Price Ilasticity Of Demand Presentation
| Introduction to Price Elasticity of Demand | ||
|---|---|---|
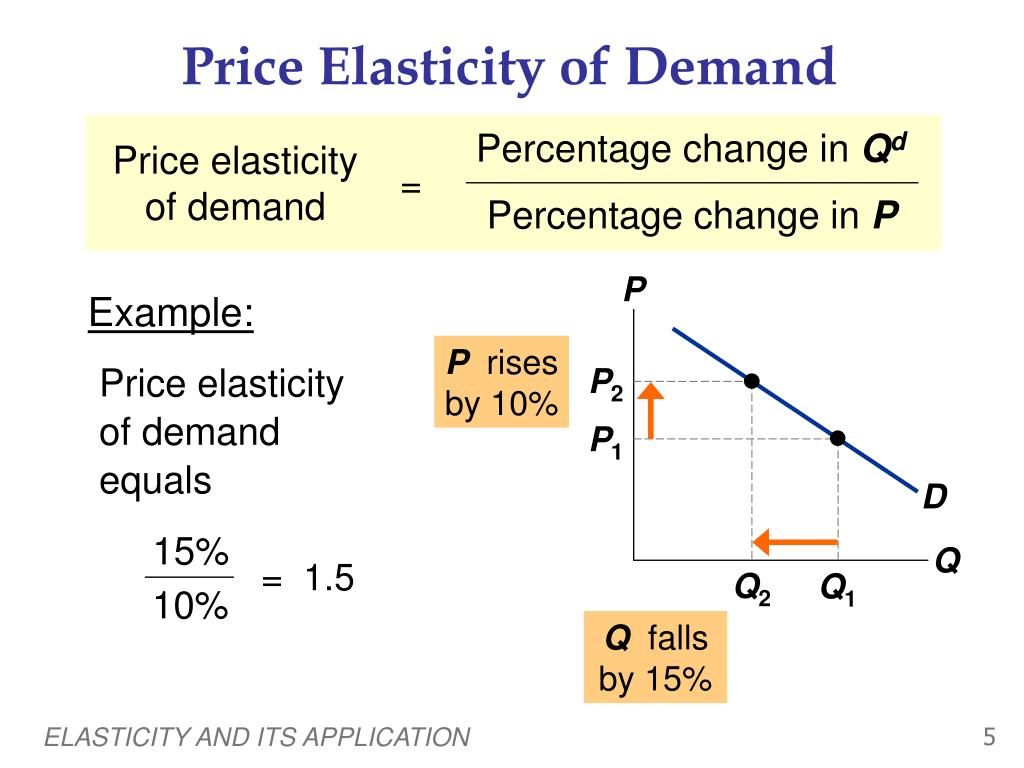
| Price elasticity of demand measures the responsiveness of quantity demanded to changes in price. It indicates how sensitive consumers are to price changes. The price elasticity of demand is calculated as the percentage change in quantity demanded divided by the percentage change in price. | ||
| 1 | ||
| Elasticity Coefficients | ||
|---|---|---|
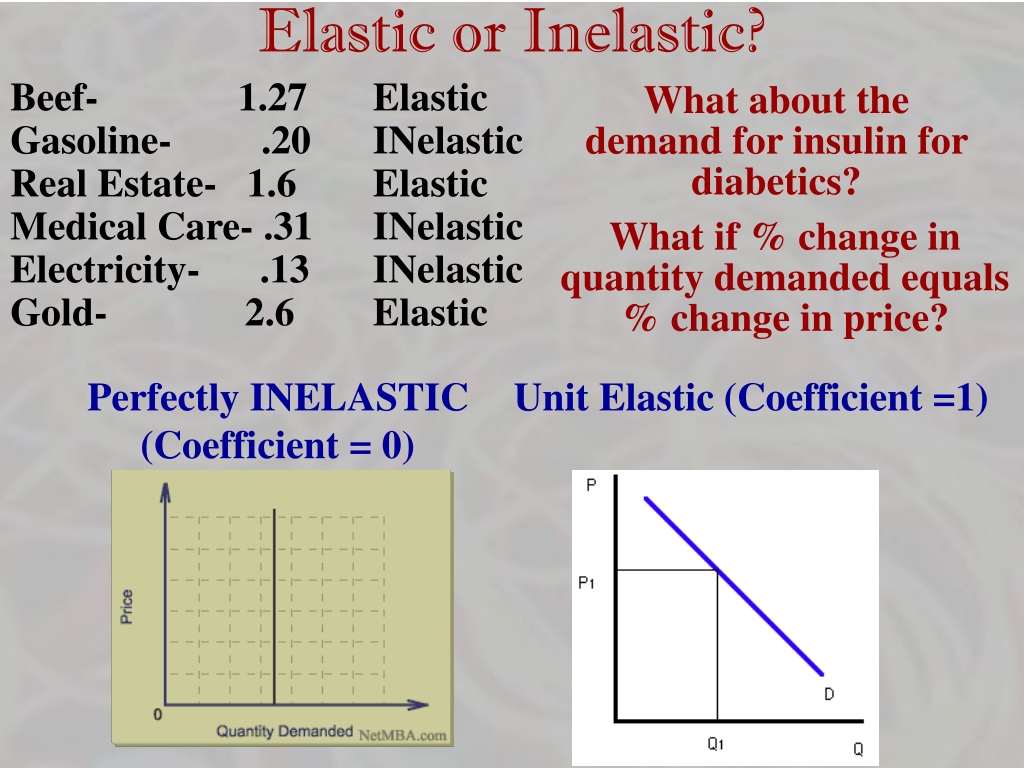
| Elasticity coefficients can be classified into three categories: elastic, inelastic, and unitary elastic. If the absolute value of the elasticity coefficient is greater than 1, demand is considered elastic. If the absolute value of the elasticity coefficient is less than 1, demand is considered inelastic. | ||
| 2 | ||
| Factors Affecting Price Elasticity of Demand | ||
|---|---|---|
