Pest Management Presentation
| Introduction to Pest Management | ||
|---|---|---|
| Pest management is the practice of controlling and eliminating pests to prevent damage to crops, property, and human health. Effective pest management involves a combination of prevention, monitoring, and control strategies. Integrated Pest Management (IPM) is a sustainable approach that aims to minimize the use of chemical pesticides. | ||
| 1 | ||
| Importance of Pest Management | ||
|---|---|---|
| Pest management is crucial for maintaining the quality and quantity of agricultural production. It helps reduce the transmission of diseases carried by pests, such as mosquitoes and rodents. Proper pest management can prevent property damage and protect public health. | ||
| 2 | ||
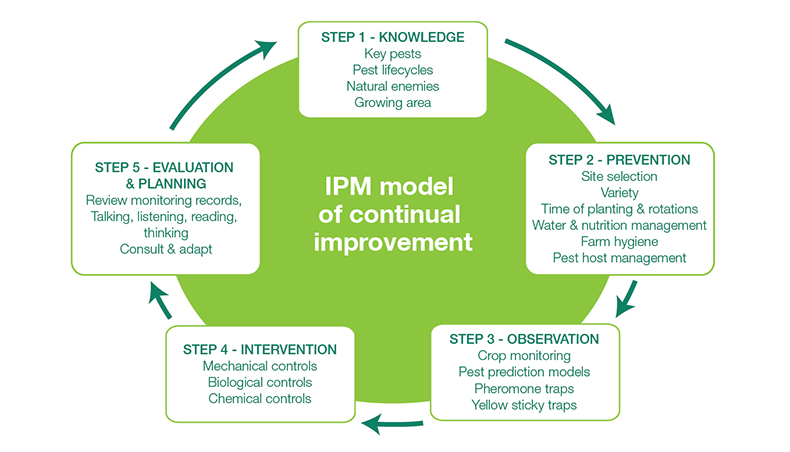
| Pest Identification and Monitoring | ||
|---|---|---|
| Identifying and monitoring pests is the first step in effective pest management. Regular inspections help determine the type and severity of pest infestations. Monitoring techniques include visual inspections, trapping, and the use of pheromone traps. | ||
| 3 | ||
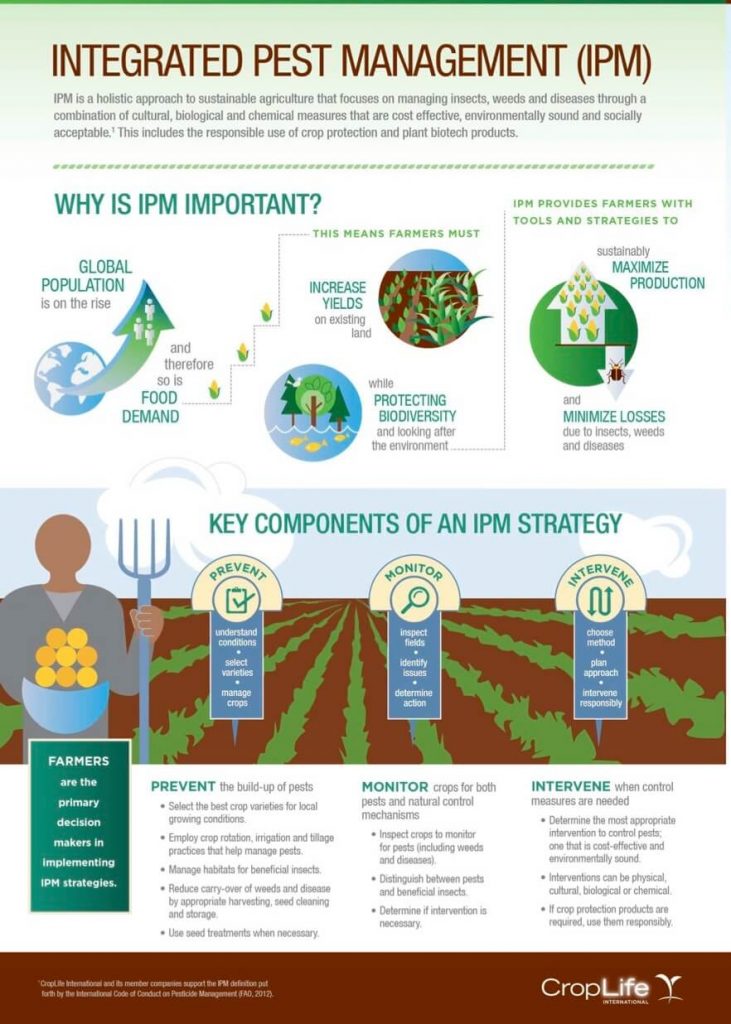
| Prevention Strategies | ||
|---|---|---|
| Implementing preventive measures is key to successful pest management. Proper sanitation practices, such as cleaning up food spills and storing food properly, can prevent pest infestations. Sealing entry points, such as cracks and gaps, helps prevent pests from entering buildings. | ||
| 4 | ||
| Cultural Control Methods | ||
|---|---|---|
| Cultural control methods involve manipulating the environment to deter pests. Crop rotation helps disrupt pest life cycles and reduce their populations. Planting pest-resistant varieties and using companion planting techniques can also deter pests. | ||
| 5 | ||
| Biological Control | ||
|---|---|---|
| Biological control involves using natural enemies to control pest populations. Predators, parasites, and pathogens can be introduced to target specific pests. This method is environmentally friendly and reduces reliance on chemical pesticides. | ||
| 6 | ||
| Mechanical and Physical Control | ||
|---|---|---|
| Mechanical control methods involve physically removing pests or using barriers to prevent their entry. Traps, vacuuming, and handpicking are examples of mechanical control. Physical barriers like screens and fences can keep pests out of specific areas. | ||
| 7 | ||
| Chemical Control | ||
|---|---|---|
| Chemical control should be used as a last resort when other methods fail. Pesticides should be chosen carefully, considering their effectiveness and potential environmental impact. Proper application techniques and adherence to safety guidelines are essential for minimizing risks. | ||
| 8 | ||
| Integrated Pest Management (IPM) | ||
|---|---|---|
| IPM is a holistic approach that combines multiple pest control methods. It focuses on long-term prevention and uses the least harmful methods first. IPM considers ecological, economic, and social factors for sustainable pest management. | ||
| 9 | ||
| Key Takeaways | ||
|---|---|---|
| Pest management is crucial for protecting crops, property, and public health. It involves pest identification, prevention, monitoring, and control strategies. Integrated Pest Management (IPM) is a sustainable approach that combines multiple methods. | ||
| 10 | ||
| References (download PPTX file for details) | ||
|---|---|---|
| Food and Agriculture Organization of the Unit... Your second bullet... Your third bullet... |  | |
| 11 | ||