Smart Sensors Presentation
| Introduction to Smart Sensors | ||
|---|---|---|
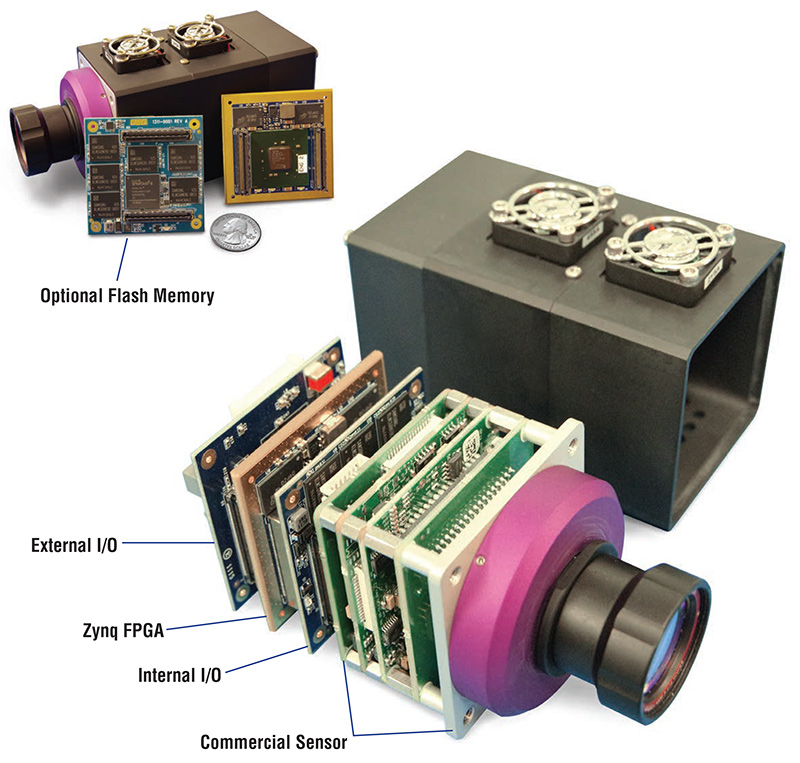
| Smart sensors are devices that can detect and measure physical, chemical, or biological inputs, and then convert them into digital signals. They are designed to be highly efficient, accurate, and capable of real-time data processing. Smart sensors play a crucial role in various industries, including healthcare, manufacturing, transportation, and environmental monitoring. | ||
| 1 | ||
| Features of Smart Sensors | ||
|---|---|---|
| Smart sensors are equipped with built-in microprocessors, which enable them to process data locally. They have the ability to communicate with other devices or networks, facilitating data sharing and analysis. Smart sensors are often embedded with artificial intelligence algorithms, allowing them to learn and adapt to changing conditions. | ||
| 2 | ||
| Applications of Smart Sensors | ||
|---|---|---|
| In healthcare, smart sensors are used for patient monitoring, disease detection, and medication adherence tracking. In manufacturing, smart sensors are employed for quality control, predictive maintenance, and process optimization. In transportation, smart sensors are utilized for traffic management, autonomous vehicles, and driver assistance systems. | ||
| 3 | ||
| Benefits of Smart Sensors | ||
|---|---|---|
| Smart sensors enable real-time monitoring, providing instant feedback and enabling prompt decision-making. They enhance efficiency by automating processes, reducing manual intervention, and minimizing errors. Smart sensors contribute to improved safety and reliability by detecting anomalies and potential hazards. | ||
| 4 | ||
| Challenges and Limitations | ||
|---|---|---|
| Privacy and security concerns arise due to the collection and transmission of sensitive data by smart sensors. Cost can be a barrier to widespread adoption, as smart sensors often require significant investment. Compatibility and interoperability issues may arise when integrating smart sensors with existing systems and infrastructure. | ||
| 5 | ||
| Future Trends in Smart Sensors | ||
|---|---|---|
