NPN Transistor Presentation
| Introduction to NPN Transistor | ||
|---|---|---|
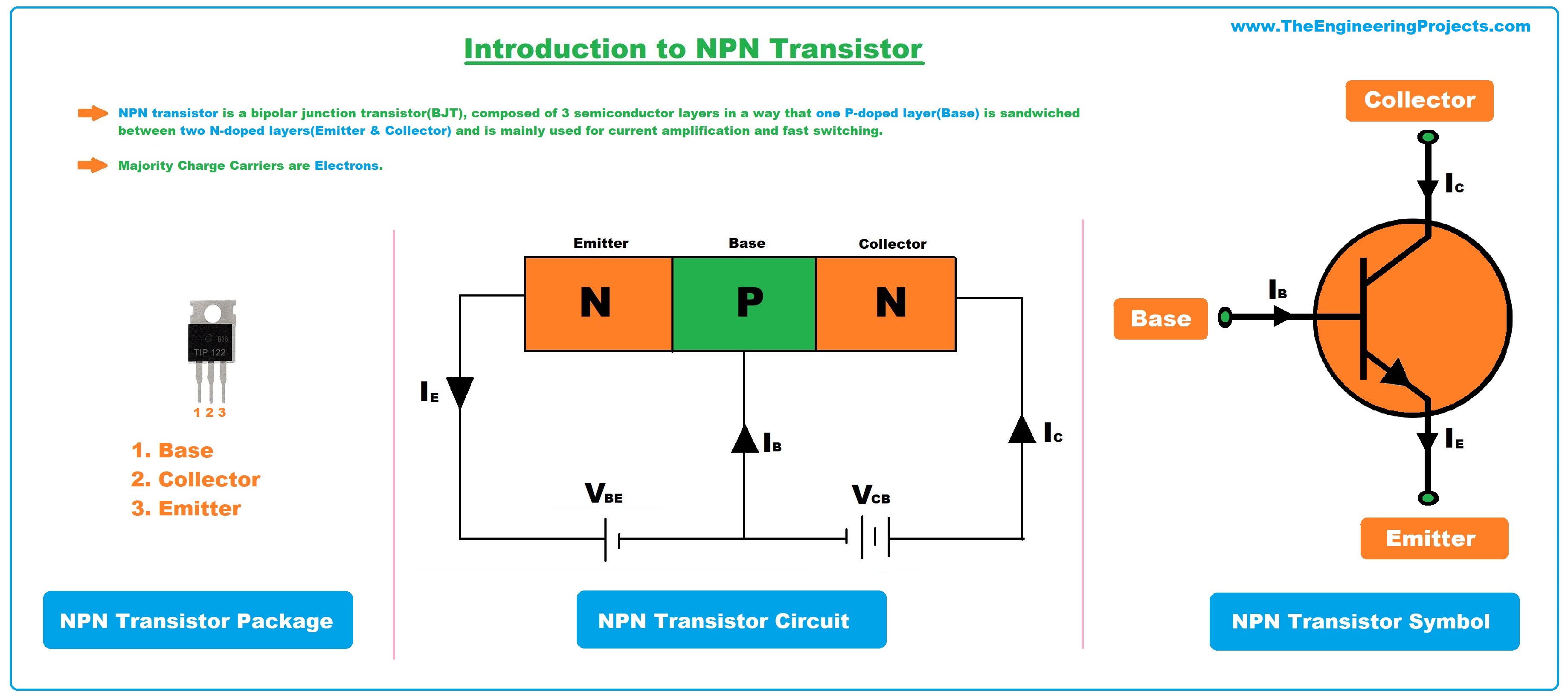
| NPN transistor is a type of bipolar junction transistor (BJT) that consists of three layers of semiconductor material. It is composed of a thin layer of p-type material sandwiched between two layers of n-type material. The layers are referred to as the emitter, base, and collector, respectively. | ||
| 1 | ||
| Working Principle of NPN Transistor | ||
|---|---|---|
| NPN transistor operates based on the flow of majority charge carriers, which are electrons in this case. When a positive voltage is applied to the base terminal, it attracts electrons from the emitter region, causing an electron current to flow from emitter to base. The electron current is then amplified as it passes through the base region and flows into the collector region. | ||
| 2 | ||
| Applications of NPN Transistor | ||
|---|---|---|
| NPN transistors are widely used in amplification circuits, such as audio and radio frequency amplifiers. They are also utilized in switching applications, where they can control the flow of current by acting as electronic switches. NPN transistors are essential components in many electronic devices, including computers, televisions, and mobile phones. | ||
| 3 | ||
| Advantages and Limitations of NPN Transistor | ||
|---|---|---|
| Advantages:
- NPN transistors offer high current gain, allowing for efficient amplification.
- They have fast switching speeds, making them suitable for high-frequency applications.
- NPN transistors are relatively inexpensive and widely available. Limitations: - NPN transistors require careful biasing to ensure proper operation. - They are sensitive to temperature variations, which can affect their performance. - NPN transistors have limited power handling capabilities compared to other transistor types. (Note: This is a brief overview of NPN transistors. For a more comprehensive understanding, additional slides may be required.) Your third bullet |  | |
| 4 | ||