Spirometry In Biology Presentation
| Introduction to Spirometry in Biology | ||
|---|---|---|
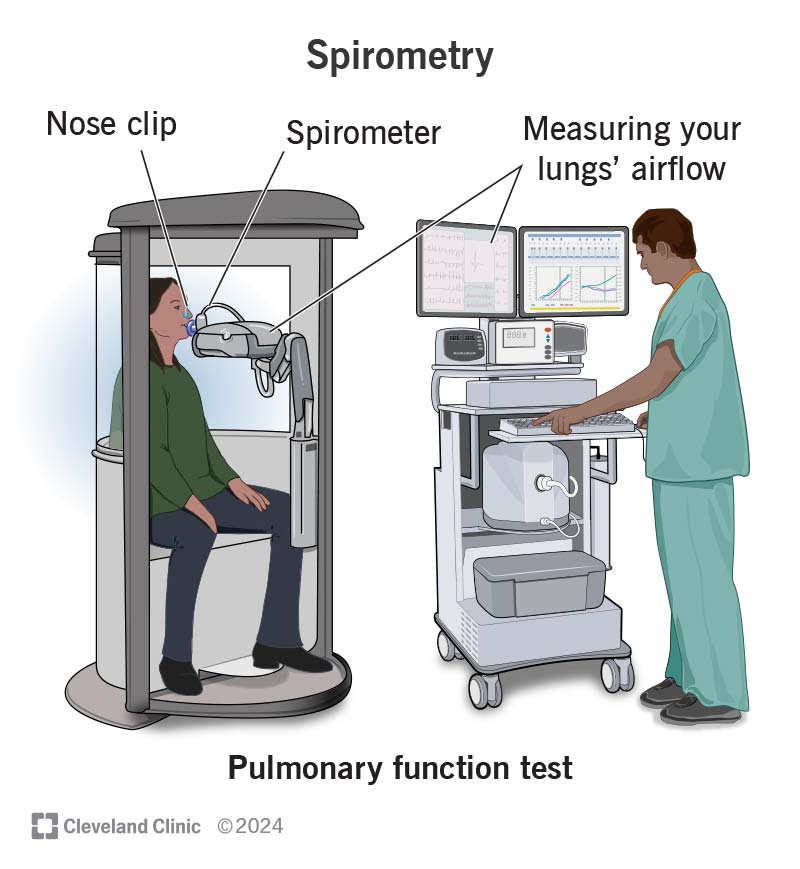
| Spirometry is a commonly used technique in biology to measure lung function. It provides valuable information about the volume and flow of air inhaled and exhaled by an individual. Spirometry is a non-invasive and reliable method that helps diagnose respiratory conditions and monitor lung health. | ||
| 1 | ||
| Principles of Spirometry | ||
|---|---|---|
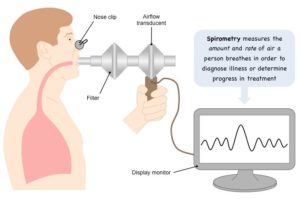
| Spirometry measures lung volumes and capacities using a spirometer, a device that records airflow. During spirometry, the individual breathes into a mouthpiece connected to the spirometer. The spirometer measures parameters such as tidal volume, inspiratory reserve volume, expiratory reserve volume, and vital capacity. | ||
| 2 | ||
| Clinical Applications of Spirometry | ||
|---|---|---|
| Spirometry is essential in diagnosing and monitoring respiratory diseases such as asthma, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), and cystic fibrosis. It helps assess the severity of lung diseases, monitor treatment effectiveness, and predict prognosis. Spirometry is also used for pre-operative assessments to evaluate lung function before surgery. | ||
| 3 | ||
| How to Perform Spirometry | ||
|---|---|---|
| The individual is instructed to take a deep breath and exhale forcefully into the spirometer. The test may be repeated several times to ensure accuracy and consistency of results. Spirometry requires proper technique and cooperation from the individual being tested to obtain reliable and valid data. | ||
| 4 | ||
| Limitations and Considerations of Spirometry | ||
|---|---|---|
| Spirometry results can be influenced by factors such as age, height, gender, and ethnicity. It may not be suitable for individuals with certain physical or cognitive limitations. Proper training and calibration of the spirometer are necessary to ensure accurate results. Note: This is a general outline for a 5-slide presentation about spirometry in biology. Additional content, visuals, and explanations can be added to each slide to provide a more comprehensive presentation. |  | |
| 5 | ||