Rainwater Harvesting Presentation
| Introduction to Rainwater Harvesting | ||
|---|---|---|
| Rainwater harvesting is the collection, storage, and use of rainwater for various purposes. It is an ancient practice that has gained popularity due to its environmental and economic benefits. Rainwater harvesting can be done at individual homes, as well as on a larger scale for communities and commercial buildings. | ||
| 1 | ||
| Benefits of Rainwater Harvesting | ||
|---|---|---|
| Conserves water resources by reducing the demand on freshwater supply. Reduces stormwater runoff, which helps prevent flooding and erosion. Provides a sustainable and reliable source of water for various non-potable uses. | ||
| 2 | ||
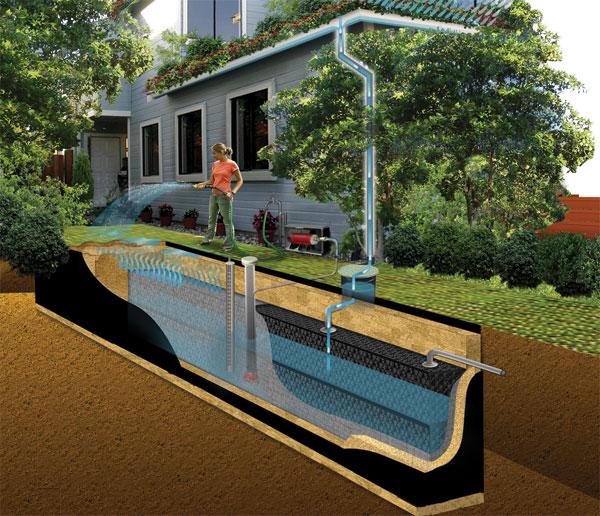
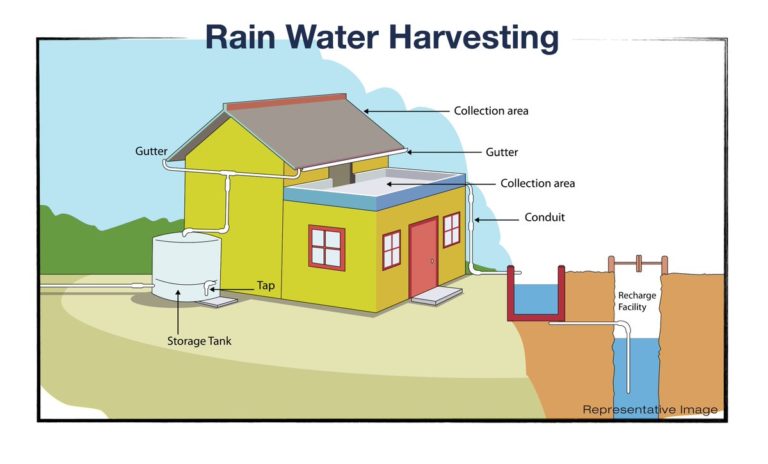
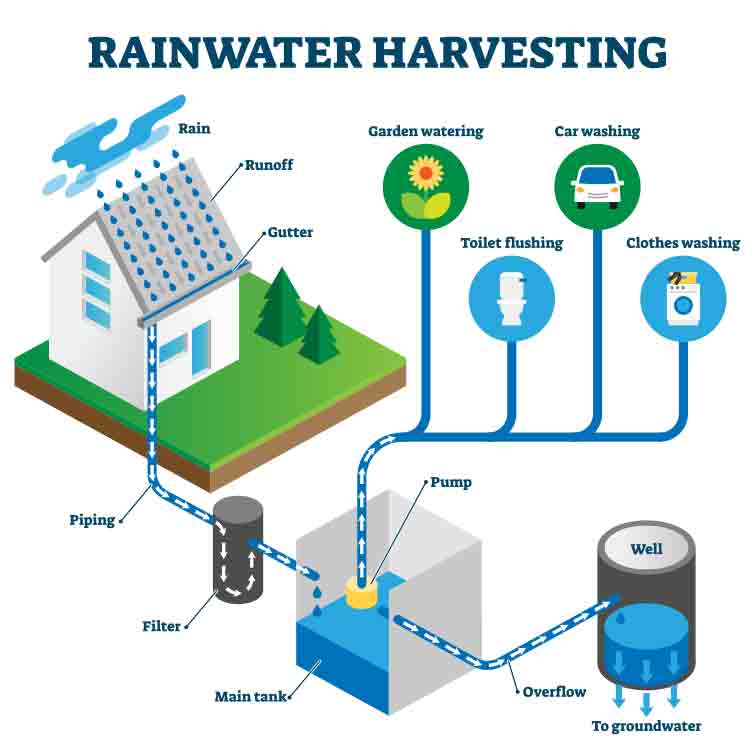
| Components of Rainwater Harvesting System | ||
|---|---|---|
| Catchment: The surface area where rainwater is collected, such as rooftops or land. Conveyance: Gutters, downspouts, and pipes that carry rainwater from the catchment to storage. Storage: Tanks, cisterns, or barrels used to store rainwater for later use. | ||
| 3 | ||
| Types of Rainwater Harvesting Systems | ||
|---|---|---|
| Roof-based systems: Collect rainwater from rooftops and direct it to storage tanks. Surface-based systems: Collect rainwater from open surfaces like lawns or driveways and channel it to storage. Combined systems: Utilize both roof-based and surface-based methods for increased efficiency. | ||
