Ozone Layer Depletion Presentation
| Introduction to Ozone Layer Depletion | ||
|---|---|---|
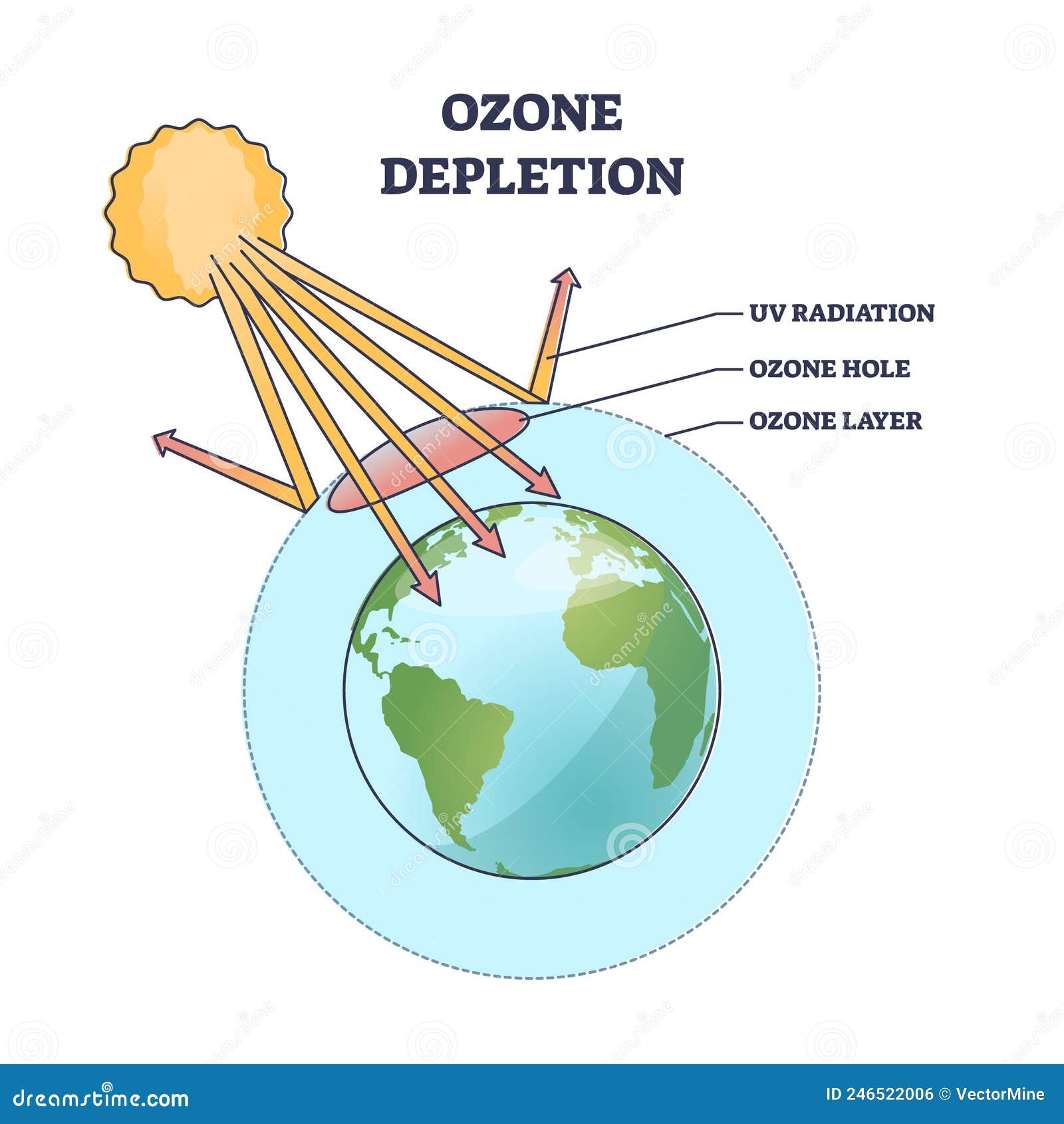
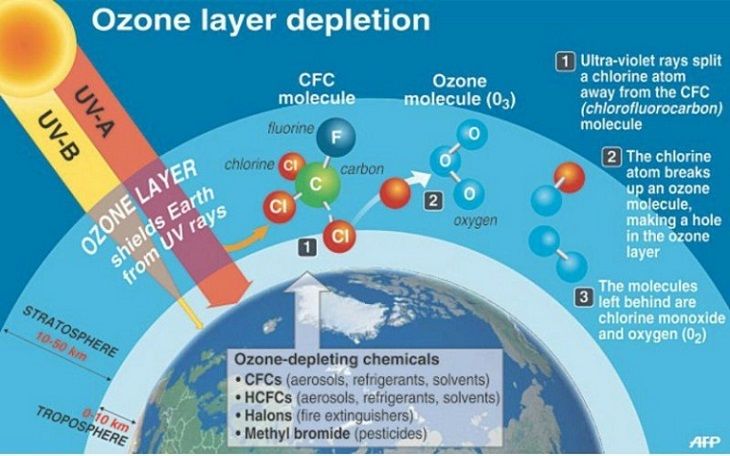
| Ozone layer depletion refers to the thinning of the ozone layer in the Earth's stratosphere. The ozone layer acts as a shield, protecting life on Earth from harmful ultraviolet (UV) radiation from the sun. The main cause of ozone layer depletion is the release of man-made chemicals called ozone-depleting substances (ODS). | ||
| 1 | ||
| Understanding Ozone Layer | ||
|---|---|---|
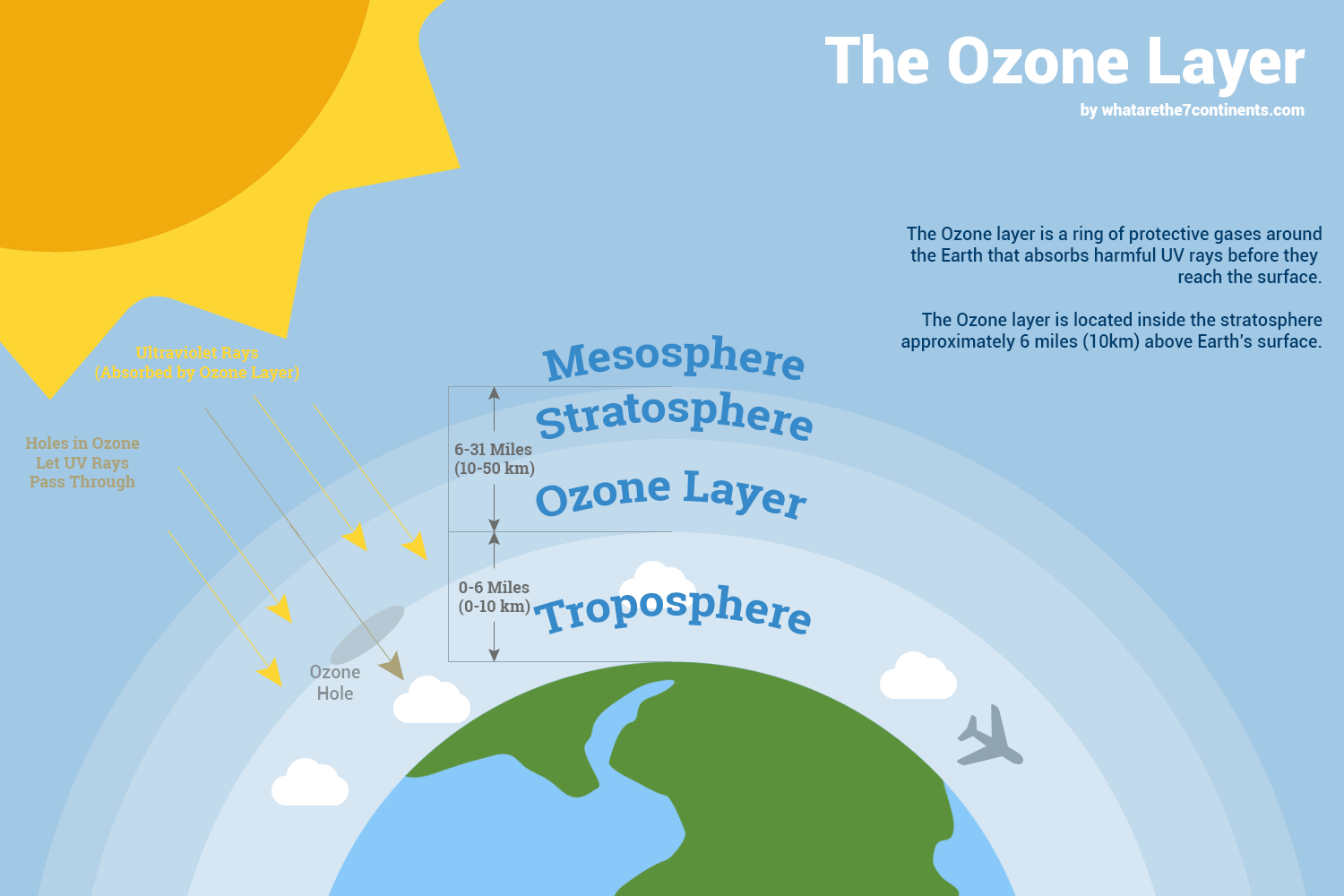
| The ozone layer is located in the Earth's stratosphere, approximately 10-50 kilometers above the surface. It contains a high concentration of ozone molecules (O3), which absorb and filter out most of the sun's harmful UV radiation. Ozone is formed naturally through the interaction of oxygen molecules (O2) with UV radiation. | ||
