Multiple Sclerosis Presentation
| Introduction to Multiple Sclerosis | ||
|---|---|---|
| Multiple sclerosis (MS) is a chronic neurological disease. It affects the central nervous system (CNS), which includes the brain and spinal cord. MS is characterized by the immune system attacking the protective covering of nerve fibers, called myelin. | ||
| 1 | ||
| Types of Multiple Sclerosis | ||
|---|---|---|
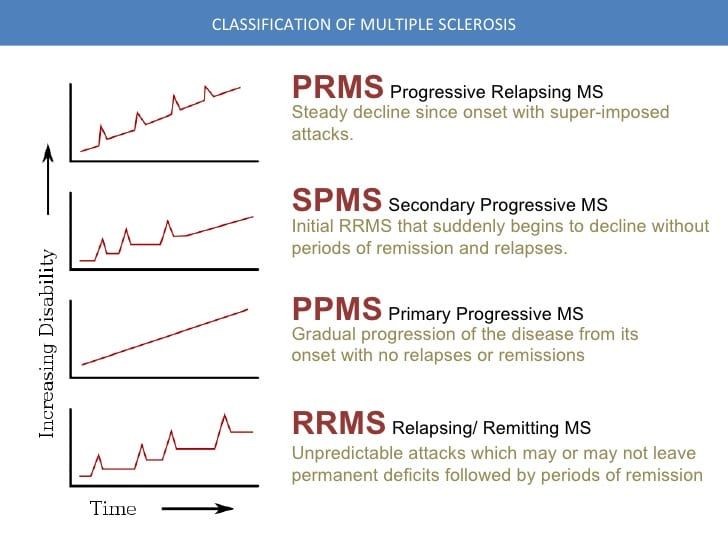
| Relapsing-Remitting MS (RRMS) is the most common type, characterized by periods of relapse followed by partial or complete recovery. Secondary Progressive MS (SPMS) occurs when RRMS transitions into a more progressive form without relapses. Primary Progressive MS (PPMS) is a progressive form from the start, without distinct relapses. | ||
| 2 | ||
| Symptoms of Multiple Sclerosis | ||
|---|---|---|
| Fatigue is a common symptom, affecting up to 80% of individuals with MS. Sensory disturbances, such as numbness or tingling, are often experienced. Motor symptoms can include muscle weakness, tremors, or coordination difficulties. |  | |
| 3 | ||
| Diagnosis of Multiple Sclerosis | ||
|---|---|---|
| Diagnosis of MS involves a combination of medical history, neurological examination, and imaging tests such as MRI. Other conditions with similar symptoms must be ruled out. The presence of specific lesions in the CNS is a key diagnostic factor. | ||
| 4 | ||
| Treatment Options for Multiple Sclerosis | ||
|---|---|---|
| Disease-modifying therapies (DMTs) aim to reduce relapses and slow disease progression. Rehabilitation programs can help manage symptoms and improve quality of life. Symptomatic treatments address specific symptoms, such as pain or spasticity. | ||
| 5 | ||
| Lifestyle Strategies for Managing Multiple Sclerosis | ||
|---|---|---|
| Regular exercise can help improve strength, balance, and overall well-being. A healthy diet, rich in fruits, vegetables, and lean proteins, is recommended. Stress management techniques, such as meditation or yoga, can help reduce symptom flare-ups. | ||
| 6 | ||
| Potential Complications of Multiple Sclerosis | ||
|---|---|---|
| Mobility issues may arise due to muscle weakness or spasticity. Cognitive changes, such as memory problems or difficulty concentrating, can occur. Emotional changes, including depression or anxiety, may be experienced. | ||
| 7 | ||
| Support and Resources for Individuals with Multiple Sclerosis | ||
|---|---|---|
| MS support groups provide a platform for sharing experiences and emotional support. National MS societies offer resources, education, and advocacy for individuals with MS. Access to healthcare professionals, such as neurologists or physical therapists, is crucial for comprehensive care. | ||
| 8 | ||
| Research and Advancements in Multiple Sclerosis | ||
|---|---|---|
| Ongoing research aims to better understand the causes and mechanisms of MS. New treatment options, including oral medications and monoclonal antibodies, are being developed. Stem cell therapy shows promise in repairing damaged myelin and promoting regeneration. | ||
| 9 | ||
| Conclusion | ||
|---|---|---|
| Multiple sclerosis is a complex and unpredictable disease affecting the central nervous system. Diagnosis and early intervention are key to managing symptoms and slowing progression. Continued research and advancements offer hope for improved treatments and quality of life for individuals with MS. | ||
| 10 | ||

:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/diagnosis-of-multiple-sclerosis-2440691_final-975f9ab094e64cc69452fb534ed4f981.png)





