Protecting Your Shopping Preferences With Differencial Privacy Presentation
| Protecting Your Shopping Preferences with Differential Privacy | ||
|---|---|---|
| Differential privacy is a technique that ensures privacy while allowing aggregate analysis of data. Shopping preferences contain valuable information that can be exploited by third parties without proper protection. By applying differential privacy to shopping preferences, users can enjoy personalized experiences without compromising their privacy. | ||
| 1 | ||
| Understanding Differential Privacy | ||
|---|---|---|
| Differential privacy adds noise to individual data points to protect privacy. It allows for statistical analysis without revealing specific details about individuals. By preserving privacy, differential privacy enables data sharing while minimizing the risk of re-identifying individuals. | ||
| 2 | ||
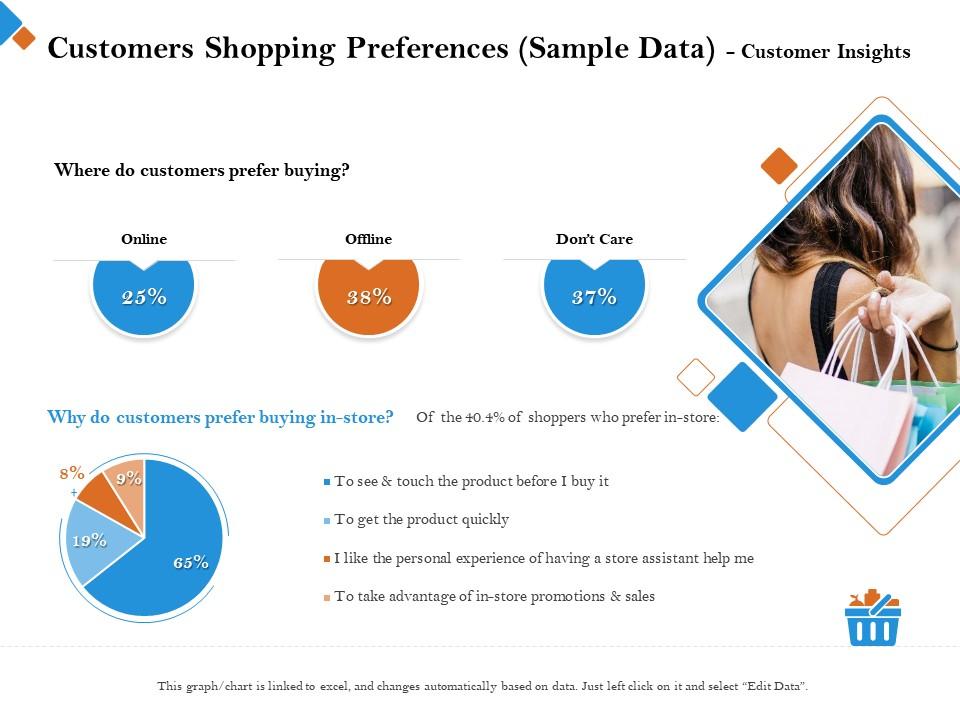
| Benefits of Protecting Shopping Preferences | ||