| 2 | ||
| Ozone-Depleting Substances (ODS) | ||
|---|---|---|
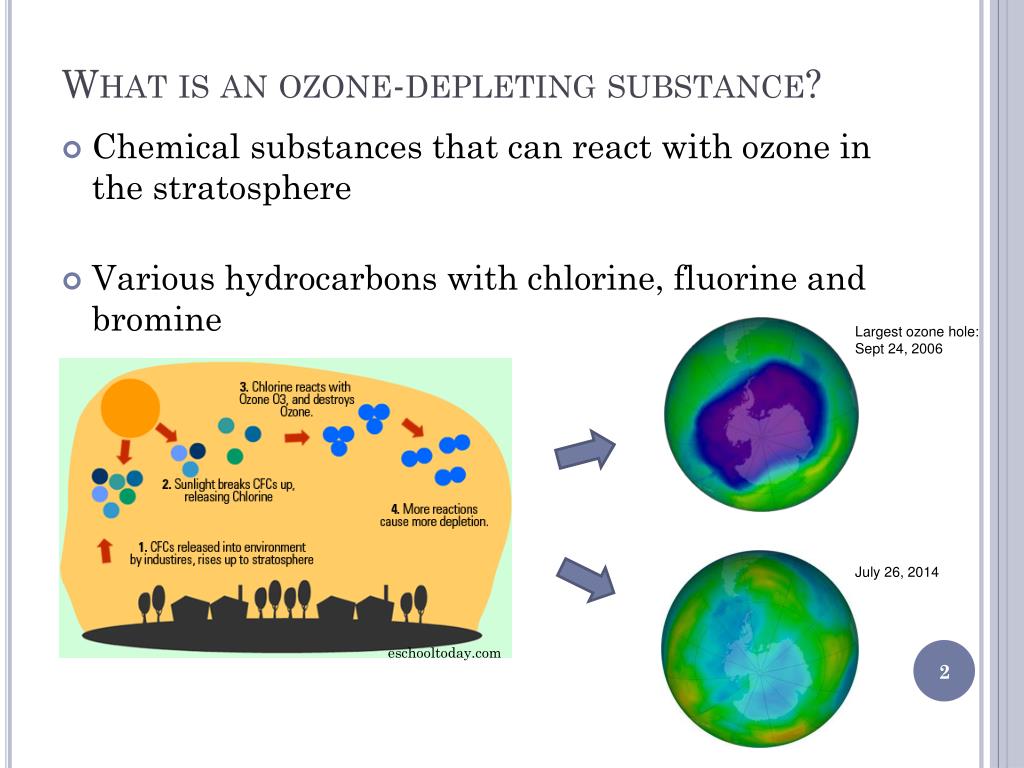
| ODS are synthetic chemicals that contain chlorine or bromine atoms, such as chlorofluorocarbons (CFCs), halons, and hydrochlorofluorocarbons (HCFCs). These chemicals are commonly used in refrigeration, air conditioning, aerosol propellants, and fire extinguishers. When released into the atmosphere, ODS rise to the stratosphere and break down ozone molecules, leading to ozone layer depletion. | ||
| 3 | ||
| Impacts of Ozone Layer Depletion | ||
|---|---|---|
| Increased exposure to UV radiation can cause skin cancer, cataracts, and weakened immune systems in humans. UV radiation can also harm marine ecosystems, leading to reduced productivity of phytoplankton and coral bleaching. Ozone layer depletion can disrupt the food chain, affecting the populations of various species, including plankton, fish, and birds. | ||
