Sloar Panel Presentation
| Introduction to Solar Panels | ||
|---|---|---|
| Solar panels are devices that convert sunlight into electricity. They are made up of photovoltaic cells that absorb sunlight and produce electric current. Solar panels are a sustainable and renewable source of energy. | ||
| 1 | ||
| How Solar Panels Work | ||
|---|---|---|
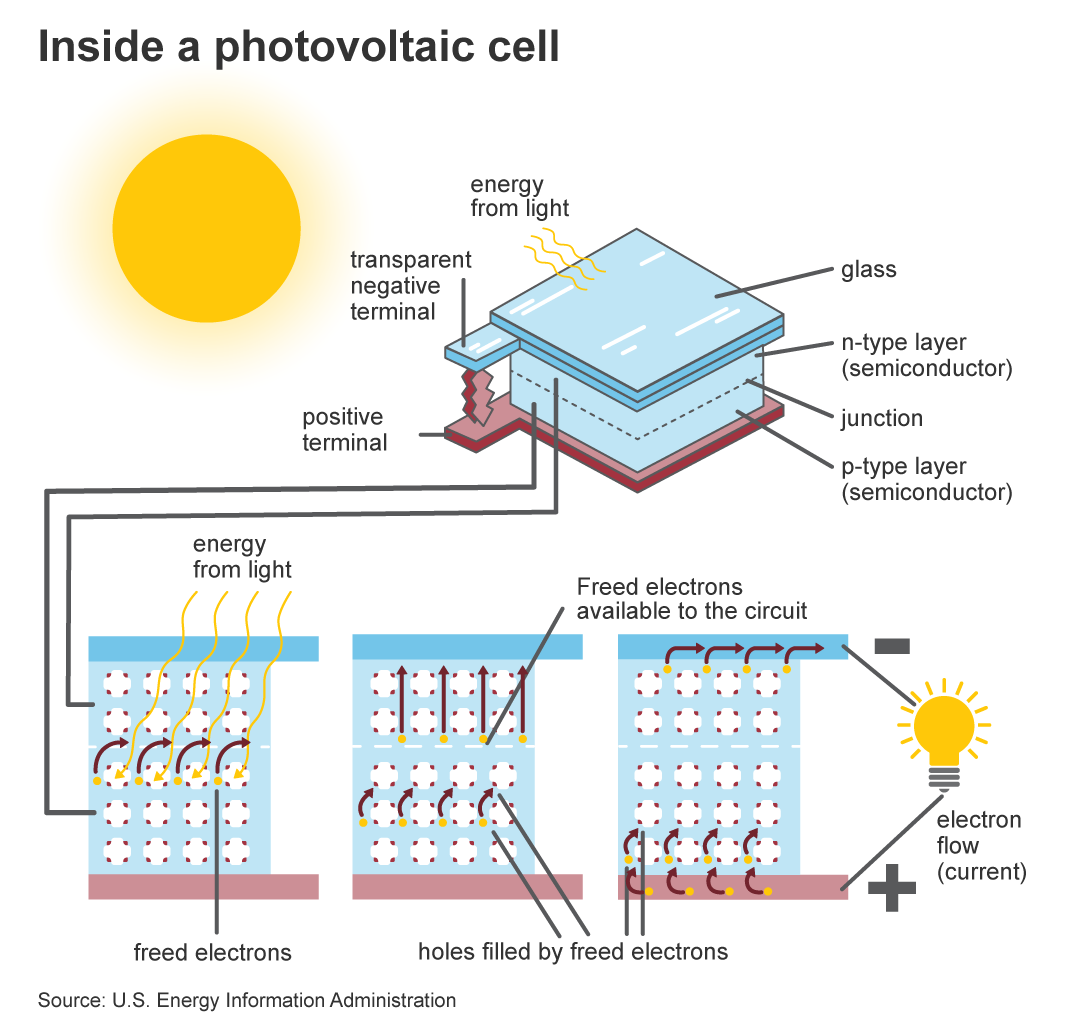
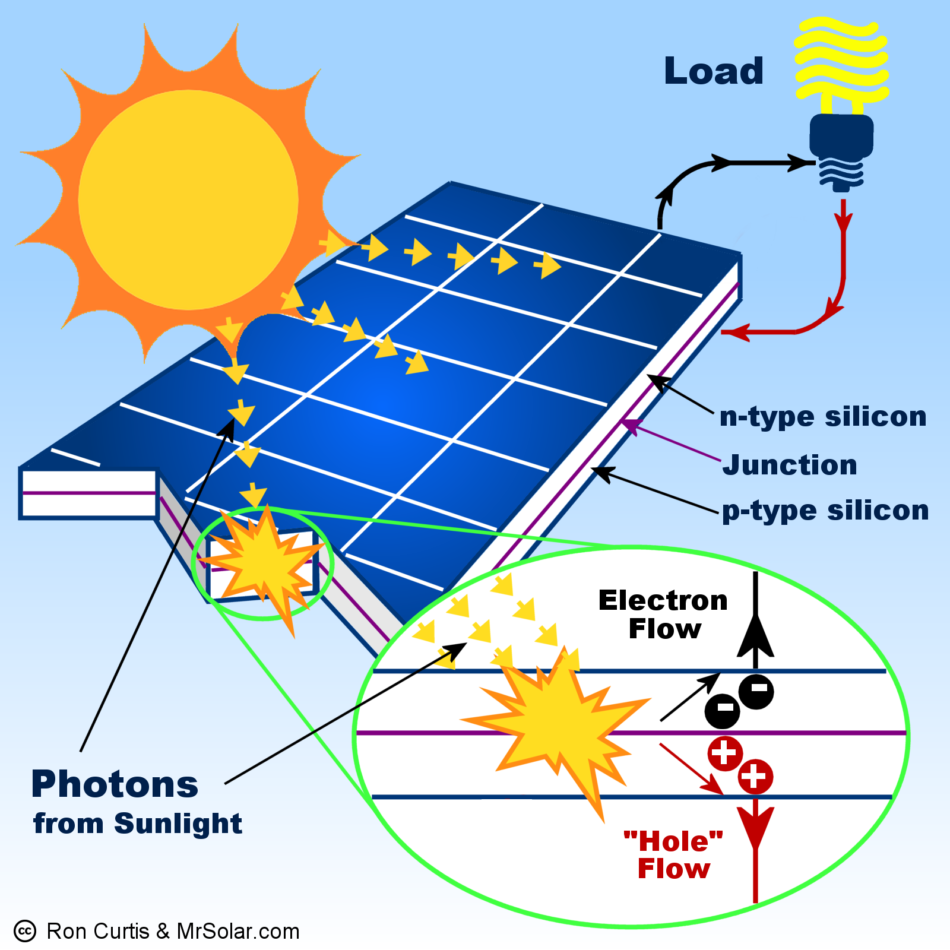
| When sunlight hits the solar panels, the photons in the light excite the electrons in the photovoltaic cells. This generates an electric current that can be harnessed and used for various purposes. The generated electricity can be stored in batteries or connected to the grid for immediate use. | ||
| 2 | ||
| Benefits of Solar Panels | ||
|---|---|---|
| Solar panels reduce reliance on fossil fuels, helping to combat climate change. They produce clean and renewable energy, reducing carbon emissions. Solar panels can save money on electricity bills in the long run. | ||
| 3 | ||
| Types of Solar Panels | ||
|---|---|---|
| Monocrystalline solar panels are made from a single crystal structure, offering high efficiency. Polycrystalline solar panels are made from multiple crystal structures, providing a cost-effective option. Thin-film solar panels are lightweight and flexible, suitable for various applications. | ||
| 4 | ||
| Installation Considerations | ||
|---|---|---|
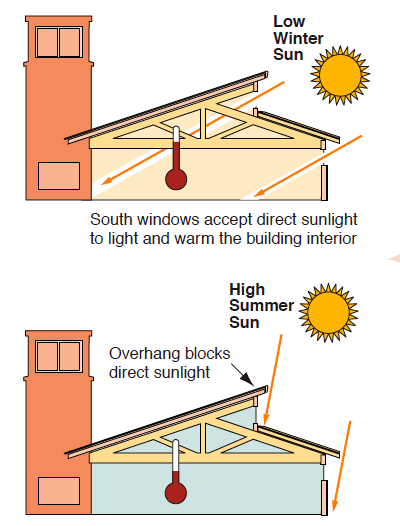
| Solar panels require proper orientation and tilt to maximize sunlight exposure. Shading should be minimized to optimize solar panel efficiency. The roof or ground space should be structurally sound to support the weight of solar panels. | ||
| 5 | ||
| Maintenance and Lifespan | ||
|---|---|---|
