PCOD Presentation
| Introduction to PCOD | ||
|---|---|---|
| Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS) is a common hormonal disorder affecting women of reproductive age. It is characterized by irregular menstrual cycles, excess androgen levels, and enlarged ovaries with multiple small cysts. PCOS can lead to various health complications, including infertility, insulin resistance, obesity, and cardiovascular disease. | ||
| 1 | ||
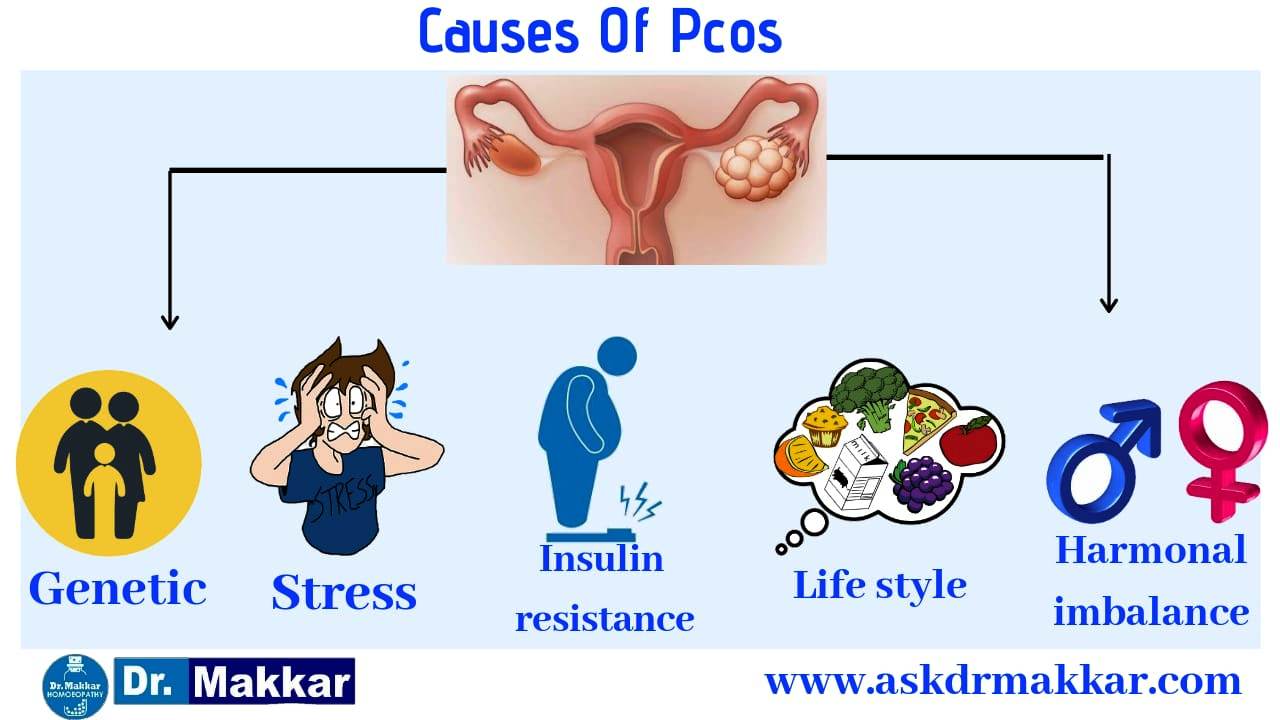
| Causes of PCOD | ||
|---|---|---|
| The exact cause of PCOS is unknown, but several factors contribute to its development. Hormonal imbalance, specifically elevated levels of androgens, plays a significant role. Insulin resistance, genetics, and environmental factors also contribute to the development of PCOD. | ||