| 4 | ||
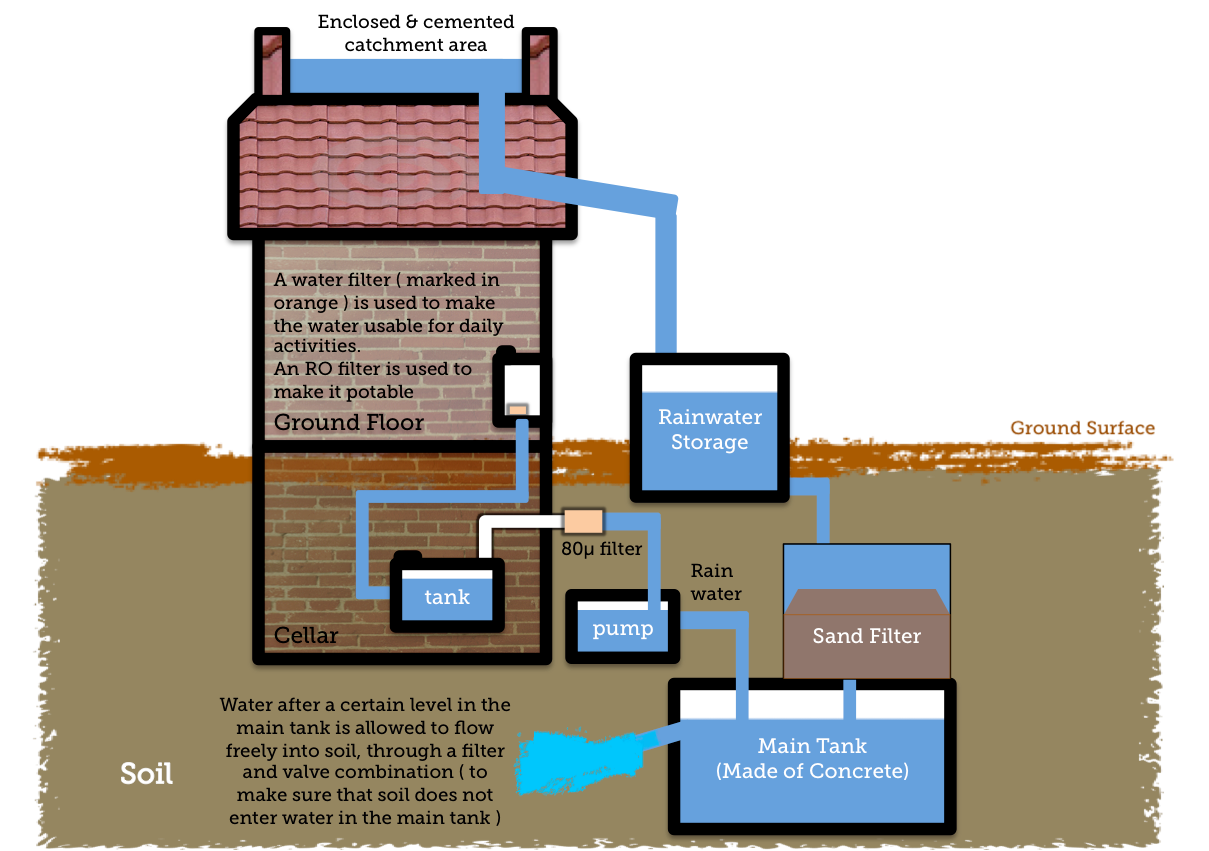
| Precautions for Safe Use of Harvested Rainwater | ||
|---|---|---|
| Regular maintenance of the storage system to prevent contamination and the growth of harmful bacteria. Use of appropriate filtration and disinfection methods to ensure water quality. Separate storage and treatment systems for potable and non-potable uses to avoid cross-contamination. | ||
| 5 | ||
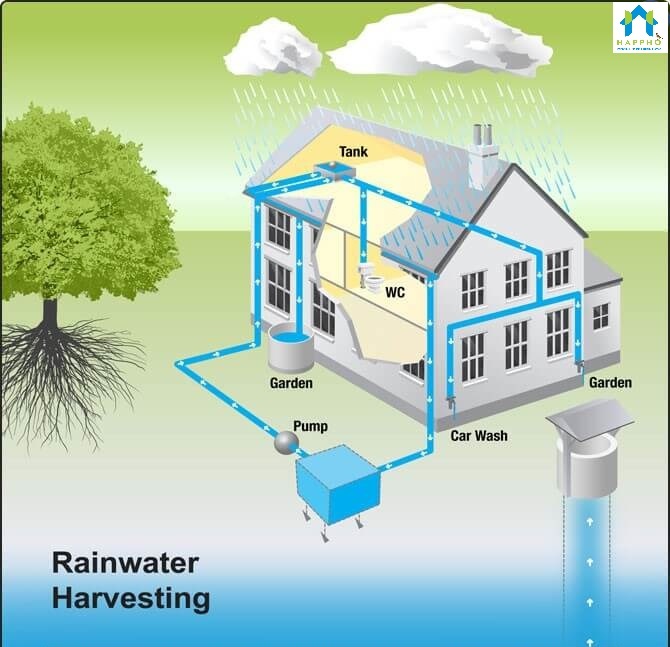
| Non-Potable Uses of Harvested Rainwater | ||
|---|---|---|
| Irrigation of landscapes, gardens, and agricultural fields. Flushing toilets, washing vehicles, or other outdoor cleaning activities. Industrial uses like cooling towers or dust suppression. | ||
| 6 | ||
| Potable Uses of Harvested Rainwater | ||
|---|---|---|
| With proper treatment and filtration, harvested rainwater can be used for drinking and cooking purposes. However, it is important to consult local regulations and guidelines before using rainwater for potable purposes. Some countries have strict regulations regarding rainwater quality and treatment requirements. | ||
| 7 | ||
| Case Studies - Successful Rainwater Harvesting Projects | ||
|---|---|---|