| 4 | ||
| Ozone Layer Recovery | ||
|---|---|---|
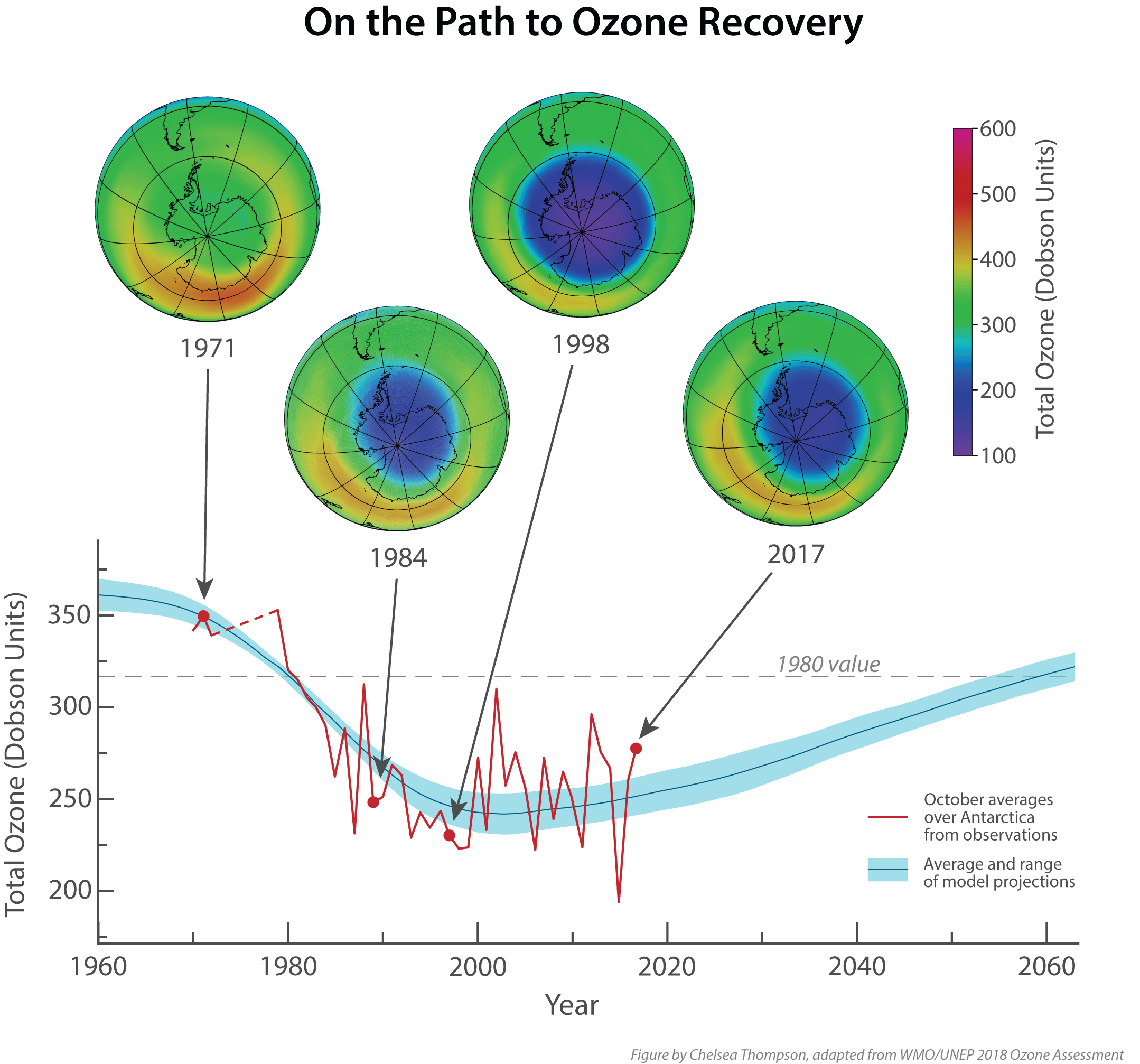
| International efforts, such as the Montreal Protocol (1987), have been crucial in reducing the production and use of ODS. The phase-out of ODS has resulted in a decline in their atmospheric concentrations, leading to partial recovery of the ozone layer. Ozone hole monitoring and research continue to be important to assess the effectiveness of global ozone protection measures. | ||
| 5 | ||
| Future Challenges | ||
|---|---|---|
| Despite progress, challenges remain in completely eliminating ODS and ensuring the full recovery of the ozone layer. Developing countries face the challenge of transitioning to ozone-friendly technologies without