| Solar panels require minimal maintenance, usually limited to regular cleaning. The average lifespan of solar panels is around 25 to 30 years. Regular inspections and monitoring can ensure optimal performance and identify any issues. | ||
| 6 | ||
| Solar Panel Efficiency | ||
|---|---|---|
| Solar panel efficiency refers to the amount of sunlight converted into electricity. Efficiency varies between different types of solar panels, with monocrystalline panels being the most efficient. Advances in technology continue to improve solar panel efficiency over time. | ||
| 7 | ||
| Solar Panel Applications | ||
|---|---|---|
| Solar panels can be used in residential, commercial, and industrial settings. They can power homes, buildings, streetlights, and even entire cities. Solar panels are also used in remote areas and for off-grid applications. | ||
| 8 | ||
| Future of Solar Panels | ||
|---|---|---|
| The demand for solar panels is expected to increase as renewable energy becomes more prevalent. Advancements in technology aim to improve efficiency and reduce costs. Integration with energy storage systems and smart grid technologies will further enhance solar panel capabilities. | ||
| 9 | ||
| Conclusion | ||
|---|---|---|
| Solar panels are a sustainable and renewable source of energy that can help combat climate change. They offer numerous benefits, including reduced reliance on fossil fuels and cost savings. The future of solar panels looks promising, with continued advancements and increased adoption. | ||
| 10 | ||
| References (download PPTX file for details) | ||
|---|---|---|
| "How Do Solar Panels Work?" Solar Energy Indu... "Types of Solar Panels." EnergySage, www.ener... "Solar Panel Maintenance, Cleaning, and Inspe... |  | |
| 11 | ||

:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/monocrystalline-solar-panel-1302108360-0aa4e05421a64d018def781b259ba751.jpg)