Newton's Law Of Cooling Presentation
| Introduction to Newton's Law of Cooling | ||
|---|---|---|
| Newton's Law of Cooling is a fundamental principle in thermodynamics. It describes the rate at which an object's temperature changes when it is in contact with a surrounding medium. The law states that the rate of temperature change is proportional to the temperature difference between the object and its surroundings. | ||
| 1 | ||
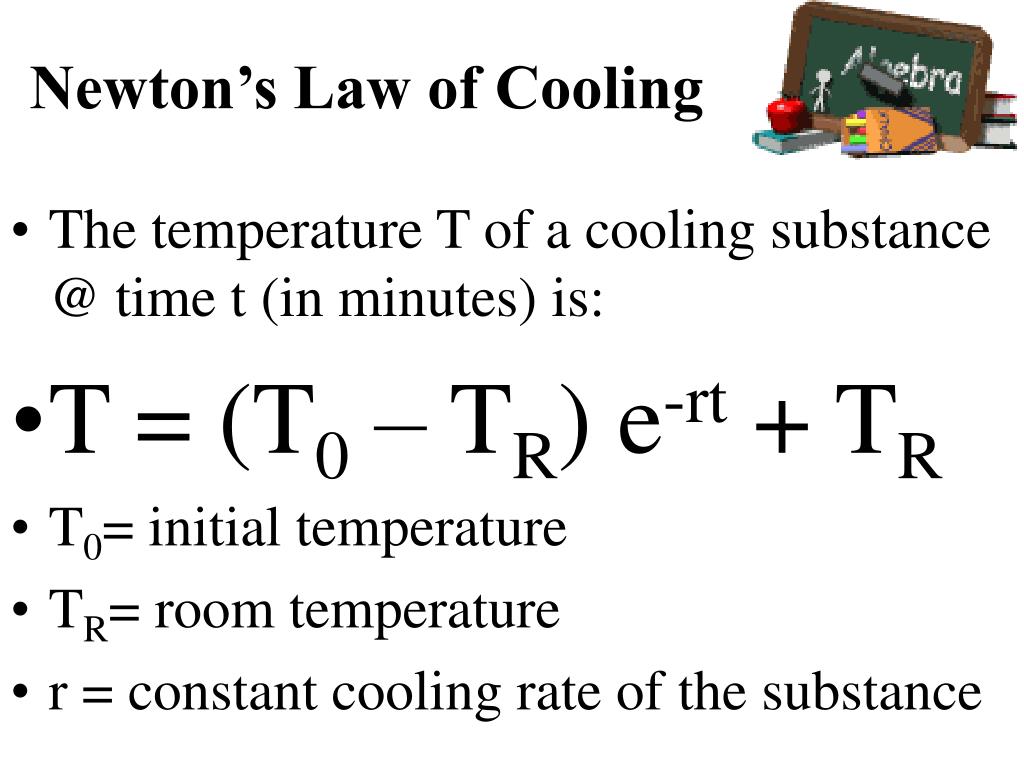
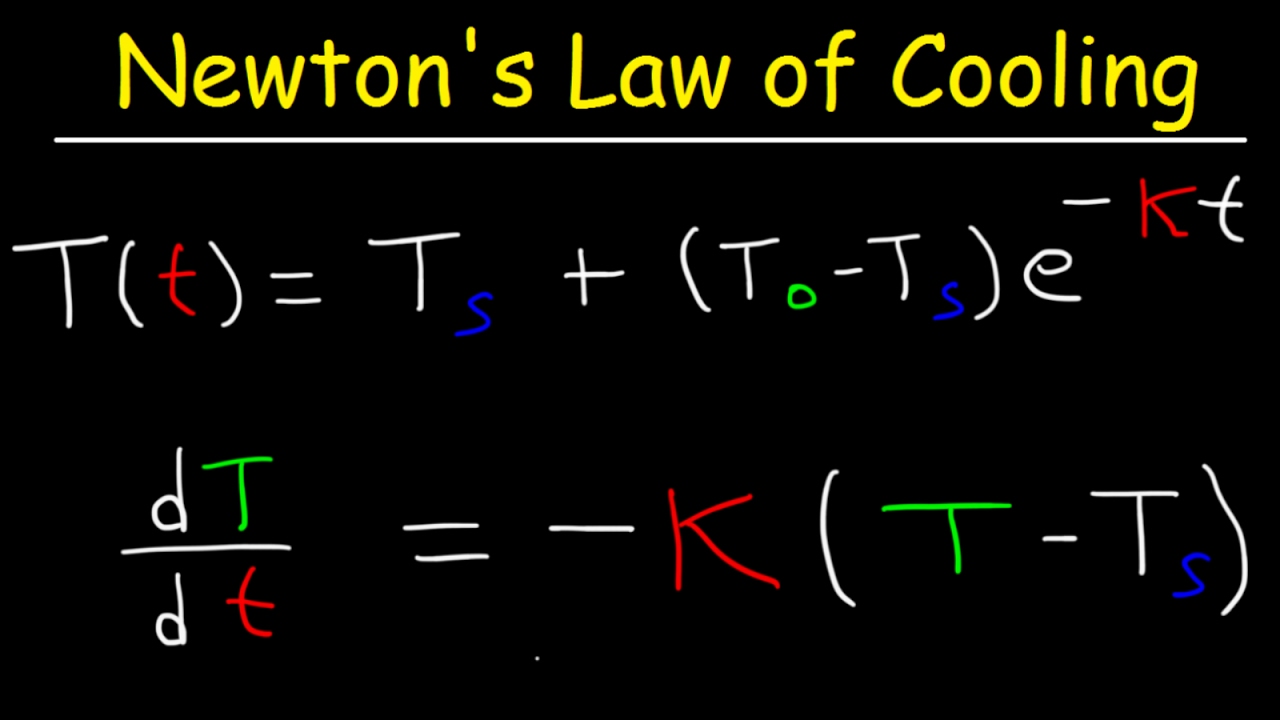
| Statement of Newton's Law of Cooling | ||
|---|---|---|
| Newton's Law of Cooling can be mathematically expressed as dT/ dt = -k(T - Ts) where dT/ dt is the rate of temperature change, T is the temperature of the object, Ts is the temperature of the surroundings, and k is the cooling constant. The negative sign indicates that temperature decreases over time. The cooling constant, k, depends on the properties of the object and the surrounding medium. |  | |
| 2 | ||
| Application of Newton's Law of Cooling | ||
|---|---|---|
| Newton's Law of Cooling is commonly used in various fields, such as meteorology, engineering, and physics. It is used to model the cooling of hot liquids, the cooling of electronic devices, and the behavior of planets in space. By applying Newton's Law of Cooling, scientists and engineers can predict temperature changes and design efficient cooling systems. | ||
| 3 | ||
| Factors Affecting Cooling Rate | ||
|---|---|---|
| The cooling rate depends on the temperature difference between the object and its surroundings. A larger temperature difference leads to a faster cooling rate. The cooling constant, k, is influenced by factors such as the surface area of the object, the thermal conductivity of the material, and the airflow around the object. Different materials have different cooling constants, which affect their cooling rates. | ||
| 4 | ||
| Limitations of Newton's Law of Cooling | ||
|---|---|---|
| Newton's Law of Cooling assumes a constant cooling constant, k, which may not be accurate in all scenarios. It assumes that the temperature difference between the object and its surroundings remains relatively small. It does not take into account factors such as radiation heat transfer or non-linear temperature changes. | ||
| 5 | ||
| Conclusion | ||
|---|---|---|
| Newton's Law of Cooling is a valuable tool for understanding temperature changes in objects. It provides a simple mathematical model for predicting cooling rates. While it has limitations, it remains widely used and serves as a foundation for more complex heat transfer theories. | ||
| 6 | ||