Ppt Orientation Presentation
| Introduction to Ppt Orientation | ||
|---|---|---|
| Ppt orientation refers to the arrangement and layout of slides in a presentation. It determines the flow and visual hierarchy of information. Proper orientation enhances the overall effectiveness and impact of the presentation. | ||
| 1 | ||
| Landscape Orientation | ||
|---|---|---|
| Landscape orientation is the default setting in PowerPoint. It provides a wider view, making it suitable for most presentations. Landscape orientation is commonly used for business presentations, educational lectures, and conferences. | ||
| 2 | ||
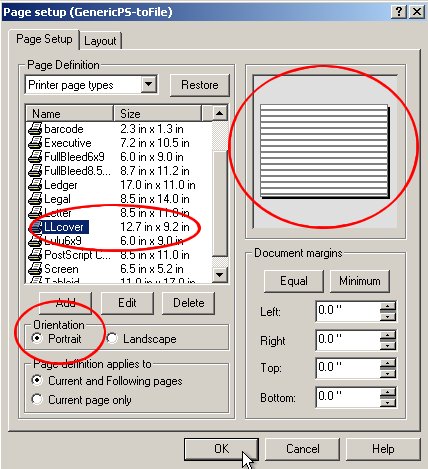
| Portrait Orientation | ||
|---|---|---|
| Portrait orientation is less commonly used in PowerPoint. It provides a taller view, ideal for presenting content with more vertical emphasis. Portrait orientation is often used for showcasing tall infographics, posters, or other visual elements. | ||
| 3 | ||
| Choosing the Right Orientation | ||
|---|---|---|
| Consider the content and purpose of your presentation when selecting the orientation. Landscape orientation is best for slides with a lot of text, charts, or horizontal visuals. Portrait orientation is suitable for slides with vertical visuals or when displaying tall images. | ||
| 4 | ||
| 5: | ||
|---|---|---|
| Your first bullet Your second bullet Your third bullet | ||
| 5 | ||
| Size Options | ||
|---|---|---|
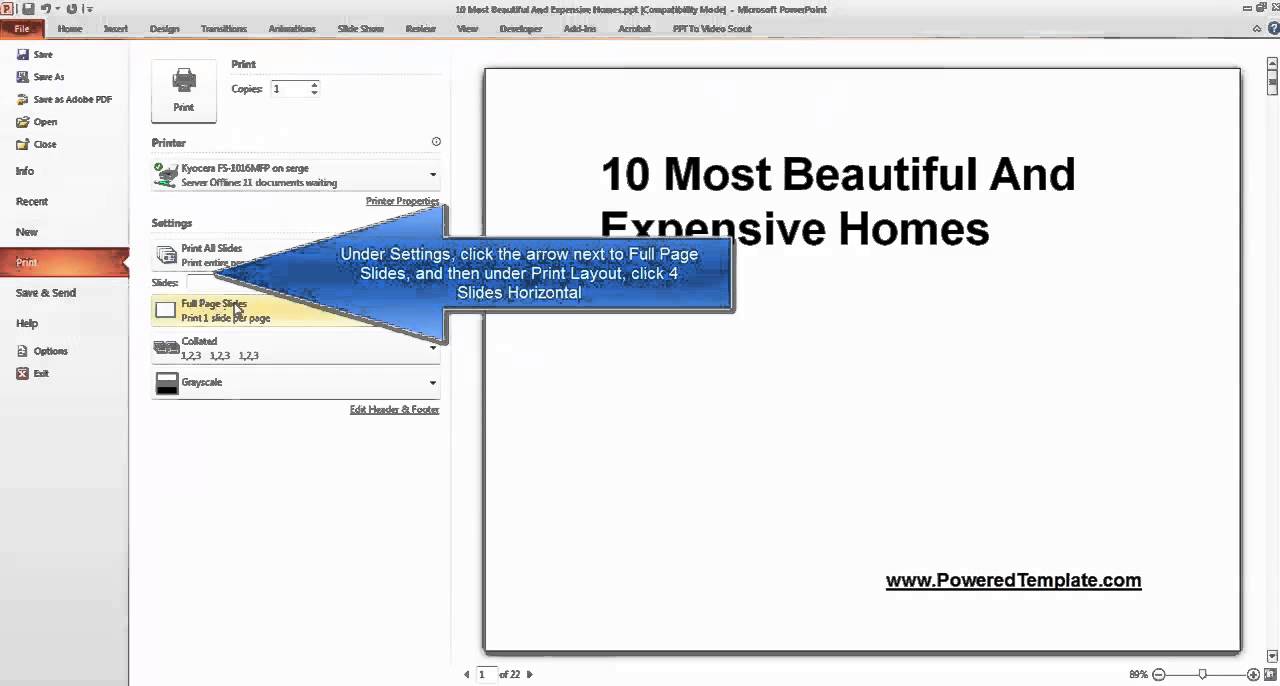
| PowerPoint offers predefined slide sizes, including standard (4:3) and widescreen (16:9). Standard slide size is suitable for older projectors or when printing handouts. Widescreen slide size is ideal for modern displays, projectors, and online sharing. | ||
| 6 | ||
| Changing | ||
|---|---|---|
| Your first bullet Your second bullet Your third bullet | ||
| 7 | ||