| 2 | ||
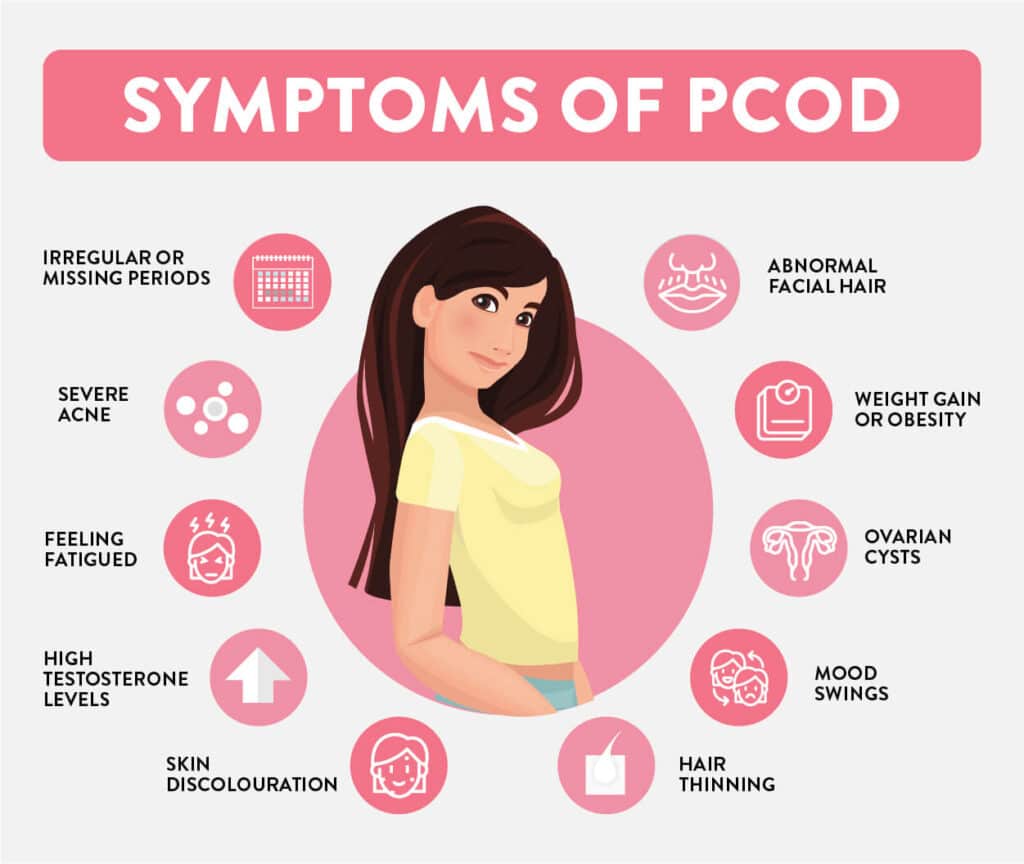
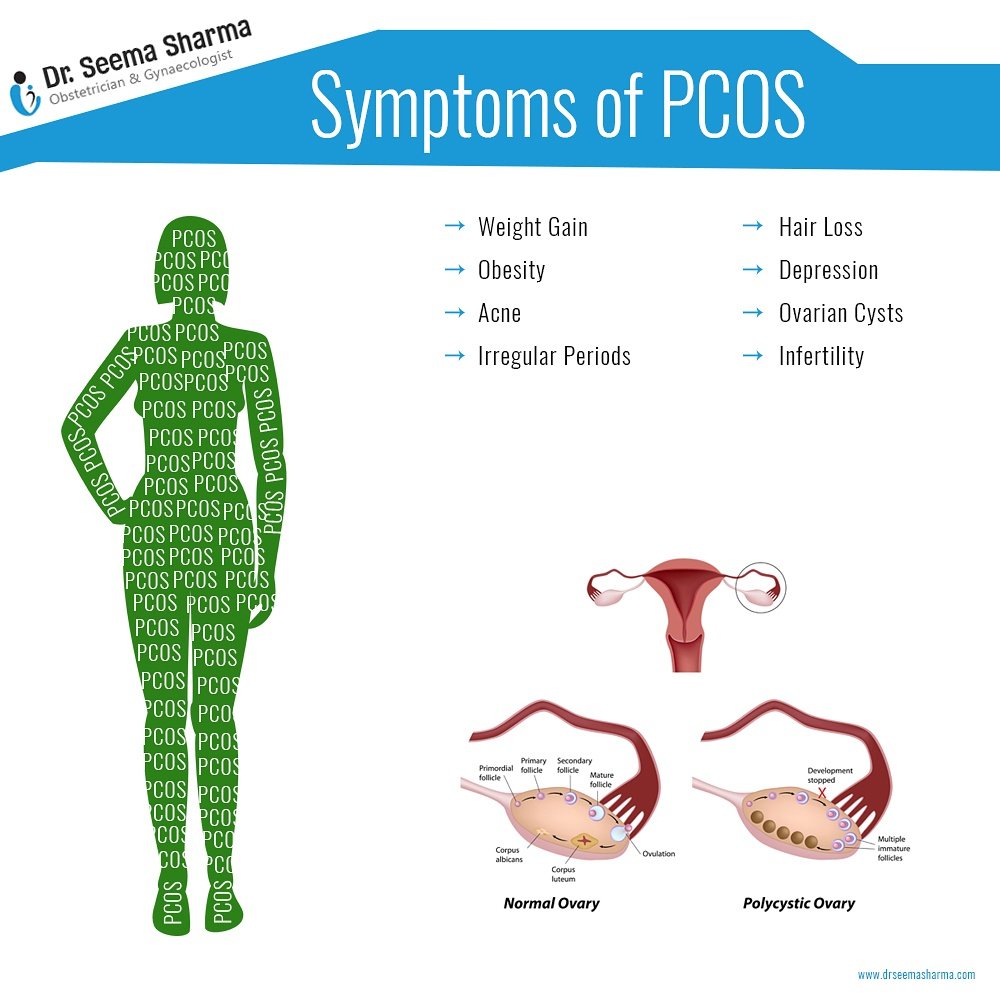
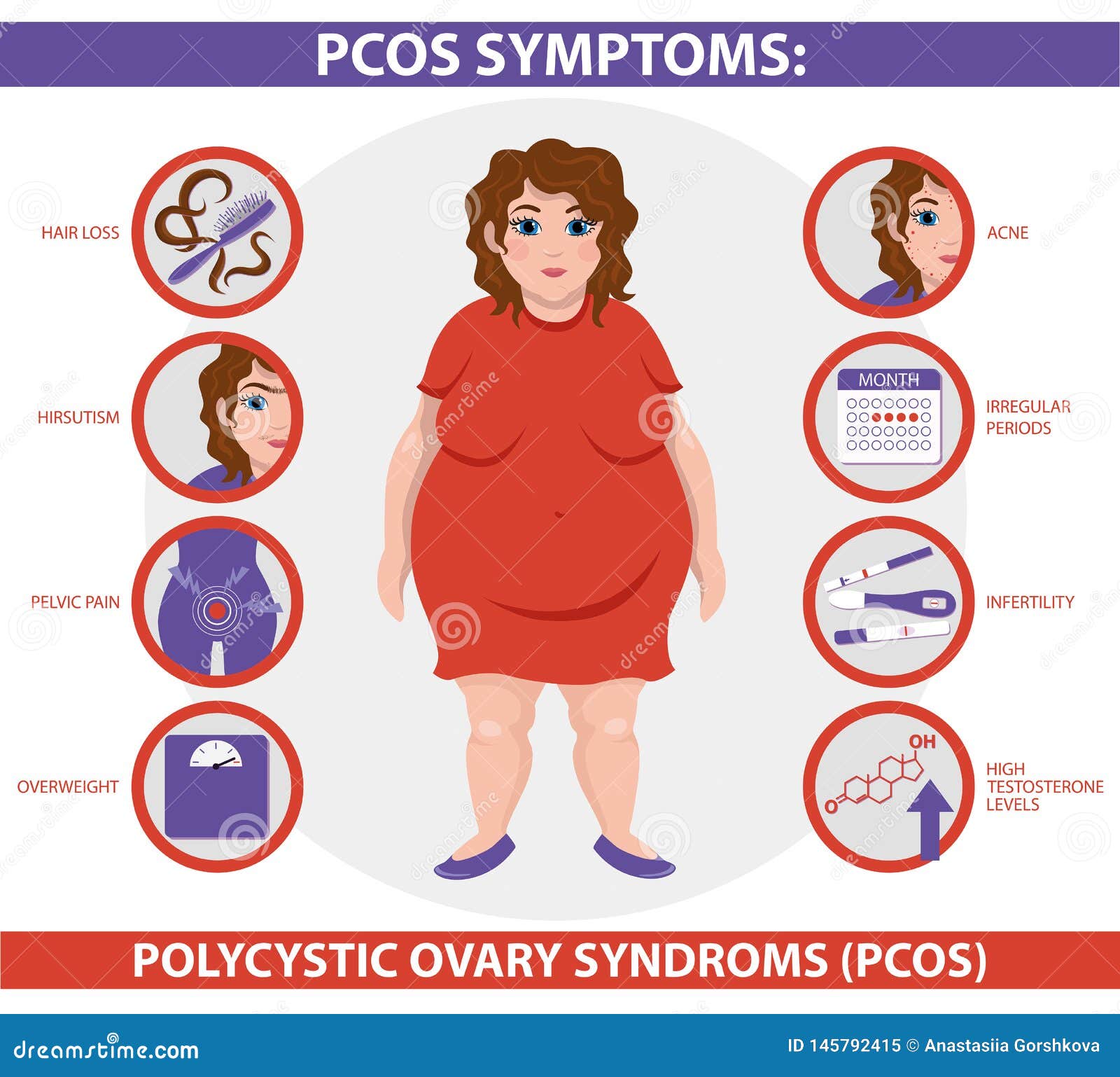
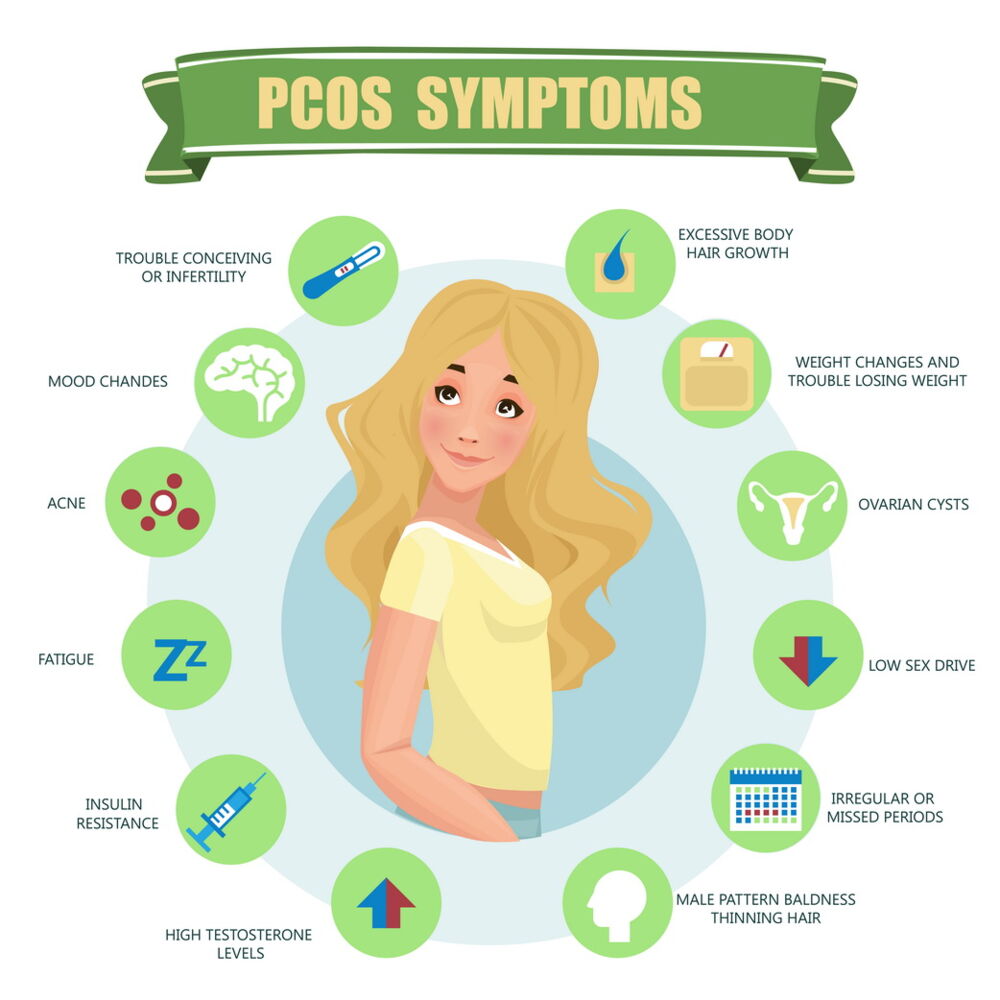
| Symptoms of PCOD | ||
|---|---|---|
| Irregular periods or no periods at all. Excessive hair growth on the face, chest, or back (hirsutism). Acne, oily skin, and dandruff. | ||
| 3 | ||
| Diagnosis of PCOD | ||
|---|---|---|
| Diagnosis is based on a combination of clinical symptoms, physical examination, and laboratory tests. Blood tests to measure hormone levels, including androgens, LH, FSH, and insulin levels. Pelvic ultrasound to visualize the ovaries for cysts and measure their size. | ||