| Availability of substitutes: The more substitutes available, the more elastic the demand. Necessity vs. luxury goods: Necessities tend to have inelastic demand, while luxury goods have elastic demand. Time period: Demand tends to be more elastic in the long run as consumers have more time to adjust their behavior. | ||
| 3 | ||
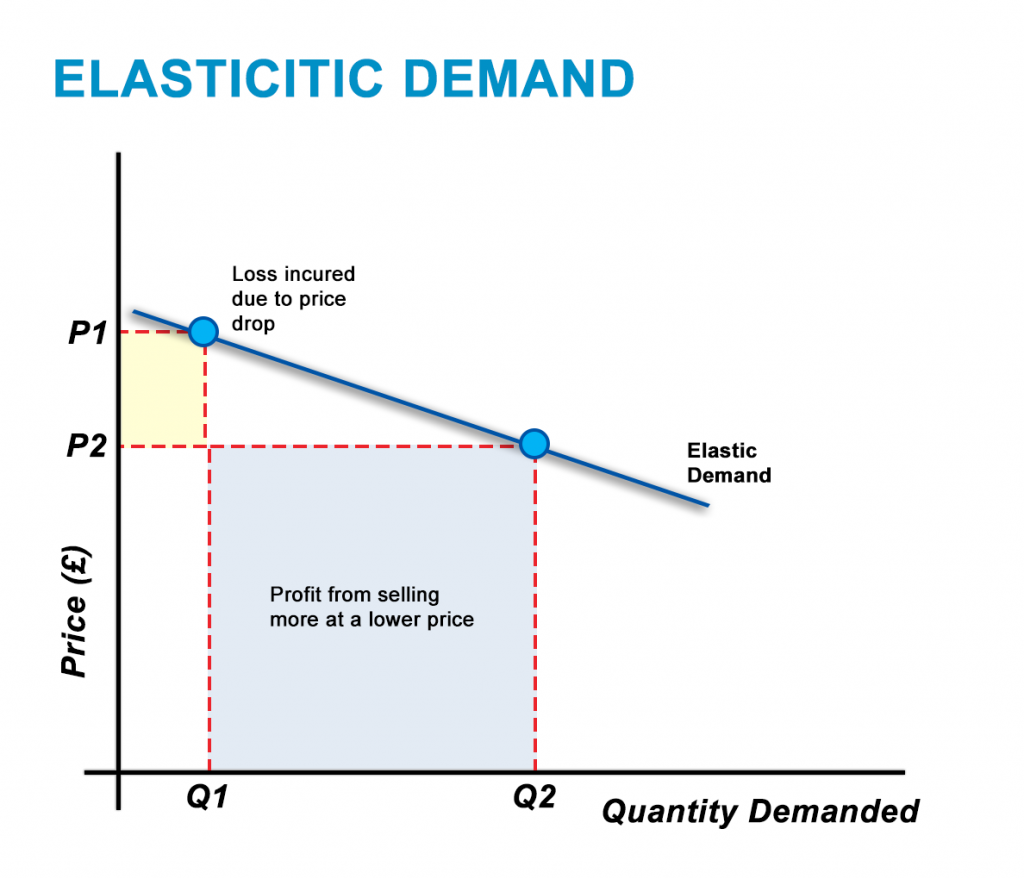
| Elastic Demand | ||
|---|---|---|
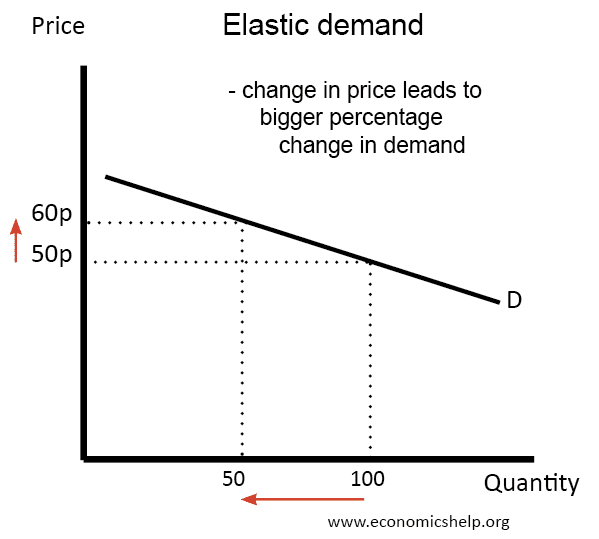
| In elastic demand, a small change in price leads to a proportionally larger change in quantity demanded. Consumers are highly sensitive to price changes in elastic demand. Elastic demand is often associated with non-essential goods or goods with many substitutes. | ||
| 4 | ||
| Inelastic Demand | ||
|---|---|---|
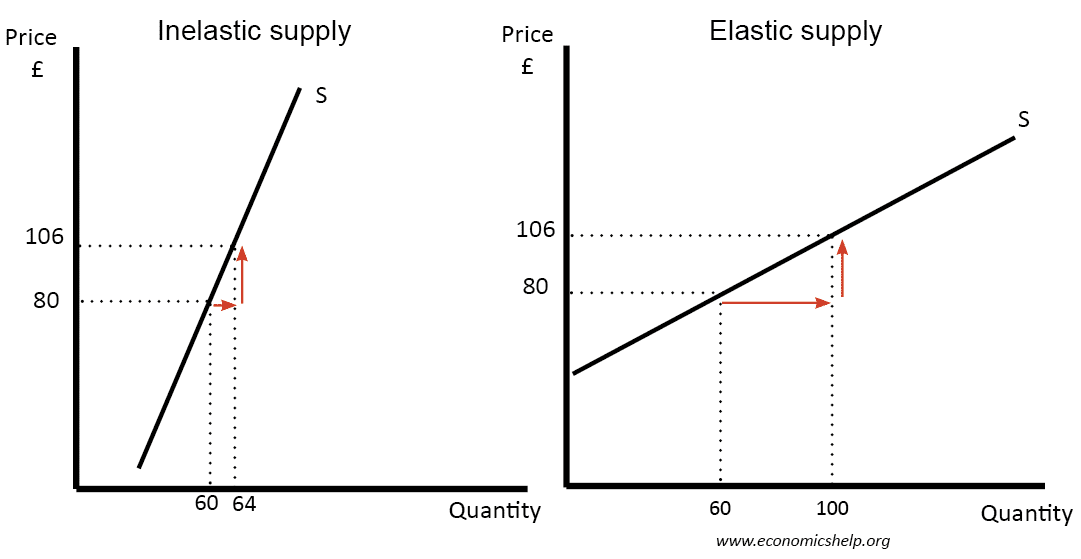
| In inelastic demand, a change in price leads to a proportionally smaller change in quantity demanded. Consumers are less sensitive to price changes in inelastic demand. Inelastic demand is often associated with essential goods or goods with few substitutes. | ||