| Orientation | ||
|---|---|---|
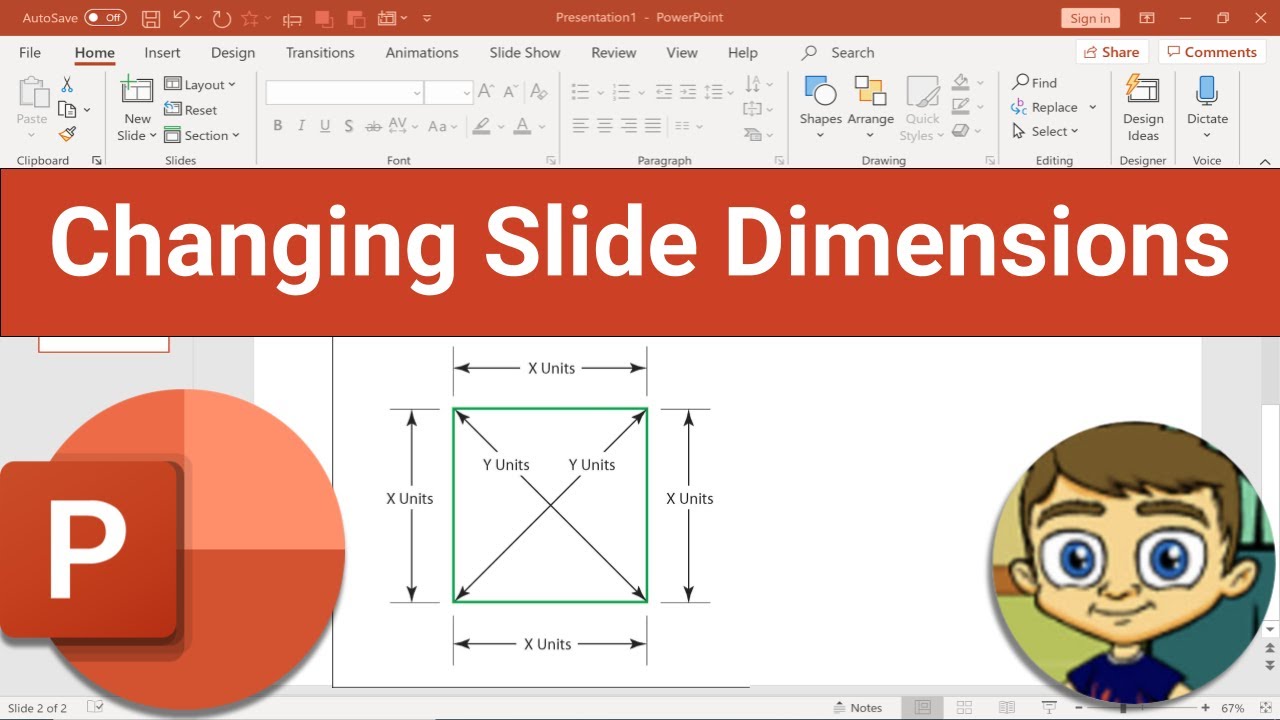
| To change the orientation of a slide, go to the "Design" tab and click on " Your second bullet Your third bullet | ||
| 8 | ||
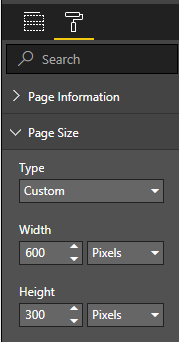
| Size." | ||
|---|---|---|
| Select "Custom Your second bullet Your third bullet | ||
| 9 | ||
| Size" and choose the desired orientation: portrait or landscape. | ||
|---|---|---|
| Remember to review and adjust the content and visuals accordingly after changing the orientation. Your second bullet Your third bullet | ||
| 10 | ||
| Design Considerations for Landscape Orientation | ||
|---|---|---|
| Utilize the wider space to include more content, charts, and images. Maintain a consistent visual hierarchy to ensure clarity and readability. Use bullet points and subheadings to break down information into easily digestible chunks. | ||
| 11 | ||
| Design Considerations for Portrait Orientation | ||
|---|---|---|
| Optimize the vertical space by using taller visuals and infographics. Keep the text concise and avoid overcrowding the slide. Utilize the top-down flow to guide the viewer's attention and create a logical structure. | ||
| 12 | ||
| Tips for Effective Orientation Choices | ||
|---|---|---|
| Understand your audience and the context of the presentation. Align the orientation with the content, purpose, and visuals of each slide. Test the presentation on different devices and projectors to ensure compatibility and legibility. | ||
| 13 | ||
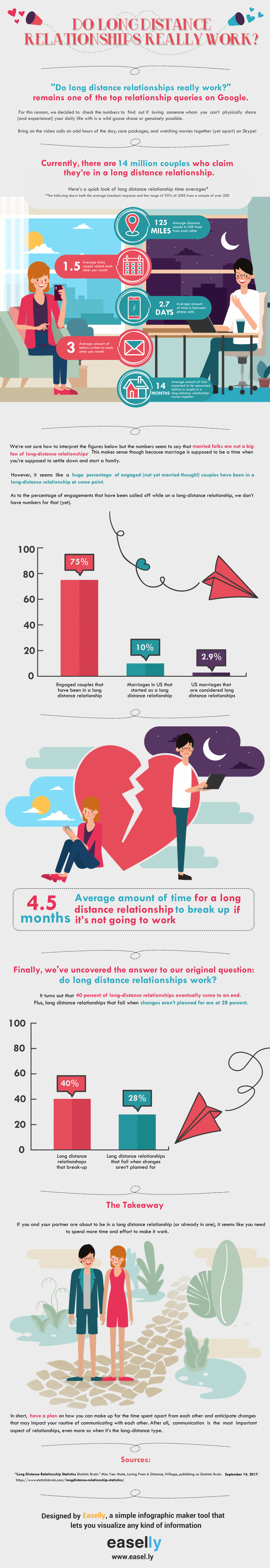
| Conclusion | ||
|---|---|---|
| Ppt orientation plays a crucial role in the overall effectiveness of a presentation. Choose the appropriate orientation based on content, purpose, and visual elements. Test and review the presentation to ensure optimal legibility and impact. | ||
| 14 | ||