Ransomware Presentation
| Introduction to Ransomware | ||
|---|---|---|
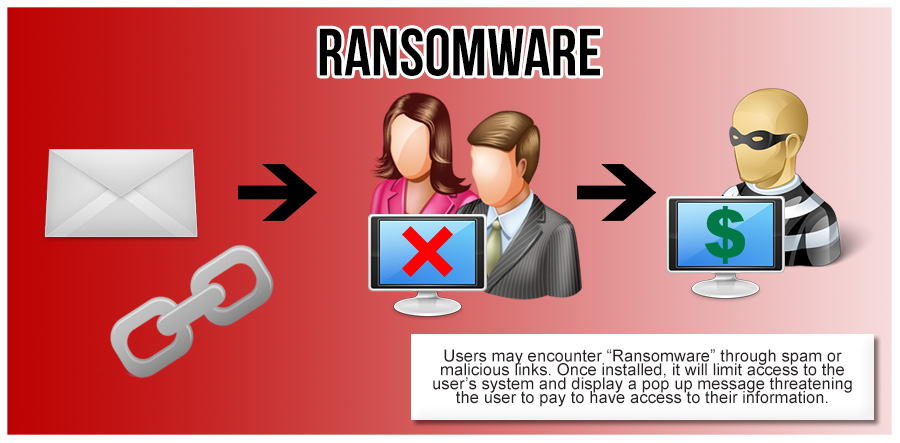
| Ransomware is a type of malicious software that encrypts files or systems and demands a ransom for their release. It is typically spread through phishing emails, malicious downloads, or exploiting vulnerabilities in software. Ransomware attacks have become increasingly common and pose a significant threat to individuals and organizations. | ||
| 1 | ||
| How Ransomware Works | ||
|---|---|---|
| Once executed, ransomware encrypts files or locks systems, making them inaccessible to the victim. The attacker then demands payment, usually in cryptocurrency, in exchange for the decryption key or system unlock. Ransomware often includes a timer or threat of permanent data deletion to pressure victims into paying the ransom. | ||
| 2 | ||
| Common Types of Ransomware | ||
|---|---|---|
| Crypto-ransomware encrypts files and demands payment for decryption. Examples include WannaCry and CryptoLocker. Locker ransomware locks the victim out of their entire system. Examples include WinLocker and Police Locker. Mobile ransomware targets smartphones and tablets, often through malicious apps or drive-by downloads. | ||
| 3 | ||
| Impact of Ransomware Attacks | ||
|---|---|---|
| Ransomware attacks can result in significant financial losses due to ransom payments, downtime, and recovery efforts. Data loss is a major concern, as victims may lose access to critical files or have them permanently deleted if demands are not met. Ransomware attacks can damage an organization's reputation and erode customer trust. | ||
| 4 | ||
| Prevention and Mitigation | ||
|---|---|---|
| Regularly backup important files and systems offline or in the cloud. Keep software and operating systems up to date with the latest security patches. Exercise caution when opening email attachments or clicking on suspicious links. | ||
| 5 | ||
| Response to Ransomware Attacks | ||
|---|---|---|
| Isolate infected systems from the network to prevent further spread. Report the incident to law enforcement and seek assistance from cybersecurity professionals. Evaluate the possibility of restoring files from backups rather than paying the ransom. | ||
| 6 | ||
| Ransomware Recovery Best Practices | ||
|---|---|---|
| Restore systems from clean backups after ensuring the infection has been contained. Strengthen security measures to prevent future attacks, such as implementing multi-factor authentication and employee training. Conduct a post-incident analysis to identify vulnerabilities and improve incident response plans. | ||
| 7 | ||
| Conclusion | ||
|---|---|---|
| Ransomware is a growing threat that can cause significant damage to individuals and organizations. Prevention, timely response, and robust recovery strategies are essential in mitigating the impact of ransomware attacks. By staying informed and implementing best practices, we can protect ourselves and our data from this evolving threat. | ||
| 8 | ||
| References (download PPTX file for details) | ||
|---|---|---|
| "Ransomware: A Beginner's Guide." Norton. Acc... https:// us.norton.com/ internetsecurity-malw... "What Is Ransomware? How It Works and How to ... |  | |
| 9 | ||