| Miniaturization and increased energy efficiency will lead to the development of smaller, more versatile smart sensors. Integration of smart sensors with edge computing and cloud platforms will enhance data processing and analysis capabilities. Advances in sensor technologies, such as MEMS and nanotechnology, will enable more precise and sensitive measurements. | ||
| 6 | ||
| Case Study: Smart Sensors in Environmental Monitoring | ||
|---|---|---|
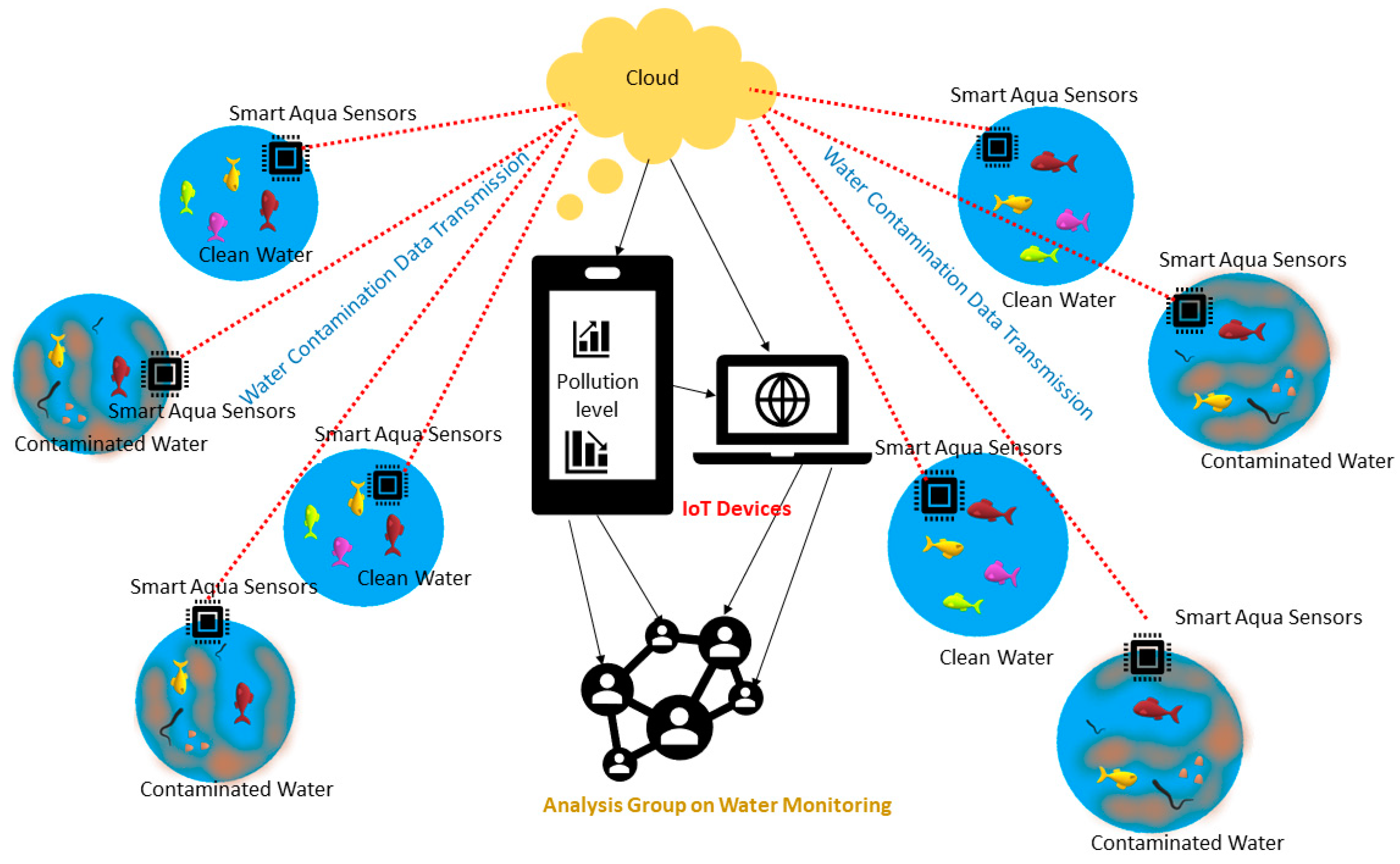
| Smart sensors are utilized in air quality monitoring systems to detect pollutants and provide real-time data for analysis. They enable early detection of environmental hazards, helping to mitigate their impact on human health and ecosystems. Smart sensors can be integrated into smart city initiatives, providing valuable insights for urban planning and resource management. | ||
| 7 | ||
| Case Study: Smart Sensors in Agriculture | ||
|---|---|---|
| Smart sensors are used in precision farming to monitor soil moisture, temperature, and nutrient levels, optimizing crop growth. They enable farmers to make data-driven decisions, leading to increased yields, reduced resource consumption, and improved sustainability. Smart sensors can also be employed in livestock monitoring, ensuring animal welfare and optimizing feeding and breeding practices. | ||
| 8 | ||
| Case Study: Smart Sensors in Smart Homes | ||
|---|---|---|
| Smart sensors are integrated into home automation systems, enabling remote monitoring and control of various home functions. They detect motion, temperature, and humidity, allowing for energy-efficient climate control and improved security. Smart sensors can also detect leaks, smoke, and other potential hazards, enhancing safety and minimizing damage. | ||
| 9 | ||
| Conclusion | ||
|---|---|---|
| Smart sensors are revolutionizing industries by enabling real-time monitoring, automation, and data-driven decision-making. Despite challenges, the future of smart sensors looks promising, with advancements in technology and increased adoption. As smart sensors continue to evolve, they will play a vital role in creating smarter, more connected, and sustainable environments. | ||
| 10 | ||