compromising development goals. Climate change may also impact the recovery of the ozone layer, as changing weather patterns and temperature can affect ozone depletion dynamics. | ||
| 6 | ||
| Public Awareness and Action | ||
|---|---|---|
| Raising public awareness about ozone layer depletion is crucial to promote responsible behavior and support policy changes. Individuals can contribute by reducing the use of ozone-depleting products, such as aerosol sprays and certain refrigerants. Supporting initiatives that promote sustainable alternatives and practices can help protect the ozone layer and mitigate climate change. | ||
| 7 | ||
| Ozone Layer Protection Successes | ||
|---|---|---|
| The Montreal Protocol has been hailed as one of the most successful environmental treaties, leading to a significant reduction in ODS production and use. The Antarctic ozone hole has shown signs of recovery, with a decrease in its size and depth in recent years. These successes highlight the importance of international cooperation and proactive measures in addressing global environmental challenges. | ||
| 8 | ||
| Key Takeaways | ||
|---|---|---|
| Ozone layer depletion is primarily caused by the release of man-made chemicals called ozone-depleting substances (ODS). Ozone layer depletion leads to increased exposure to harmful UV radiation, posing risks to human health and ecosystems. International efforts and public awareness are crucial for the recovery and protection of the ozone layer. | ||
| 9 | ||
| References (download PPTX file for details) | ||
|---|---|---|
| United Nations Environment Programme (UNEP). ... National Aeronautics and Space Administration... World Meteorological Organization (WMO). (202... |  | |
| 10 | ||