Peteridophytes Presentation
| Introduction to Peteridophytes | ||
|---|---|---|
| Peteridophytes are a group of plants that belong to the division Pteridophyta. They are commonly known as ferns and are found in various habitats worldwide. Peteridophytes reproduce via spores and have a distinct life cycle involving alternating generations. | ||
| 1 | ||
| Characteristics of Peteridophytes | ||
|---|---|---|
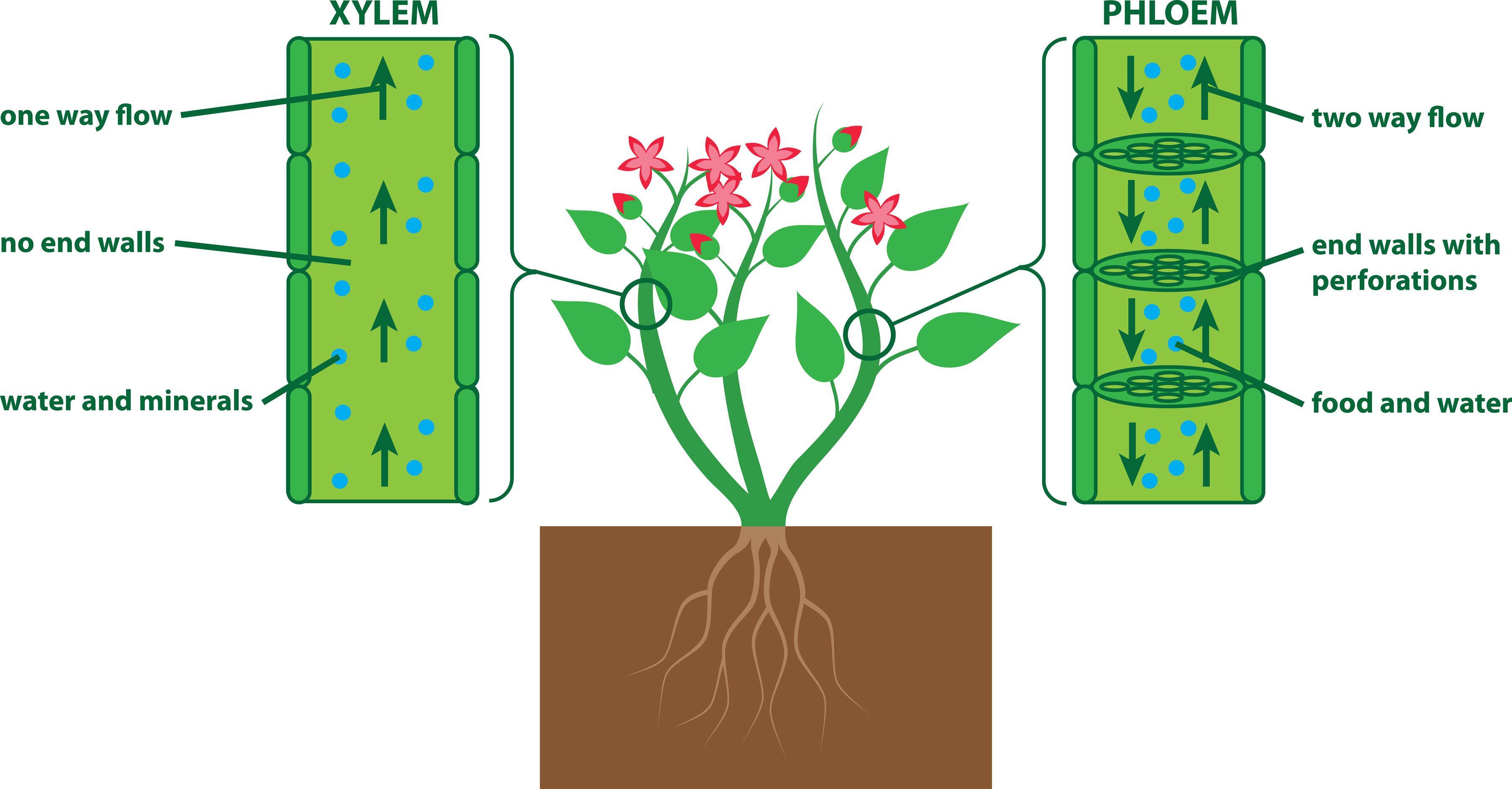
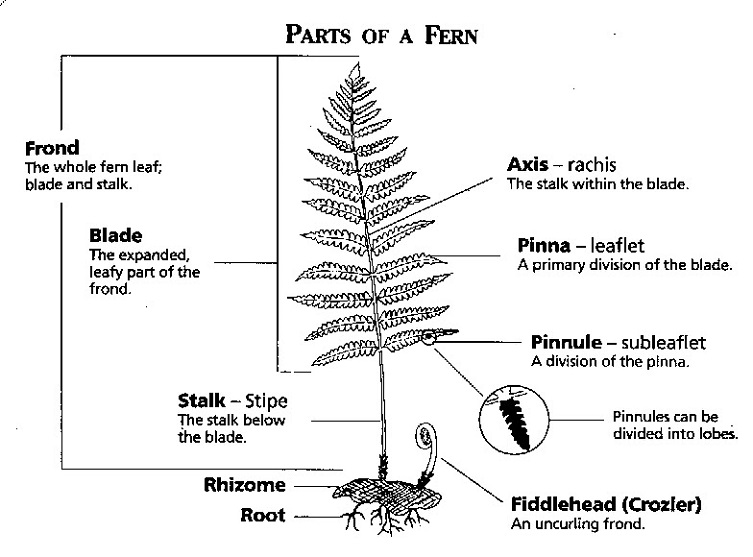
| Peteridophytes have vascular tissues that allow for the transport of water and nutrients throughout the plant. They have leaves called fronds, which are often divided into smaller leaflets. Unlike flowering plants, Peteridophytes do not produce flowers or seeds. | ||
| 2 | ||
| Diversity of Peteridophytes | ||
|---|---|---|
| There are approximately 12,000 known species of Peteridophytes, making them the second-largest group of vascular plants after angiosperms. They vary in size from small, delicate ferns to large tree ferns that can reach heights of up to 20 meters. Peteridophytes display a wide range of leaf shapes, including simple, pinnate, bipinnate, and palmate forms. | ||
| 3 | ||
| Reproduction in Peteridophytes | ||
|---|---|---|
| Peteridophytes have a unique reproductive cycle involving two distinct generations: the sporophyte and the gametophyte. The sporophyte generation is the dominant phase and produces spores through meiosis. Spores germinate into the gametophyte generation, which produces gametes for sexual reproduction. | ||
| 4 | ||
| Habitat and Distribution | ||
|---|---|---|
| Peteridophytes can be found in a variety of habitats, including forests, wetlands, deserts, and even on rocky surfaces. They are particularly abundant in tropical rainforests where they form a significant component of the understory vegetation. Some species of Peteridophytes are adapted to grow in extreme environments, such as high-altitude mountains and arid regions. | ||
