Renal Functional Tests Presentation
| Introduction to Renal Functional Tests | ||
|---|---|---|
| Renal functional tests are diagnostic tests that evaluate the function of the kidneys. These tests help in assessing renal health, detecting abnormalities, and monitoring treatment efficacy. Renal functional tests are essential for diagnosing and managing various kidney disorders. | ||
| 1 | ||
| Glomerular Filtration Rate (GFR) | ||
|---|---|---|
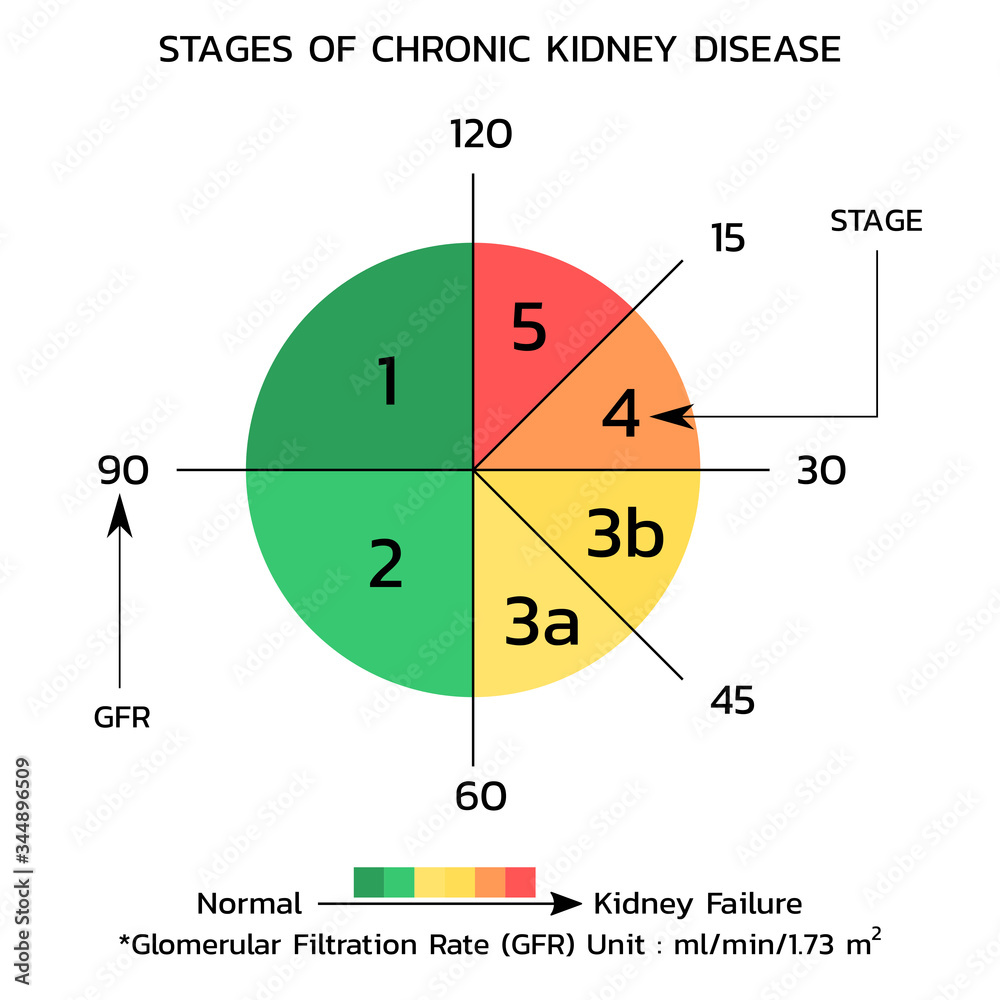
| GFR is considered the best indicator of overall kidney function. GFR measures the rate at which the kidneys filter waste products and excess fluids from the blood per minute. GFR can be estimated using equations like the Cockcroft-Gault or the Modification of Diet in Renal Disease (MDRD) formula. | ||
| 2 | ||
| Blood Urea Nitrogen (BUN) Test | ||
|---|---|---|
| BUN is a commonly performed renal functional test. BUN measures the amount of urea nitrogen in the blood, which reflects the kidneys' ability to remove waste products. Elevated BUN levels may indicate impaired kidney function or dehydration. | ||
| 3 | ||
| Creatinine Clearance Test | ||
|---|---|---|
| Creatinine clearance is a direct measure of kidney function. This test calculates the rate at which the kidneys clear creatinine, a waste product of muscle metabolism, from the blood. Creatinine clearance is considered more accurate than serum creatinine levels alone. | ||