| The Singapore Water Story: Singapore implemented an extensive rainwater harvesting system to reduce water dependence on neighboring countries. Keshav Srushti, India: A residential complex that relies solely on rainwater for all its water needs, including drinking water. The Solaire Building, New York City: A commercial building that uses rainwater for toilet flushing, irrigation, and cooling tower makeup. | ||
| 8 | ||
| Challenges and Considerations | ||
|---|---|---|
| Initial cost and installation of rainwater harvesting systems can be a barrier for some individuals or communities. Adequate space for storage tanks or cisterns may be limited in urban areas. Local regulations and water rights laws may impact the feasibility and implementation of rainwater harvesting. | ||
| 9 | ||
| Conclusion | ||
|---|---|---|
| Rainwater harvesting is an effective and sustainable method of utilizing rainwater for various purposes. It helps conserve water resources, reduce stormwater runoff, and provides a reliable source of water. With proper precautions, rainwater can be used for both non-potable and potable uses, contributing to a more sustainable future. | ||
| 10 | ||
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/beginners-guide-to-rainwater-harvesting-5089884_V3-d4a6f6a568fc4f348598d9b98f96b6b7.png)
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/rainwater-harvesting-system-isometric-diagram-1201105579-34cb7b27492f42c387b89fd903a16ba4.jpg)