| 5 | ||
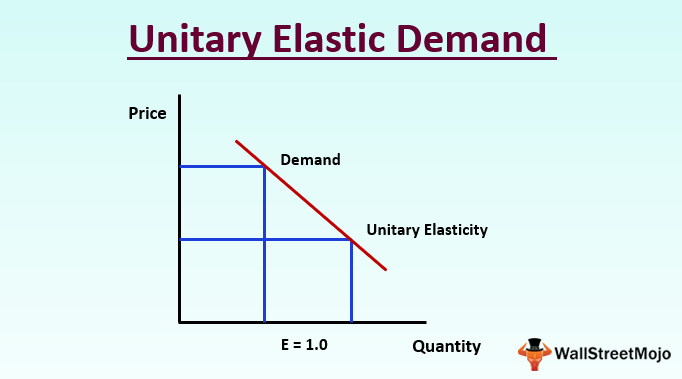
| Unitary Elastic Demand | ||
|---|---|---|
| Unitary elastic demand occurs when the percentage change in quantity demanded is equal to the percentage change in price. The revenue remains the same when price changes in unitary elastic demand. Unitary elastic demand is rare in reality but provides a midpoint between elastic and inelastic demand. | ||
| 6 | ||
| Importance of Price Elasticity of Demand | ||
|---|---|---|
| Price elasticity of demand helps businesses determine optimal pricing strategies. It provides insights into the sensitivity of consumers to price changes. Understanding price elasticity of demand helps businesses forecast changes in demand and plan production accordingly. | ||
| 7 | ||
| Price Elasticity Values | ||
|---|---|---|
| The price elasticity coefficient can be positive or negative. A positive coefficient indicates a normal or direct relationship between price and quantity demanded. A negative coefficient indicates an inverse or reverse relationship between price and quantity demanded. | ||
| 8 | ||
| Calculating Price Elasticity of Demand | ||
|---|---|---|
| Price elasticity of demand is calculated using the formula: % change in quantity demanded / % change in price. The midpoint formula is often used to calculate price elasticity when there are large changes in price and quantity demanded. Your third bullet | ||
| 9 | ||
| Summary | ||
|---|---|---|
| Price elasticity of demand measures the responsiveness of quantity demanded to changes in price. Elasticity coefficients can be elastic, inelastic, or unitary elastic. Factors affecting price elasticity include availability of substitutes, necessity vs. luxury goods, and time period. | ||
| 10 | ||
| References (download PPTX file for details) | ||
|---|---|---|
| Smith, J. (2020). Introduction to Price Elast... Johnson, L. (2019). Factors Affecting Price E... Peterson, M. (2018). Calculating Price Elasti... |  | |
| 11 | ||