Parasitic Computing Presentation
| Introduction to Parasitic Computing | ||
|---|---|---|
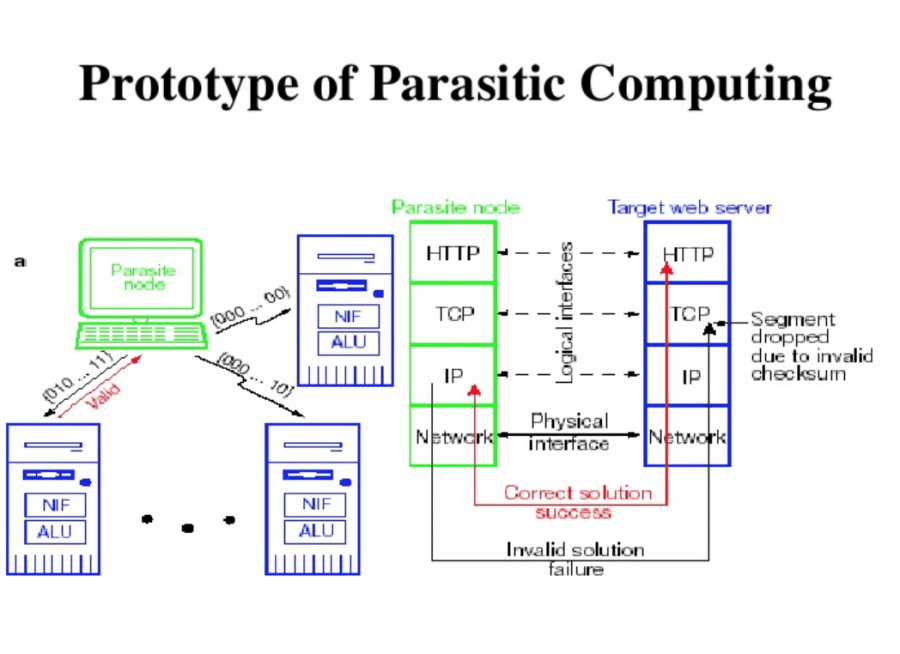
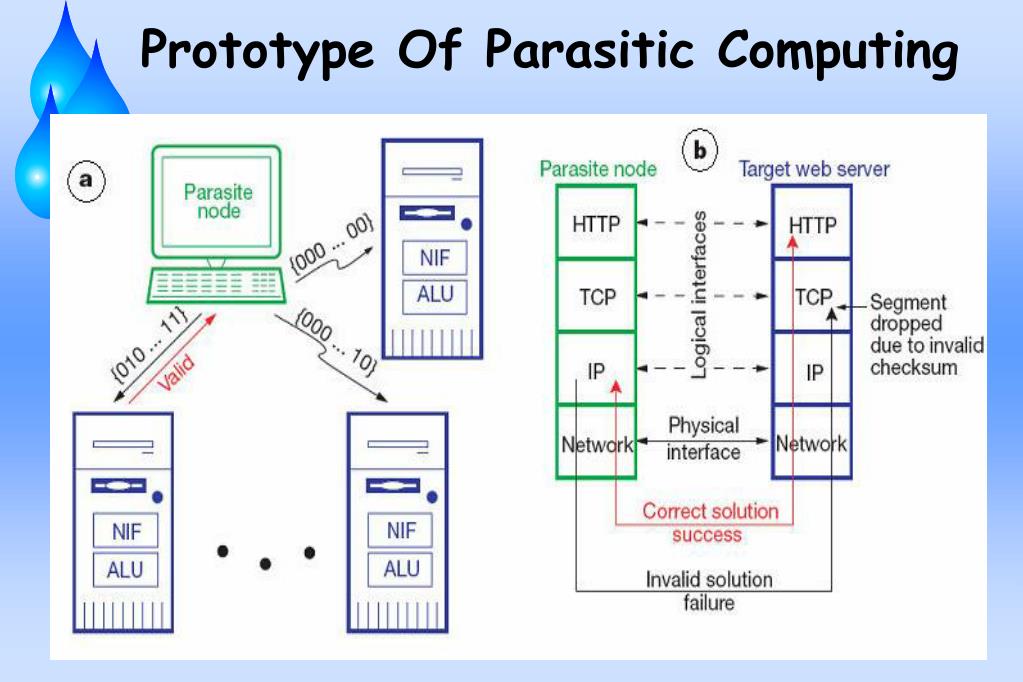
| Parasitic computing is a novel form of computing that exploits the computing power of unsuspecting devices or systems. It leverages the idle resources of these devices to perform complex computations without their owners' knowledge or consent. This approach allows for distributed computing without the need for a dedicated infrastructure. | ||
| 1 | ||
| How Parasitic Computing Works | ||
|---|---|---|
| Parasitic computing relies on the principle of computational resource borrowing. By injecting specially crafted requests or queries into a target system, these requests can be processed using the system's resources. The output or response generated by the target system can then be used to obtain desired computation results. | ||
| 2 | ||
| Advantages of Parasitic Computing | ||
|---|---|---|
| Scalability: Parasitic computing can harness the collective computational power of a large number of devices or systems, making it highly scalable. Cost-effectiveness: It eliminates the need for dedicated infrastructure, reducing costs associated with setting up and maintaining computing resources. Energy efficiency: Parasitic computing maximizes the utilization of idle resources, making it energy-efficient compared to traditional computing methods. | ||
| 3 | ||
| Potential Applications of Parasitic Computing | ||
|---|---|---|
| Cryptanalysis: Parasitic computing can be used to perform computationally intensive tasks such as breaking cryptographic algorithms or deciphering codes. Data processing: It can be applied to process large datasets or perform complex simulations using the idle resources of numerous devices. Optimization problems: Parasitic computing can help solve optimization problems by distributing subtasks across multiple devices to find the best solution. | ||
| 4 | ||
| Ethical Considerations and Concerns | ||
|---|---|---|
| Consent: The use of parasitic computing raises ethical concerns regarding the consent of device owners, as their resources are utilized without explicit permission. Security risks: Attackers could exploit vulnerabilities in target systems to inject malicious code or steal sensitive information during parasitic computing. Legal implications: The unauthorized use of computing resources may violate laws and regulations, making parasitic computing potentially illegal in certain jurisdictions. |  | |
| 5 | ||
| Conclusion | ||
|---|---|---|
| Parasitic computing offers a unique approach to distributed computing, leveraging idle resources for complex computations. Its advantages include scalability, cost-effectiveness, and energy efficiency. However, ethical considerations, security risks, and legal implications must be carefully evaluated before implementing parasitic computing in practice. | ||
| 6 | ||