Photosynthesis Presentation
| Introduction to Photosynthesis | ||
|---|---|---|
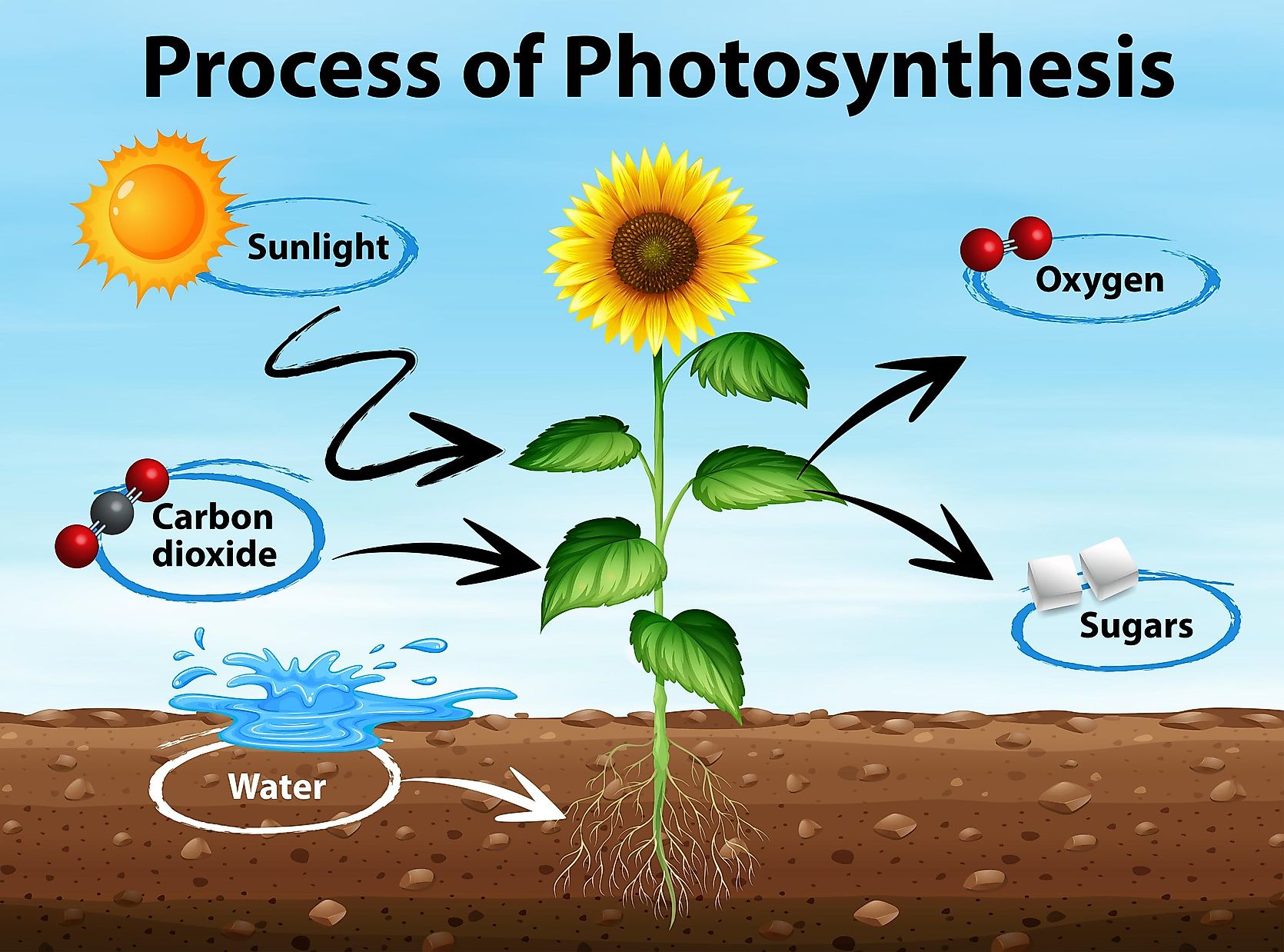
| Photosynthesis is the process by which green plants and some other organisms convert sunlight into chemical energy. It is a crucial process for the survival of life on Earth as it produces oxygen and organic compounds. The main components required for photosynthesis are light energy, water, and carbon dioxide. | ||
| 1 | ||
| Chloroplasts and Pigments | ||
|---|---|---|
| Chloroplasts are specialized organelles found in plant cells that carry out photosynthesis. Chlorophyll is the primary pigment in chloroplasts that absorbs sunlight. Other pigments, such as carotenoids, help to capture a broader range of light wavelengths. | ||
| 2 | ||
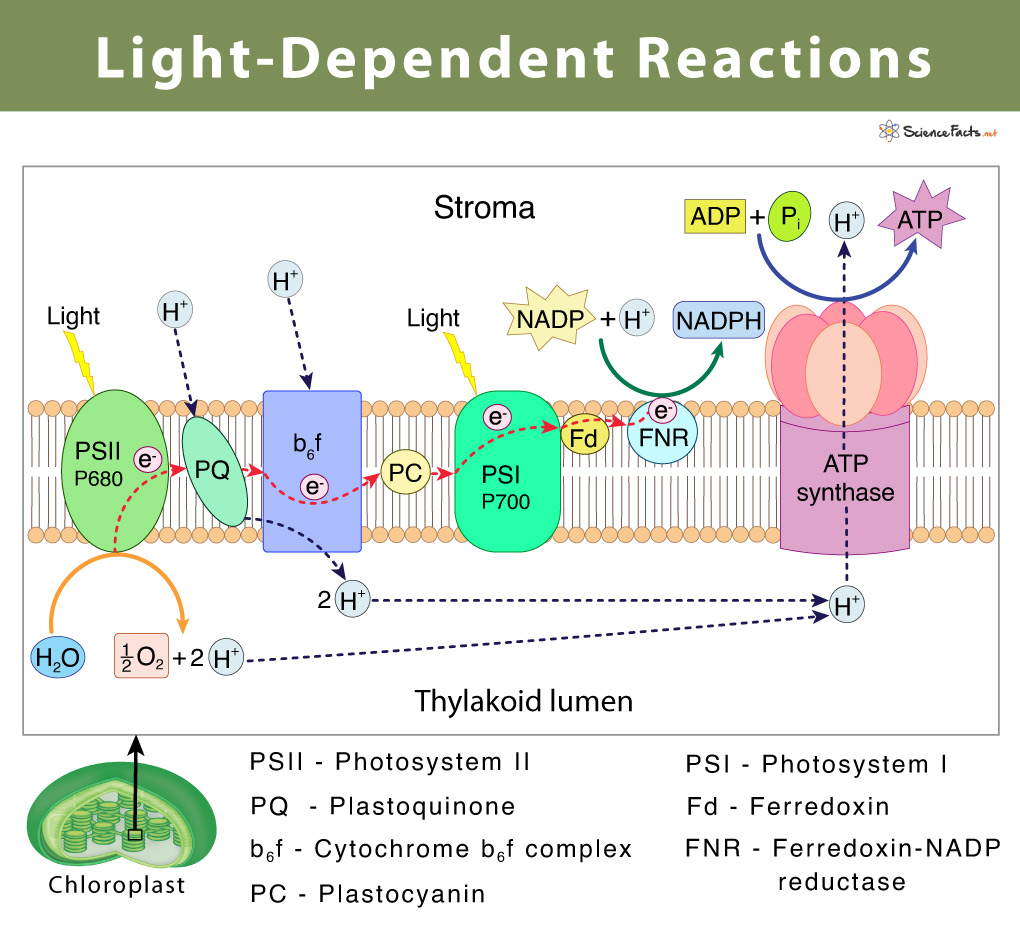
| Light-Dependent Reactions | ||
|---|---|---|
| The first stage of photosynthesis is the light-dependent reactions that take place in the thylakoid membranes of chloroplasts. During this process, light energy is absorbed by chlorophyll and converted into chemical energy in the form of ATP and NADPH. Water molecules are also split, releasing oxygen as a byproduct. | ||
| 3 | ||
| Calvin Cycle (Light-Independent Reactions) | ||
|---|---|---|
| The second stage of photosynthesis is the Calvin Cycle, also known as the light-independent reactions or dark reactions. This cycle occurs in the stroma of chloroplasts and uses ATP and NADPH from the light-dependent reactions. Carbon dioxide is converted into glucose through a series of enzyme-catalyzed reactions. | ||
| 4 | ||
| Factors Affecting Photosynthesis | ||
|---|---|---|
| Light intensity: Higher light intensity increases the rate of photosynthesis until a certain point where it plateaus. Carbon dioxide concentration: Higher CO2 levels enhance photosynthesis up to a certain threshold. Temperature: Optimal temperatures promote photosynthesis, but extreme temperatures can inhibit the process. | ||
| 5 | ||
| Importance of Photosynthesis | ||
|---|---|---|