|---|---|---|
| Protects sensitive information such as personal preferences, buying habits, and interests. Reduces the risk of targeted advertising and potential exploitation by marketers. Ensures that your shopping choices remain private, safeguarding your personal identity and preventing data misuse. | ||
| 3 | ||
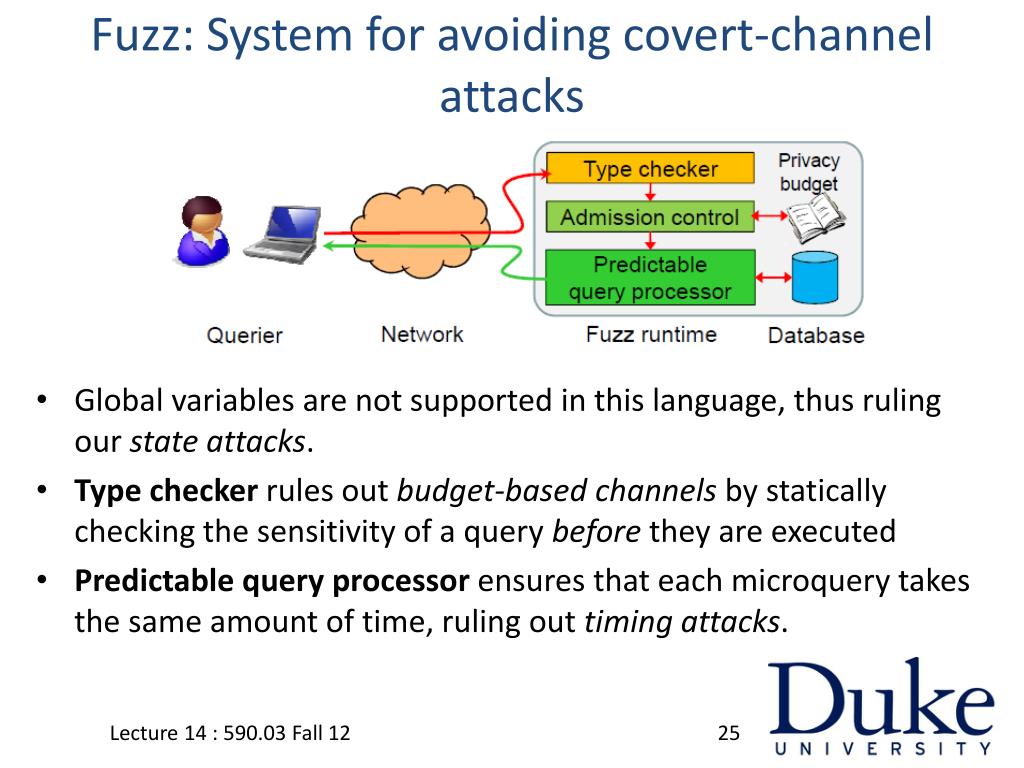
| Implementing Differential Privacy Techniques | ||
|---|---|---|
| Aggregating data in groups instead of individual records helps to maintain privacy. Adding random noise to the data before analysis prevents individual identification. Applying differential privacy techniques to shopping preferences ensures statistical accuracy while protecting individual privacy. | ||
| 4 | ||
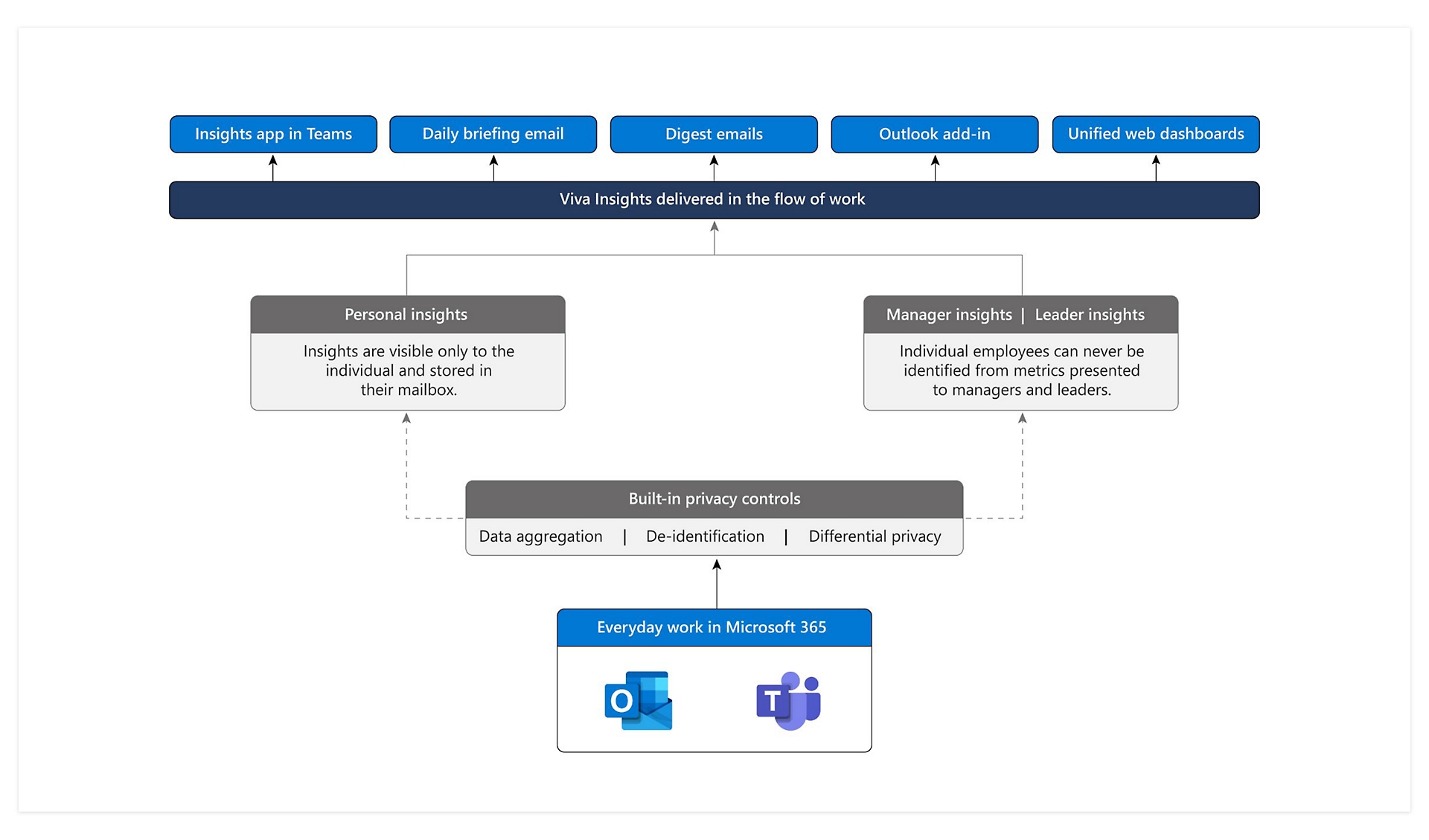
| Enhancing User Control | ||
|---|---|---|
