Signals And Systems Presentation
| Introduction to Signals and Systems | ||
|---|---|---|
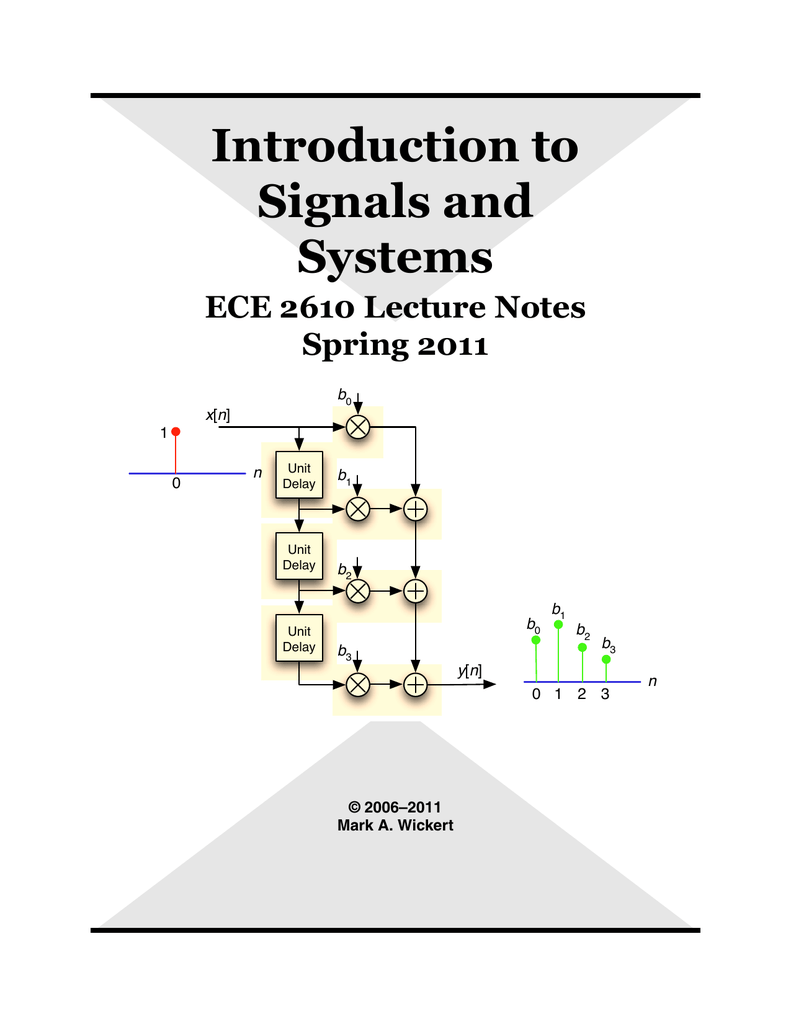
| Signals are functions that carry information about a physical phenomenon or a process. Systems are entities that process signals, transforming them in some way to achieve a desired output. Signals can be continuous or discrete, while systems can be linear or nonlinear. | ||
| 1 | ||
| Types of Signals | ||
|---|---|---|
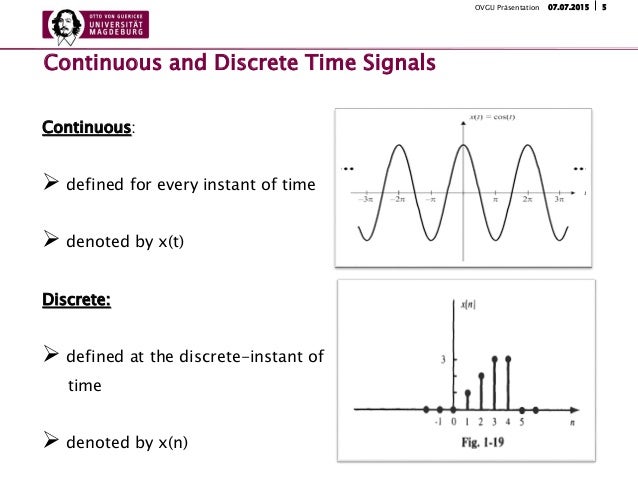
| Continuous-time signals are defined for all values of time within a specified range. Discrete-time signals are defined only at specific time instances. Analog signals are continuous in both time and amplitude. | ||
| 2 | ||
| Properties of Signals | ||
|---|---|---|