| Photosynthesis is responsible for maintaining oxygen levels in the atmosphere, essential for respiration of all living organisms. It is the primary source of organic compounds, including glucose, which serves as a fuel for cellular respiration. Photosynthesis also plays a vital role in the global carbon cycle, reducing the amount of carbon dioxide in the atmosphere. | ||
| 6 | ||
| Adaptations for Photosynthesis | ||
|---|---|---|
| Plants have evolved various adaptations to optimize photosynthesis, such as broad leaves to capture more sunlight. Some plants, like cacti, have specialized structures like spines to reduce water loss while maximizing photosynthesis. Aquatic plants have adaptations to absorb carbon dioxide from water, such as specialized leaf structures or root systems. | ||
| 7 | ||
| Photosynthesis in Other Organisms | ||
|---|---|---|
| Although plants are the primary photosynthetic organisms, other organisms like algae and some bacteria also perform photosynthesis. Algae, including phytoplankton, play a significant role in marine ecosystems as primary producers. Cyanobacteria, also known as blue-green algae, were the first organisms to carry out oxygenic photosynthesis. | ||
| 8 | ||
| Photosynthesis and Human Activities | ||
|---|---|---|
| Human activities, such as deforestation and burning fossil fuels, contribute to increased carbon dioxide levels, affecting the balance of photosynthesis. Understanding photosynthesis helps in crop production and improving agricultural practices. Photosynthesis is the basis for renewable energy sources like solar panels that convert sunlight into electricity. | ||
| 9 | ||
| Conclusion | ||
|---|---|---|
| Photosynthesis is a vital process that converts sunlight into chemical energy, producing oxygen and organic compounds. It occurs in chloroplasts through two stages: light-dependent reactions and the Calvin Cycle. Understanding photosynthesis is crucial for understanding the Earth's ecosystems and developing sustainable practices. | ||
| 10 | ||
| References (download PPTX file for details) | ||
|---|---|---|
| Campbell, N. A., & Reece, J. B. (2008). Biolo... Taiz, L., & Zeiger, E. (2010). Plant Physiolo... Your third bullet... |  | |
| 11 | ||
/cross-section-chloroplast-58d2e3815f9b5846830a7186.jpg)