RURAL DEVELOPMENT Presentation
| Introduction to Rural Development | ||
|---|---|---|
| Rural development refers to the process of improving the economic, social, and environmental conditions in rural areas. It aims to enhance the quality of life for rural communities by addressing various challenges and promoting sustainable development. Rural development encompasses a wide range of sectors, including agriculture, infrastructure, education, healthcare, and entrepreneurship. | ||
| 1 | ||
| Importance of Rural Development | ||
|---|---|---|
| Rural development is essential for reducing poverty and inequality, as a significant portion of the world's poor live in rural areas. It helps to create employment opportunities and boost economic growth in rural regions, reducing the migration of rural populations to urban areas. By investing in rural development, governments can ensure food security, improve education and healthcare services, and promote sustainable agricultural practices. | ||
| 2 | ||
| Key Strategies for Rural Development | ||
|---|---|---|
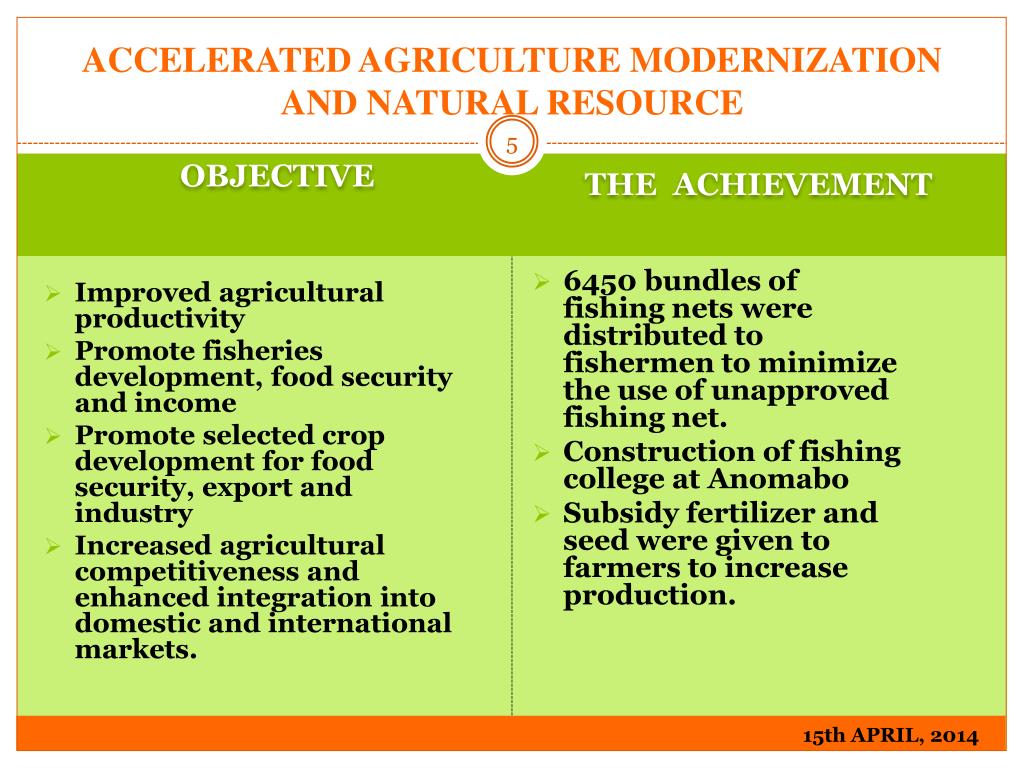
| Promoting agricultural innovation and modernization to increase productivity and income for rural farmers. Improving rural infrastructure, such as roads, electricity, and water supply, to connect rural areas with urban centers and markets. Encouraging entrepreneurship and small-scale industries in rural areas to generate employment opportunities and stimulate local economies. | ||
| 3 | ||
| Challenges in Rural Development | ||
|---|---|---|
| Limited access to basic services, such as education, healthcare, and clean water, due to remoteness and inadequate infrastructure. Lack of investment in rural areas, resulting in low agricultural productivity and limited employment opportunities. Environmental degradation and climate change impacts, which affect rural livelihoods and agricultural practices. | ||
| 4 | ||
| Successful Rural Development Initiatives | ||
|---|---|---|