| 4 | ||
| Urinalysis | ||
|---|---|---|
| Urinalysis examines the physical, chemical, and microscopic properties of urine. It helps in detecting various kidney-related abnormalities such as proteinuria, hematuria, and urinary tract infections. Urinalysis is a cost-effective and non-invasive renal functional test. | ||
| 5 | ||
| Renal Imaging | ||
|---|---|---|
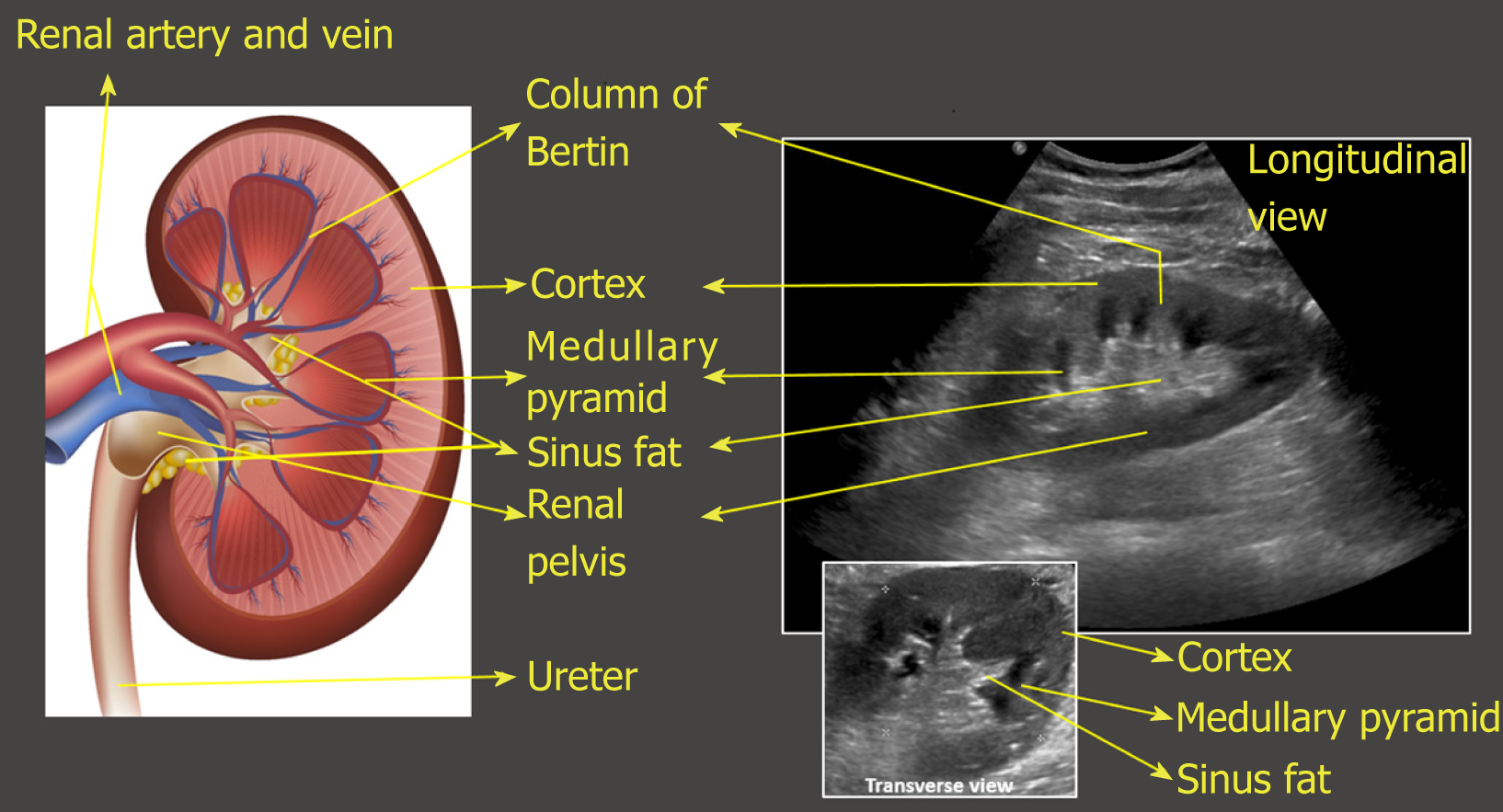
| Renal imaging techniques, such as ultrasound, CT scan, or MRI, provide detailed images of the kidneys. These tests help in identifying structural abnormalities, such as kidney stones, tumors, or cysts. Renal imaging is useful in diagnosing and monitoring kidney diseases. | ||
| 6 | ||
| Renal Biopsy | ||
|---|---|---|
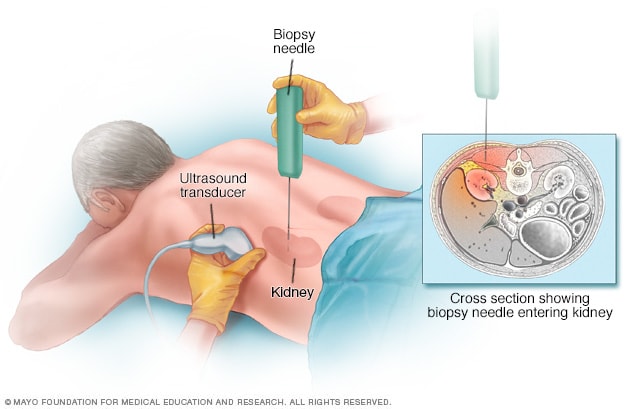
| Renal biopsy involves the extraction of a small sample of kidney tissue for microscopic examination. It is performed to diagnose and determine the severity of various kidney diseases, such as glomerulonephritis or nephrotic syndrome. Renal biopsy provides valuable information about the specific cause and extent of kidney damage. | ||
| 7 | ||
| Electrolyte Levels | ||
|---|---|---|
| Electrolyte tests measure the levels of essential minerals, such as sodium, potassium, and calcium, in the blood. Kidney dysfunction can lead to imbalances in electrolyte levels, which can affect various bodily functions. Monitoring electrolyte levels helps in detecting and managing kidney-related electrolyte imbalances. | ||
| 8 | ||
| Cystatin C Test | ||
|---|---|---|
| Cystatin C is a protein produced by all nucleated cells at a constant rate. Cystatin C levels in the blood are inversely related to renal function. Cystatin C test is used as an alternative marker to estimate GFR, especially in certain populations like the elderly or those with obesity. | ||
| 9 | ||
| Conclusion | ||
|---|---|---|
| Renal functional tests are crucial in evaluating kidney function and diagnosing kidney disorders. These tests provide valuable information about glomerular filtration rate, waste product clearance, electrolyte balance, and urinary abnormalities. Early detection and monitoring of renal function through appropriate renal functional tests can help in timely intervention and improved patient outcomes. | ||
| 10 | ||
| References (download PPTX file for details) | ||
|---|---|---|
| National Kidney Foundation. (2021). Glomerula... Lab Tests Online. (2021). Blood Urea Nitrogen... Mayo Clinic Laboratories. (2021). Creatinine ... |  | |
| 11 | ||