| Amplitude refers to the magnitude or strength of a signal. Frequency represents the number of cycles or oscillations per unit of time. Phase describes the relative position in the cycle of a periodic signal. | ||
| 3 | ||
| Types of Systems | ||
|---|---|---|
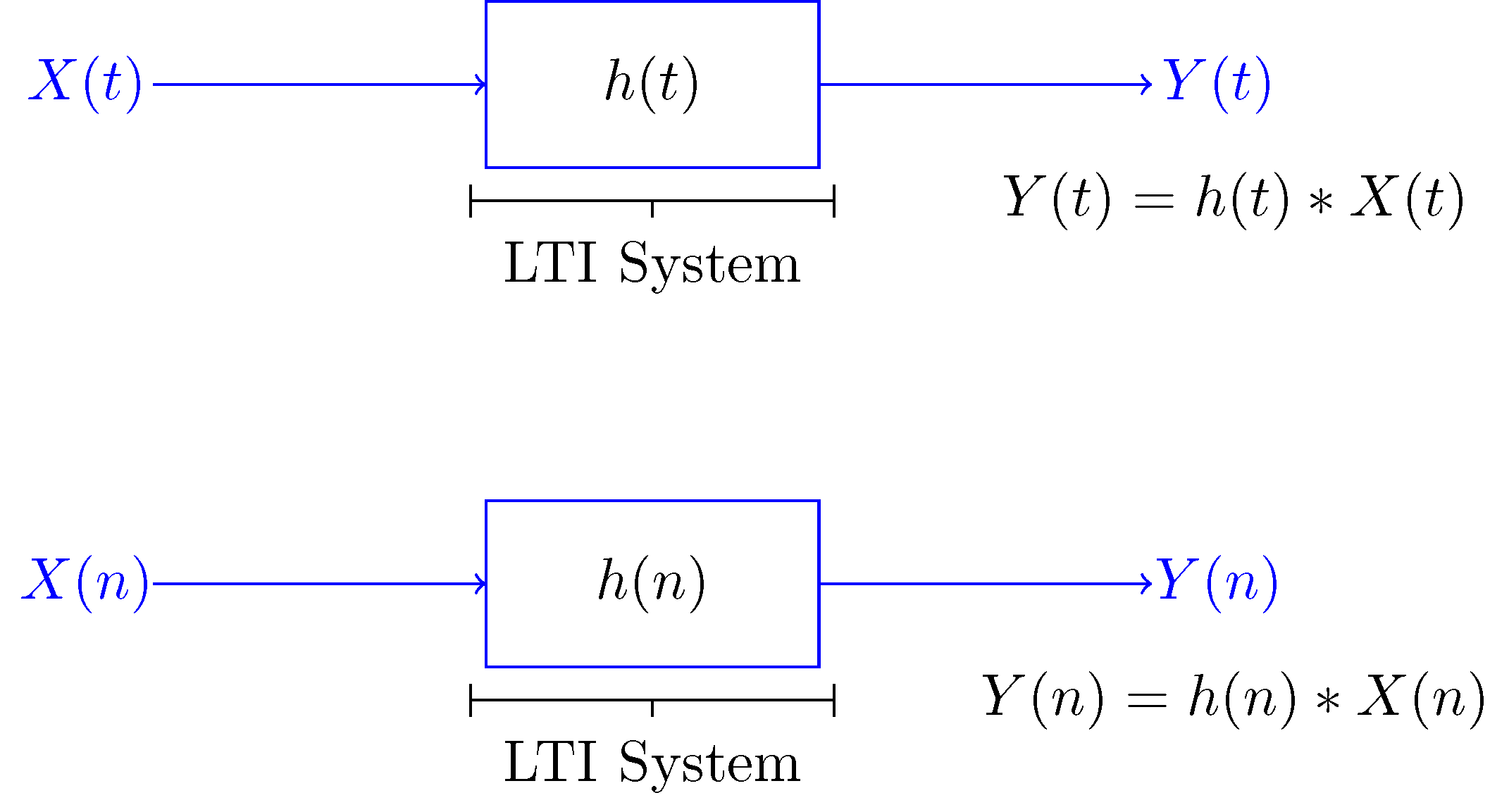
| Linear systems satisfy the properties of superposition and homogeneity, meaning the output is a linear combination of the inputs. Time-invariant systems have characteristics that do not change over time. Causal systems produce outputs that depend only on the current and past inputs, not future inputs. | ||
| 4 | ||
| Applications of Signals and Systems | ||
|---|---|---|
| Communication systems utilize signals to transmit information over long distances. Control systems use signals to regulate and manipulate physical processes. Image and video processing systems analyze and enhance visual signals. | ||
| 5 | ||