Queues Presentation
| Introduction to Queues | ||
|---|---|---|
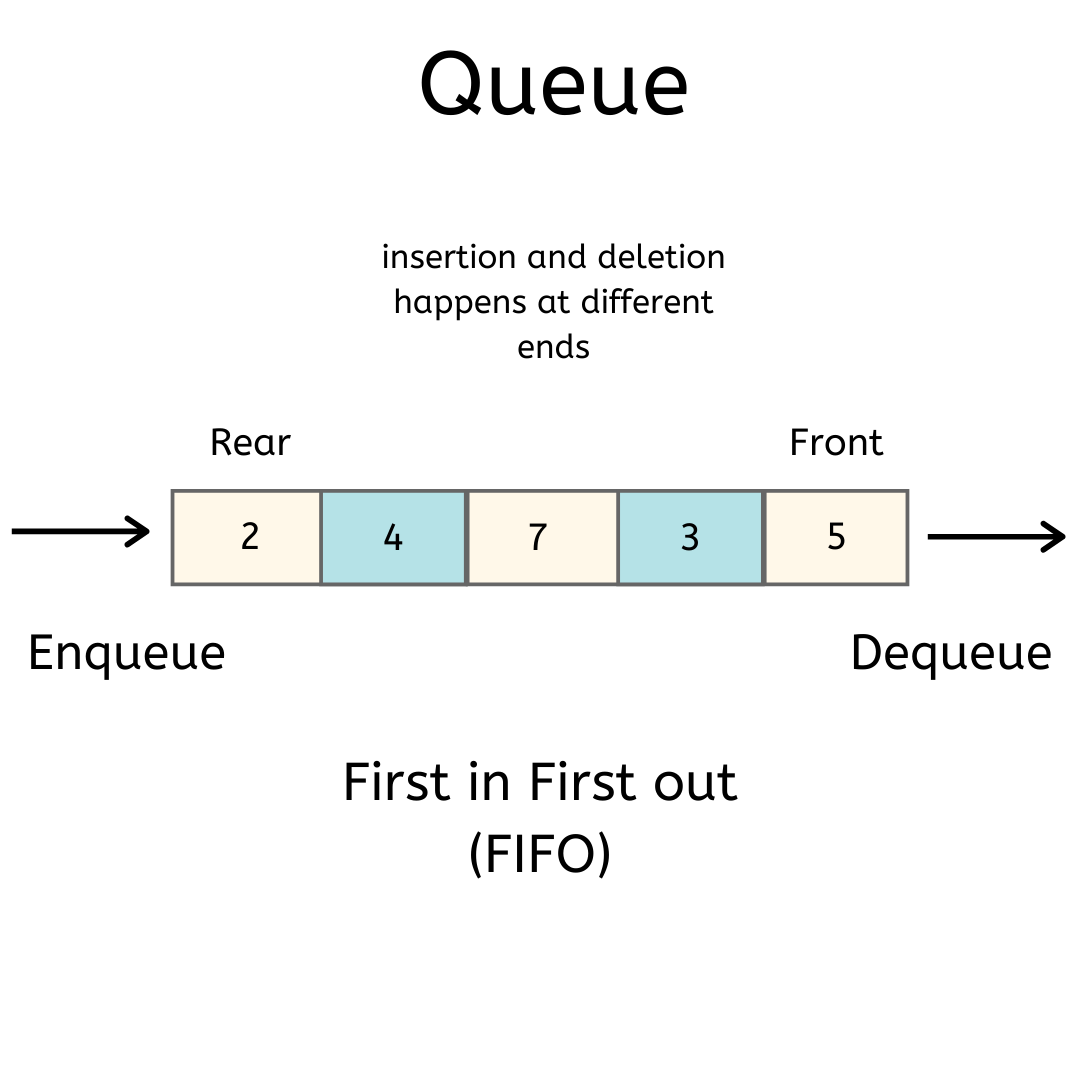
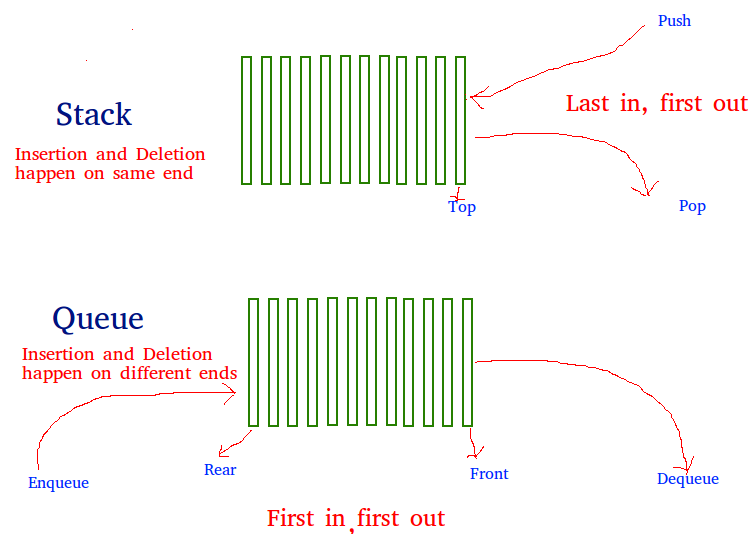
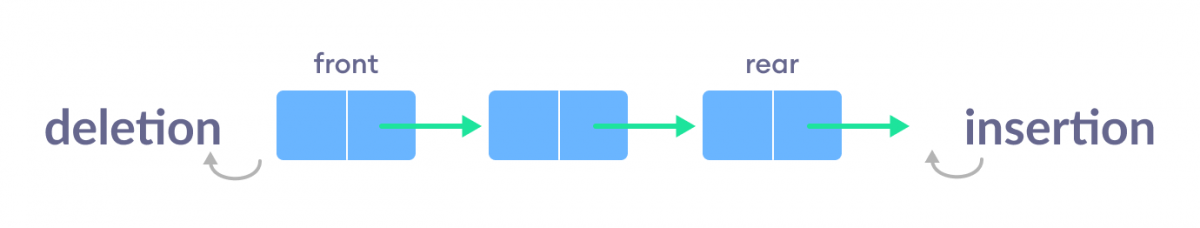
| A queue is a data structure that follows the first-in, first-out (FIFO) principle. Queues are used to manage and process data in a sequential order. Elements are added to the back of the queue and removed from the front. | ||
| 1 | ||
| Main Operations | ||
|---|---|---|
| Enqueue: Adding an element to the back of the queue. Dequeue: Removing the element from the front of the queue. Peek: Viewing the element at the front without removing it. | ||
| 2 | ||
| Real-life Examples | ||
|---|---|---|
| Waiting in line at a grocery store checkout. Handling print jobs in a printer. Processing messages in a messaging app. | ||
| 3 | ||
| Implementation of Queues | ||
|---|---|---|
| Queues can be implemented using arrays or linked lists. Arrays provide constant-time access to elements. Linked lists allow dynamic resizing and efficient insertion/ removal. | ||
| 4 | ||
| Types of Queues | ||
|---|---|---|
| Linear Queue: A simple queue with a fixed size. Circular Queue: A queue that wraps around to the beginning when reaching the end. Priority Queue: Assigns a priority value to each element and processes them accordingly. | ||
| 5 | ||
| Time Complexity | ||
|---|---|---|
| Enqueue operation: O(1) - Constant time complexity. Dequeue operation: O(1) - Constant time complexity. Peek operation: O(1) - Constant time complexity. | ||
| 6 | ||
| Use Cases | ||
|---|---|---|
| Task scheduling in operating systems. Multi-threaded programming. CPU scheduling algorithms. | ||
| 7 | ||
| Advantages of Queues | ||
|---|---|---|
| Ensures fairness by following the FIFO principle. Efficient for managing data in a sequential order. Can be easily implemented and understood. | ||
| 8 | ||
| Limitations of Queues | ||
|---|---|---|
| Fixed size queues have limited capacity. Linear queues can cause memory wastage. Priority queues can be complex to implement. | ||
| 9 | ||
| Summary | ||
|---|---|---|
| Queues are a fundamental data structure with various real-life applications. They follow the FIFO principle and are efficient for managing data in a sequential order. Queues can be implemented using arrays or linked lists, and different types of queues exist for specific use cases. | ||
| 10 | ||