Semi Conductor Presentation
| Introduction to Semiconductors | ||
|---|---|---|
| Semiconductors are materials that have electrical conductivity between conductors (such as metals) and insulators (such as nonmetals). They are crucial components in electronic devices, allowing the control and manipulation of electrical signals. Examples of semiconductors include silicon, germanium, and gallium arsenide. | ||
| 1 | ||
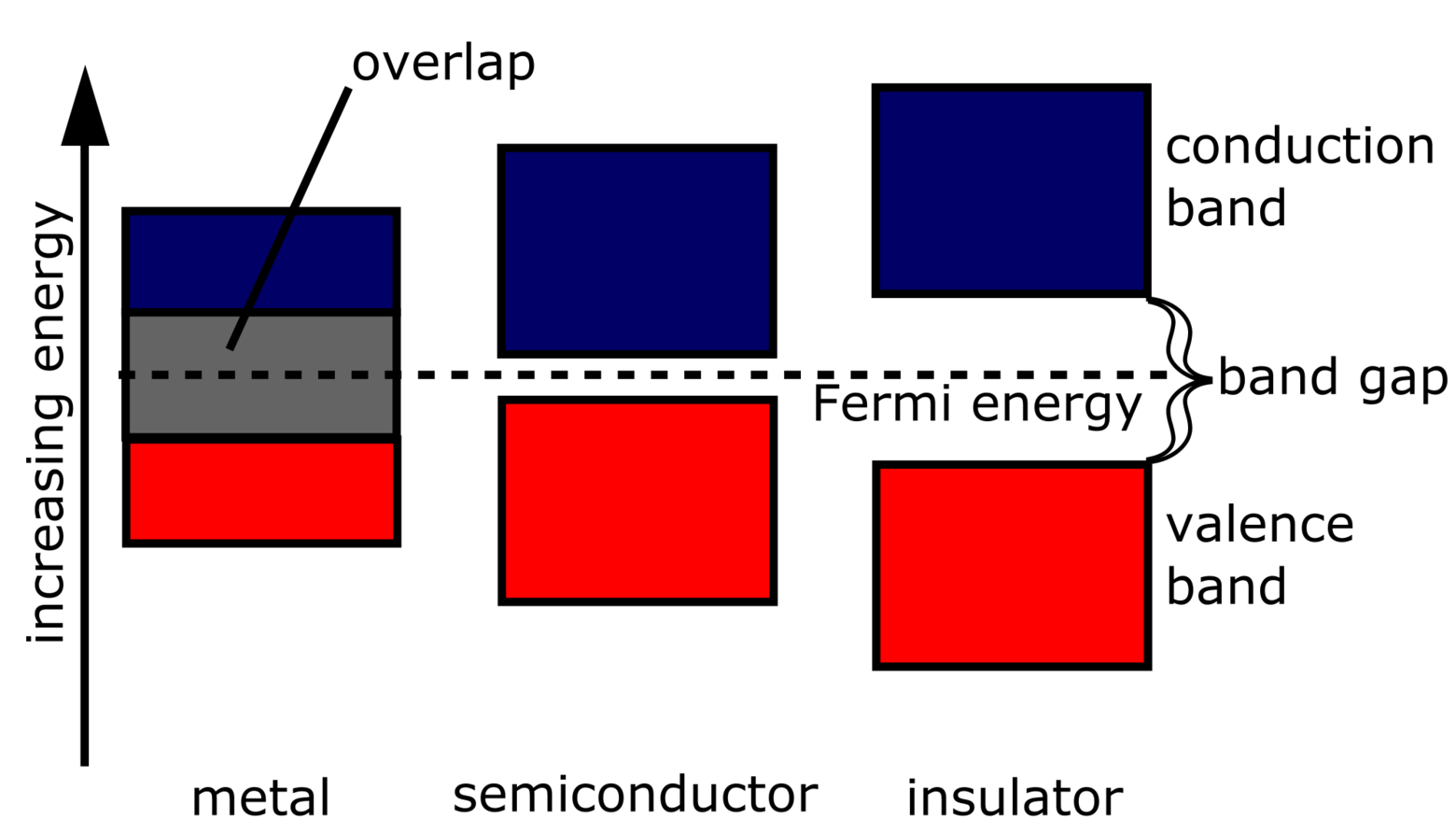
| Band Gap and Conductivity | ||
|---|---|---|
| Semiconductors have a band gap, which is the energy difference between the valence band and the conduction band. The size of the band gap determines the conductivity of a semiconductor: a smaller gap means higher conductivity, while a larger gap means lower conductivity. By manipulating the band gap, semiconductors can be tailored for specific applications, such as in diodes, transistors, and solar cells. | ||
| 2 | ||
| Doping and Carrier Concentration | ||
|---|---|---|
| Doping is the process of intentionally adding impurities to a semiconductor to alter its electrical properties. Two types of doping are used: n-type (adding elements with extra electrons) and p-type (adding elements with missing electrons). Doping creates excess charge carriers (electrons or holes) in the semiconductor, increasing its conductivity and enabling electronic device functionality. | ||
| 3 | ||
| Transistors and Integrated Circuits | ||
|---|---|---|
| Transistors are the fundamental building blocks of modern electronics, and they rely on semiconductor materials. A transistor is a three-layered device with two p-n junctions, which can amplify and switch electronic signals. Integrated circuits (ICs) are made by combining numerous transistors and other electronic components onto a single semiconductor chip, enabling the creation of complex electronic systems. | ||
| 4 | ||
| Applications of Semiconductors | ||
|---|---|---|
| Semiconductors are used in a wide range of applications, including computers, smartphones, televisions, and automotive electronics. They enable the miniaturization of electronic devices, making them faster, more efficient, and compact. Other applications include LEDs (light-emitting diodes), lasers, sensors, and power devices for efficient energy conversion. | ||
| 5 | ||
| References (download PPTX file for details) | ||
|---|---|---|
| Streetman, B. G., & Banerjee, S. K. (2006). S... Bhattacharya, P. (2011). Semiconductor optoel... Sze, S. M., & Ng, K. K. (2006). Physics of se... |  | |
| 6 | ||
/examples-of-electrical-conductors-and-insulators-608315_v3-5b609152c9e77c004f6e8892.png)