| 5 | ||
| Ecological Importance | ||
|---|---|---|
| Peteridophytes play a crucial role in ecosystem functioning, contributing to nutrient cycling and soil formation. They provide habitat and food for various animals, including insects, birds, and mammals. As primary producers, ferns contribute to the overall productivity and stability of ecosystems. | ||
| 6 | ||
| Economic Significance | ||
|---|---|---|
| Peteridophytes have been used by humans for various purposes throughout history. Some species, such as the bracken fern, have edible shoots that are consumed in certain cultures. Certain ferns are cultivated as ornamental plants for gardens and landscaping. | ||
| 7 | ||
| Threats and Conservation | ||
|---|---|---|
| Habitat loss and fragmentation pose significant threats to Peteridophytes, particularly in areas of deforestation and urbanization. Invasive species can also threaten native fern populations by outcompeting them for resources. Conservation efforts focus on protecting and restoring fern habitats, as well as promoting awareness about their ecological importance. | ||
| 8 | ||
| Fun Facts about Peteridophytes | ||
|---|---|---|
| Ferns have been around for over 360 million years, making them one of the oldest plant groups on Earth. Some ferns can reproduce asexually through a process called vegetative propagation. The fiddleheads of certain fern species are considered a delicacy and are used in culinary dishes. | ||
| 9 | ||
| Conclusion | ||
|---|---|---|
| Peteridophytes, or ferns, are a diverse group of plants with unique characteristics and life cycles. They have ecological importance, contribute to ecosystem functioning, and have economic significance. Conservation efforts are crucial to protect and preserve fern habitats and their biodiversity. | ||
| 10 | ||