Stainting Technique Presentation
| Introduction to Staining Technique | ||
|---|---|---|
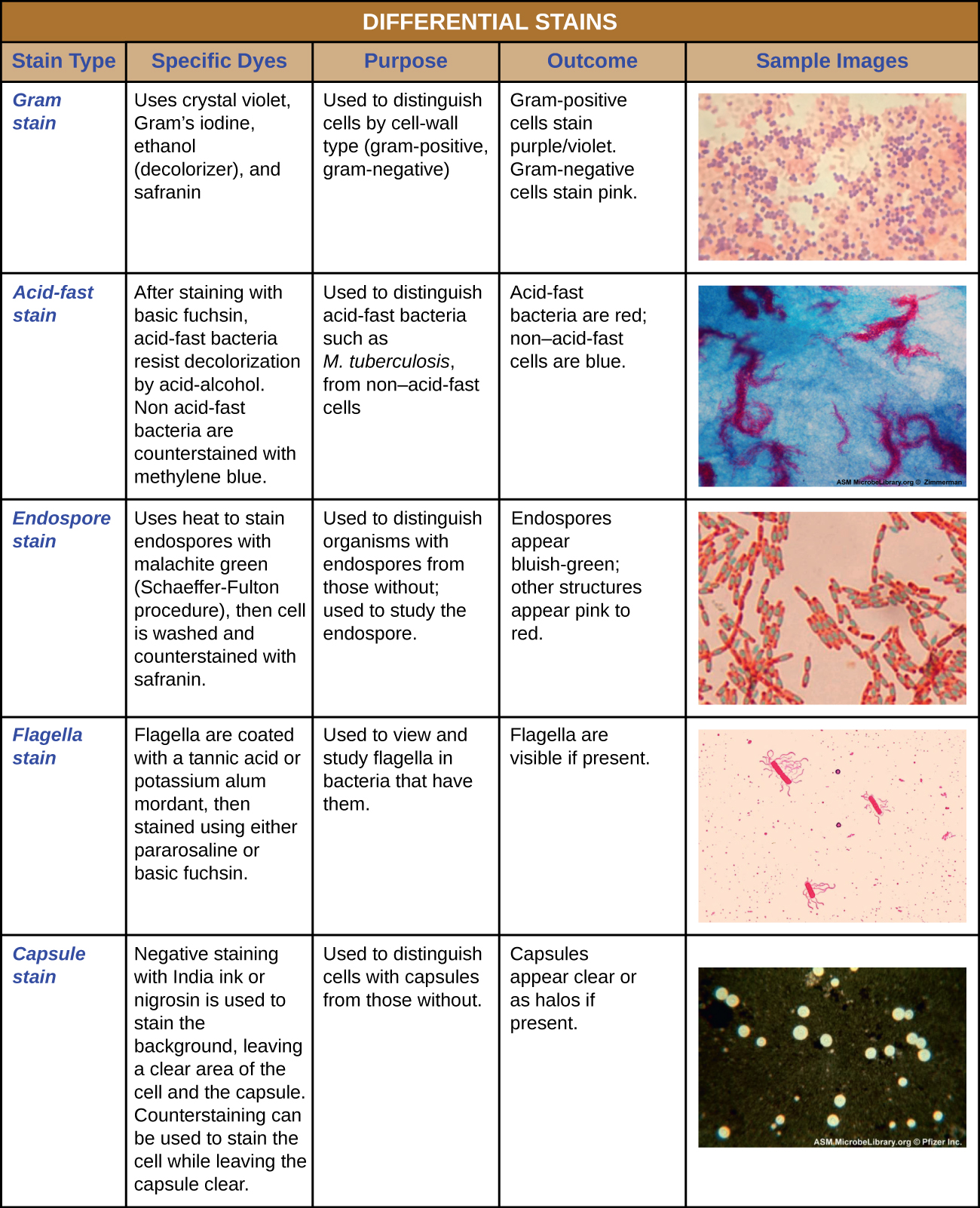
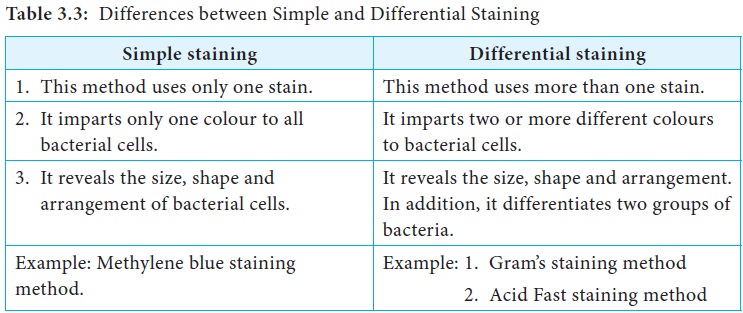
| Staining technique is a method used in microscopy to enhance the visibility of cells or tissues. It involves the application of dyes or stains to highlight specific structures or components within the sample. Staining techniques can be used in various fields such as pathology, microbiology, and histology. | ||
| 1 | ||
| Types of Stains | ||
|---|---|---|
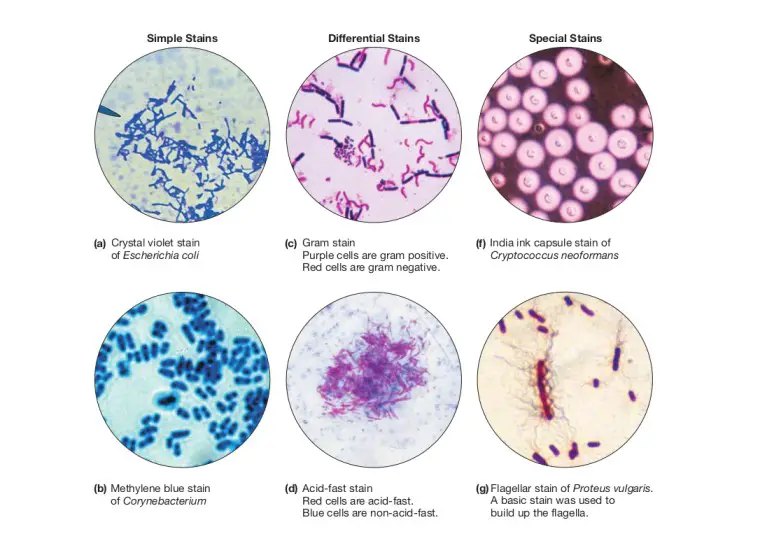
| Hematoxylin and eosin (H&E) stain is commonly used in histology to visualize cellular structures. Gram stain is utilized in microbiology to differentiate bacteria based on their cell wall composition. Immunohistochemistry (IHC) stains specific proteins or antigens in tissues, aiding in disease diagnosis. |  | |
| 2 | ||
| Preparation of Samples | ||
|---|---|---|
| Prior to staining, samples are usually fixed to preserve their structure and prevent degradation. Different fixation methods include formalin, methanol, or glutaraldehyde, depending on the sample type. Samples are then embedded in paraffin or frozen, sectioned, and mounted on glass slides for staining. | ||
| 3 | ||
| Staining Process | ||
|---|---|---|
| The staining process typically involves a series of steps, including deparaffinization and rehydration for paraffin-embedded samples. Stains are applied to the samples, either through direct contact or through chemical reactions with specific components. Excess stain is removed by rinsing with water or buffer solutions. | ||
| 4 | ||
| Common Staining Techniques | ||
|---|---|---|
| Hematoxylin and eosin (H&E) stain is used to visualize nuclei (blue) and cytoplasm (pink) in tissues. Periodic Acid-Schiff (PAS) stain is used to detect glycogen and other carbohydrates in cells or tissues. Giemsa stain is commonly used for blood smears to identify parasites, bacteria, and other cell types. |  | |