| 4 | ||
| Treatment Options for PCOD | ||
|---|---|---|
| Lifestyle modifications, including regular exercise and a balanced diet, are crucial for managing PCOS. Medications, such as oral contraceptives, anti-androgens, and insulin-sensitizing drugs, may be prescribed. Fertility treatments, such as ovulation induction or in vitro fertilization (IVF), may be recommended for women trying to conceive. | ||
| 5 | ||
| Managing PCOD through Lifestyle Changes | ||
|---|---|---|
| Regular exercise helps improve insulin sensitivity, regulate menstrual cycles, and manage weight. Following a balanced diet, low in refined carbohydrates and saturated fats, can help manage insulin resistance and weight. Stress management techniques, such as meditation or yoga, can help reduce cortisol levels and improve symptoms. | ||
| 6 | ||
| Potential Complications of PCOD | ||
|---|---|---|
| Infertility or difficulty conceiving due to irregular ovulation. Increased risk of developing type 2 diabetes and metabolic syndrome. Obesity and weight gain, which can further aggravate hormonal imbalances. | ||
| 7 | ||
| PCOD and Mental Health | ||
|---|---|---|
| PCOS can have a significant impact on mental health, leading to depression, anxiety, and poor self-esteem. Women with PCOS may experience body image issues due to hirsutism, weight gain, or acne. Seeking support from healthcare professionals, support groups, or therapy can be beneficial in managing mental health concerns. | ||
| 8 | ||
| PCOD and Pregnancy | ||
|---|---|---|
| Women with PCOS may face challenges in getting pregnant, but it is not impossible. Fertility treatments, such as ovulation induction or IVF, can help increase the chances of conceiving. Early prenatal care is crucial to monitor and manage potential complications during pregnancy. | ||
| 9 | ||
| Summary and Conclusion | ||
|---|---|---|
| PCOS is a common hormonal disorder affecting women of reproductive age, characterized by irregular periods, excess androgen levels, and enlarged ovaries with cysts. Diagnosis involves a combination of clinical symptoms, physical examination, and laboratory tests. Management includes lifestyle modifications, medications, and fertility treatments. | ||
| 10 | ||