| Users should have the ability to opt-in or opt-out of data sharing. Transparent disclosure of data collection and usage practices is essential. Providing control mechanisms empowers users to make informed decisions about their privacy. | ||
| 5 | ||
| Collaboration and Privacy Protection | ||
|---|---|---|
| Collaborative data analysis can be achieved by sharing aggregated information while preserving privacy. Differential privacy techniques ensure that individual preferences are protected during collaborative efforts. By combining data from multiple sources, businesses can gain insights while preserving customer privacy. | ||
| 6 | ||
| Industry Examples | ||
|---|---|---|
| E-commerce platforms can use differential privacy to protect customer shopping preferences and provide personalized recommendations. Retailers can analyze aggregated data to identify trends and improve inventory management without compromising customer privacy. Advertisers can leverage differential privacy to target specific customer segments without breaching individual privacy. | ||
| 7 | ||
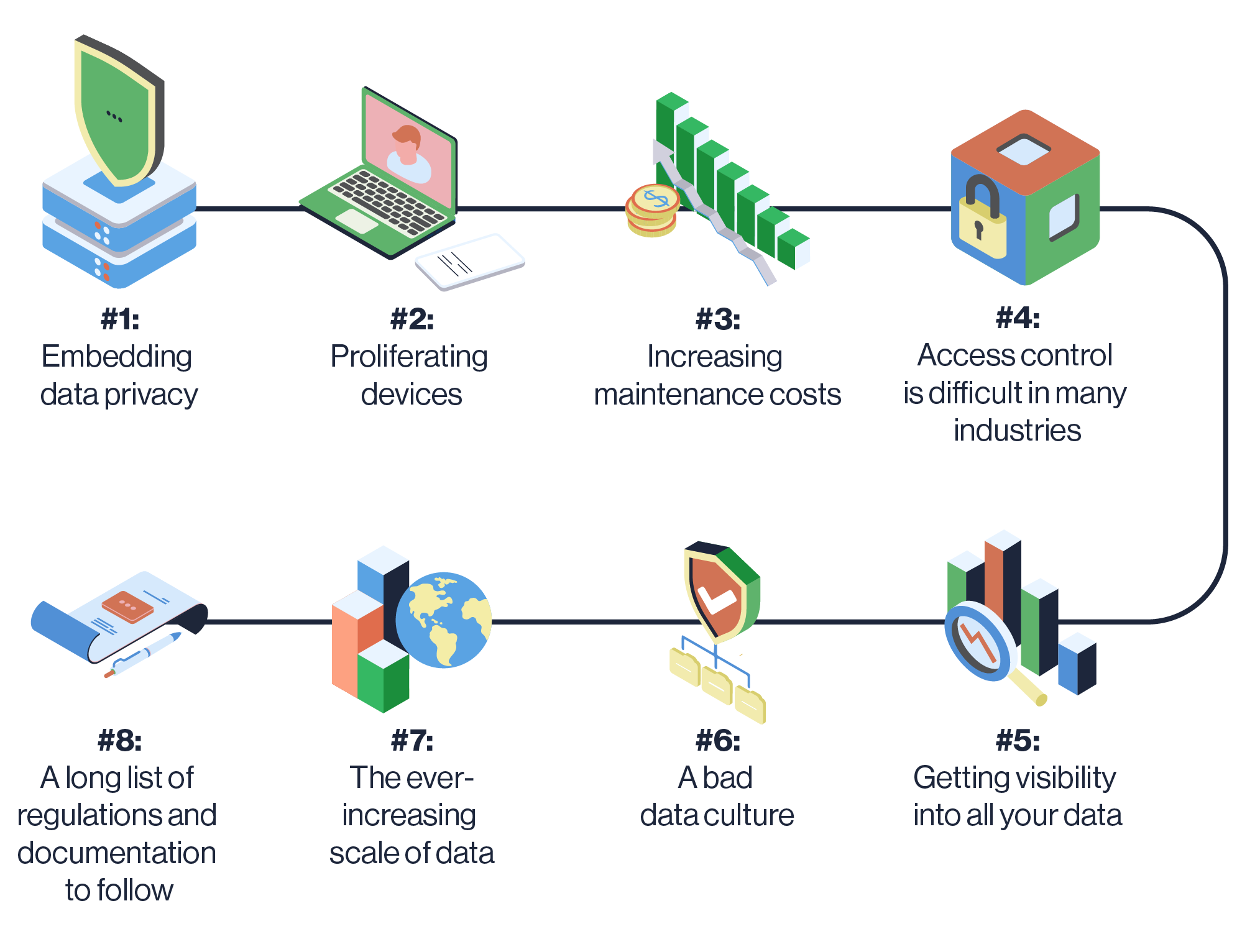
| Challenges and Limitations | ||
|---|---|---|
| Balancing privacy and utility can be challenging when adding noise to data. Ensuring the accuracy of statistical analysis while protecting individual privacy requires careful implementation. Differential privacy techniques may require additional computational resources and expertise. | ||
| 8 | ||
| Conclusion | ||
|---|---|---|
| Protecting shopping preferences with differential privacy safeguards personal information while enabling meaningful analysis. Users can enjoy personalized experiences without compromising their privacy. Differential privacy is a powerful tool for businesses to gain insights while respecting consumer privacy. | ||
| 9 | ||
| Q&A | ||
|---|---|---|
| Open the floor for questions and discussion regarding protecting shopping preferences with differential privacy. Your second bullet Your third bullet |  | |
| 10 | ||