| 5 | ||
| Specialized Staining Techniques | ||
|---|---|---|
| Silver staining is employed to visualize structures like nerve fibers, reticular fibers, or basement membranes. Oil Red O stain is used to detect lipid droplets in cells or tissues. Toluidine blue stain is used to identify mast cells in histological samples. | ||
| 6 | ||
| Advantages of Staining Techniques | ||
|---|---|---|
| Staining techniques provide contrast and enhance the visibility of cellular structures. They aid in the identification and classification of various cell types, microorganisms, or pathological conditions. Staining techniques help in diagnosing diseases and understanding biological processes. | ||
| 7 | ||
| Limitations of Staining Techniques | ||
|---|---|---|
| Different stains have specific affinities, limiting their applicability to certain structures or components. Staining techniques may alter the sample's native morphology or introduce artifacts. Interpretation of stained samples requires expertise and may be subjective. | ||
| 8 | ||
| Recent Advances in Staining Techniques | ||
|---|---|---|
| Fluorescent dyes and immunofluorescence techniques enable specific visualization of proteins or antigens. Multiplex staining techniques allow simultaneous detection of multiple targets within the same sample. Digital imaging and automated analysis tools enhance the efficiency and accuracy of staining interpretation. | ||
| 9 | ||
| Conclusion | ||
|---|---|---|
| Staining techniques play a crucial role in visualizing cellular structures and aiding in disease diagnosis. Advancements in staining techniques continue to improve our understanding of biological processes. With proper sample preparation and expertise, staining techniques provide valuable insights in various scientific and medical fields. | ||
| 10 | ||