Psoriasis : Existing And Advances In Treatment Presentation
| Introduction to Psoriasis | ||
|---|---|---|
| Psoriasis is a chronic autoimmune skin condition. It affects around 125 million people worldwide. It is characterized by red, scaly patches on the skin. | ||
| 1 | ||
| Existing Treatments for Psoriasis | ||
|---|---|---|
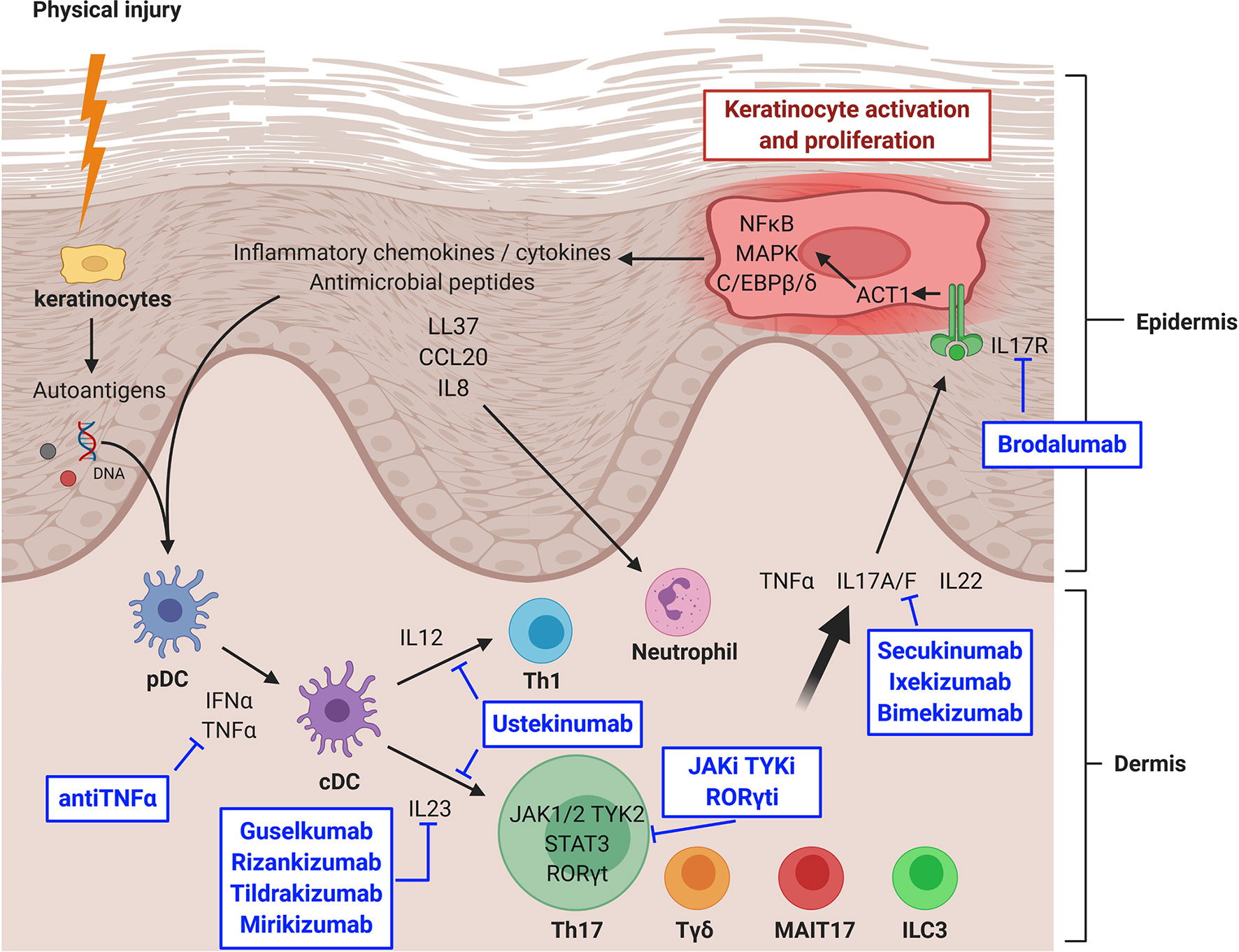
| Topical treatments, such as corticosteroids and retinoids, are commonly used for mild to moderate psoriasis. Phototherapy involves exposing the skin to ultraviolet light to reduce inflammation and slow down the production of skin cells. Systemic medications, such as oral immunosuppressants and biologic drugs, are prescribed for severe cases. | ||
| 2 | ||
| Advances in Topical Treatments | ||
|---|---|---|
| Calcitriol and calcipotriene are vitamin D analogs that help slow down the growth of skin cells. Topical corticosteroids combined with calcipotriene have shown improved efficacy in reducing inflammation and scaling. Topical JAK inhibitors, like tofacitinib, have also shown promising results in reducing symptoms of psoriasis. | ||
| 3 | ||
| Advances in Phototherapy | ||
|---|---|---|
| Narrowband UVB therapy is a newer form of phototherapy that is more targeted and effective. Excimer laser treatment delivers a high-intensity UVB light to specific areas, minimizing exposure to healthy skin. Combination therapies, such as adding topical medications or systemic drugs, have shown enhanced results with phototherapy. | ||
| 4 | ||
| Advances in Systemic Medications | ||
|---|---|---|
| Biologic drugs, including TNF inhibitors, IL-17 inhibitors, and IL-23 inhibitors, have revolutionized psoriasis treatment. These medications target specific molecules involved in the immune response, reducing inflammation and skin cell production. Newer biologics, such as IL-23 and IL-17 dual inhibitors, have shown even higher rates of skin clearance. | ||
| 5 | ||
| Emerging Therapies | ||
|---|---|---|
| Janus kinase (JAK) inhibitors, like baricitinib and upadacitinib, are being explored as potential oral treatments for psoriasis. Small molecule inhibitors, such as phosphodiesterase-4 inhibitors, are being studied for their anti-inflammatory properties. Gene therapies, including gene editing techniques like CRISPR-Cas9, hold promise for targeting the underlying genetic causes of psoriasis. | ||
| 6 | ||
| Personalized Medicine Approach | ||
|---|---|---|
| Advances in understanding psoriasis genetics and biomarkers allow for personalized treatment approaches. Genetic testing can help identify specific genes and pathways involved in an individual's psoriasis. Tailored treatment plans can be developed based on the patient's genetic profile and response to different medications. | ||
| 7 | ||
| Lifestyle Management | ||
|---|---|---|
| Healthy lifestyle choices, including a balanced diet, regular exercise, stress management, and avoiding triggers, can help manage psoriasis. Moisturizing the skin regularly and using gentle cleansers can help alleviate dryness and itching. Quitting smoking and limiting alcohol consumption can also improve psoriasis symptoms. | ||
| 8 | ||
| Conclusion | ||
|---|---|---|
| Psoriasis treatment has come a long way, with various options available for different severities. Advances in topical treatments, phototherapy, systemic medications, and emerging therapies offer hope for improved outcomes. Personalized medicine and lifestyle management play crucial roles in optimizing treatment success and overall well-being. | ||
| 9 | ||
| Questions and Answers | ||
|---|---|---|
| Open the floor for any questions or clarifications about psoriasis treatment. Encourage discussion and provide additional information as needed. Thank the audience for their attention and participation. | ||
| 10 | ||