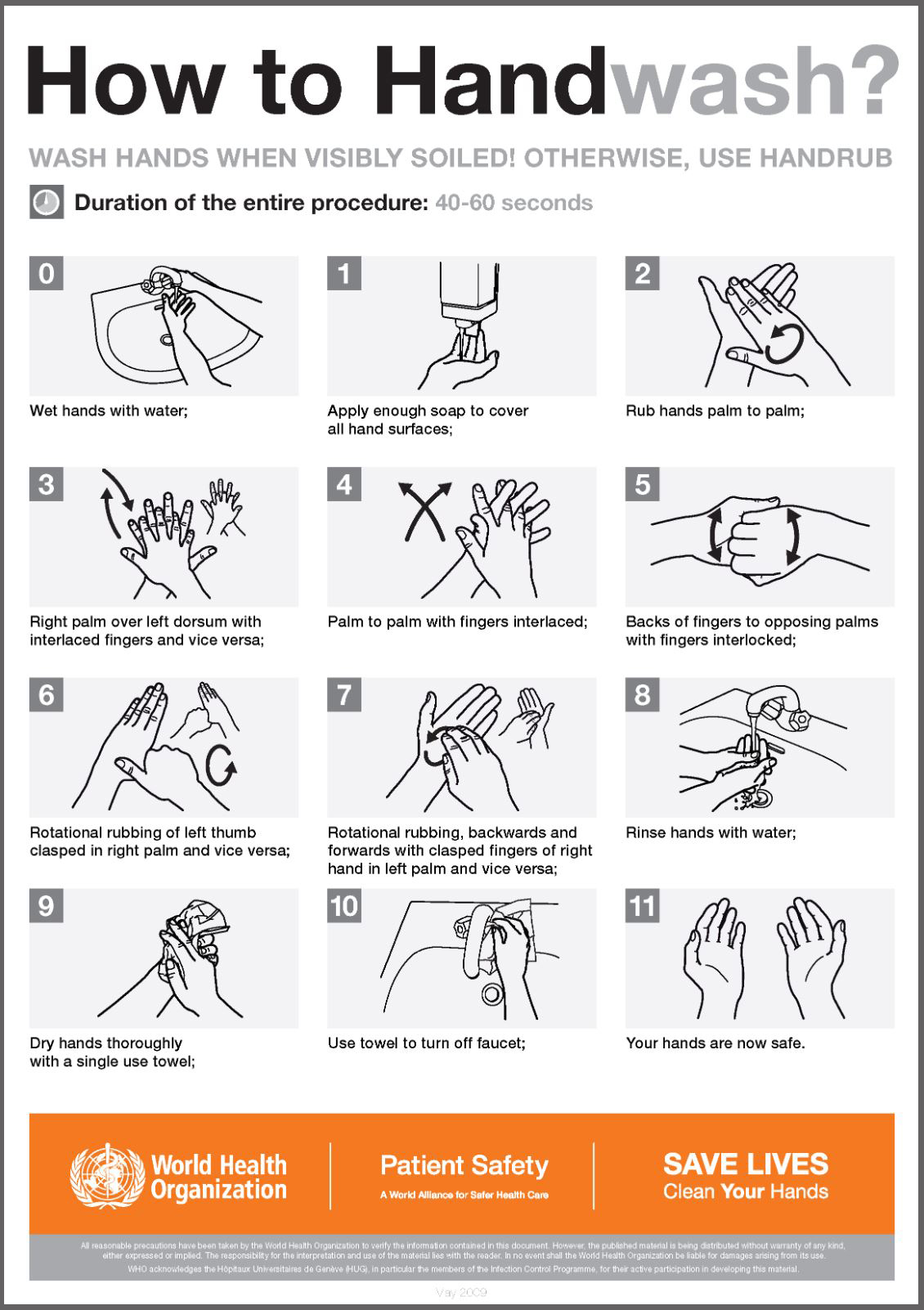
| Good hand hygiene practices, such as regular handwashing, can help prevent the spread of Staphylococcus. Proper wound care and infection control measures in healthcare settings are crucial in preventing healthcare-associated infections. Vaccines for some Staphylococcus infections, such as Staphylococcus aureus, are being developed. | ||
| 7 | ||
| Antibiotic Resistance in Staphylococcus | ||
|---|---|---|
| Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) is a major concern due to its resistance to multiple antibiotics. The inappropriate use of antibiotics contributes to the development of antibiotic-resistant strains. Antimicrobial stewardship programs aim to promote appropriate antibiotic use and reduce the prevalence of antibiotic resistance. | ||
| 8 | ||
| Research and Future Directions | ||
|---|---|---|
| Ongoing research focuses on developing new antibiotics and alternative treatment options for Staphylococcus infections. The study of the molecular mechanisms of Staphylococcus virulence and antibiotic resistance is essential for targeted therapies. Improved surveillance and infection control measures are needed to combat the spread of antibiotic-resistant Staphylococcus strains. | ||
| 9 | ||
| Conclusion | ||
|---|---|---|
| Staphylococcus is a diverse group of bacteria that can cause a range of infections. Prevention, early diagnosis, and appropriate treatment are key in managing Staphylococcus infections. Continued research and efforts to control antibiotic resistance are essential in combating Staphylococcus-related diseases. | ||
| 10 | ||

:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/staphylococcus_aureus_bac-57bf23e93df78cc16e1dff45.jpg)