| The Mahatma Gandhi National Rural Employment Guarantee Act (MGNREGA) in India, which provides guaranteed employment opportunities for rural households. The Grameen Bank in Bangladesh, which pioneered microfinance and provided small loans to rural entrepreneurs, particularly women. The Rural Electrification Program in Brazil, which brought electricity to remote rural communities, improving their quality of life and economic opportunities. | ||
| 5 | ||
| Role of Technology in Rural Development | ||
|---|---|---|
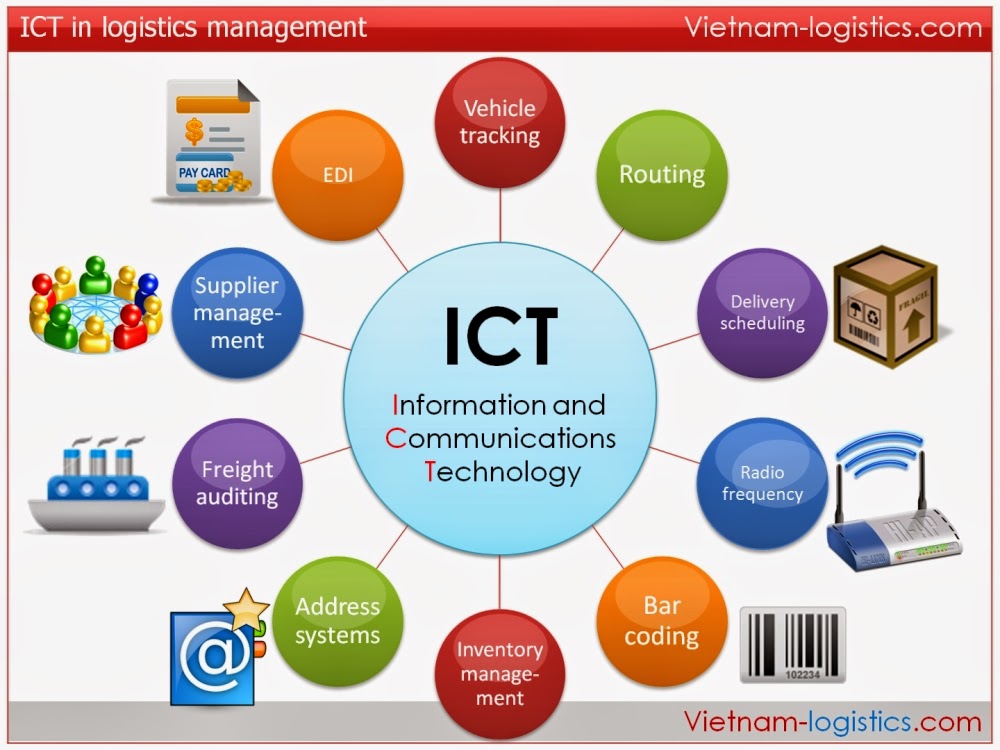
| Information and communication technologies (ICTs) can bridge the digital divide by providing access to information, education, and markets for rural communities. Precision agriculture technologies, such as remote sensing and drones, can improve agricultural practices, increase productivity, and reduce environmental impact. Mobile banking and e-commerce platforms enable rural entrepreneurs to access financial services and expand their customer base. | ||
| 6 | ||
| Sustainable Rural Development | ||
|---|---|---|
| Sustainable rural development focuses on balancing economic, social, and environmental objectives to ensure long-term well-being for rural communities. It involves promoting renewable energy sources, sustainable land use practices, and biodiversity conservation. Engaging local communities, including women and indigenous groups, in decision-making processes and empowering them to participate in sustainable development initiatives. | ||
| 7 | ||
| Conclusion | ||
|---|---|---|
| Rural development plays a crucial role in reducing poverty, improving livelihoods, and fostering sustainable growth in rural areas. By addressing challenges, implementing effective strategies, and leveraging technology, governments and stakeholders can create prosperous and resilient rural communities. Continued investment and collaboration are essential for achieving sustainable rural development and creating a more equitable and inclusive society. | ||
| 8 | ||
| References (download PPTX file for details) | ||
|---|---|---|
| World Bank. (2021). Rural Development. Retrie... Food and Agriculture Organization of the Unit... United Nations Development Programme. (2021).... |  | |
| 9 | ||