Moral Ethics Presentation
| Introduction to Moral Ethics | ||
|---|---|---|
| Moral ethics refers to the study of right and wrong actions, decisions, and behaviors. It involves understanding and applying ethical principles to guide human conduct. Moral ethics examines questions of what is morally right or wrong and how individuals should act. | ||
| 1 | ||
| Importance of Moral Ethics | ||
|---|---|---|
| Moral ethics provides a framework for individuals to make ethical decisions in various situations. It helps maintain social order and promotes harmonious relationships among people. Moral ethics contributes to personal growth, integrity, and a sense of responsibility towards others. | ||
| 2 | ||
| Ethical Theories | ||
|---|---|---|
| Deontological ethics emphasizes the inherent rightness or wrongness of actions, regardless of outcomes. Teleological ethics focuses on the consequences of actions and the greater good. Virtue ethics emphasizes the development of moral character and virtues to guide ethical behavior. | ||
| 3 | ||
| Ethical Principles | ||
|---|---|---|
| Respect for autonomy: Recognizing and respecting individuals' right to make their own decisions. Beneficence: Acting in ways that promote the well-being and welfare of others. Non-maleficence: Avoiding causing harm or minimizing harm to others. | ||
| 4 | ||
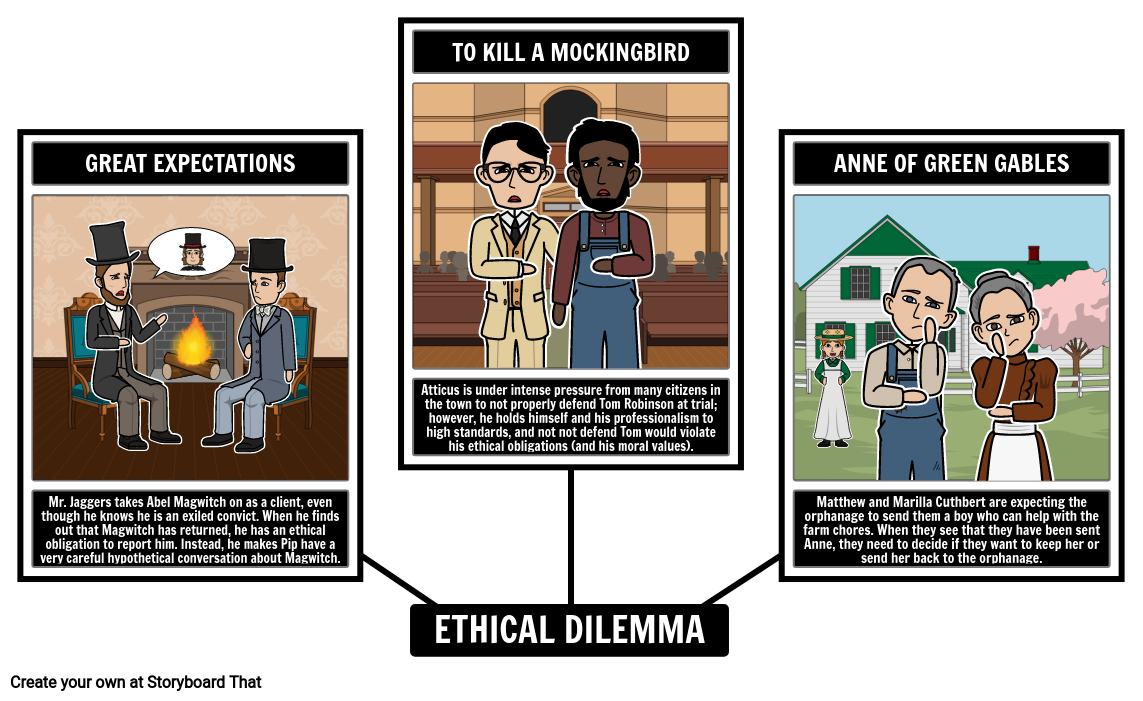
| Moral Dilemmas | ||
|---|---|---|
| Moral dilemmas arise when there is a conflict between two or more ethical principles or values. They often require individuals to make difficult decisions with no clear right or wrong answer. Moral dilemmas can arise in personal, professional, or societal contexts. | ||
| 5 | ||
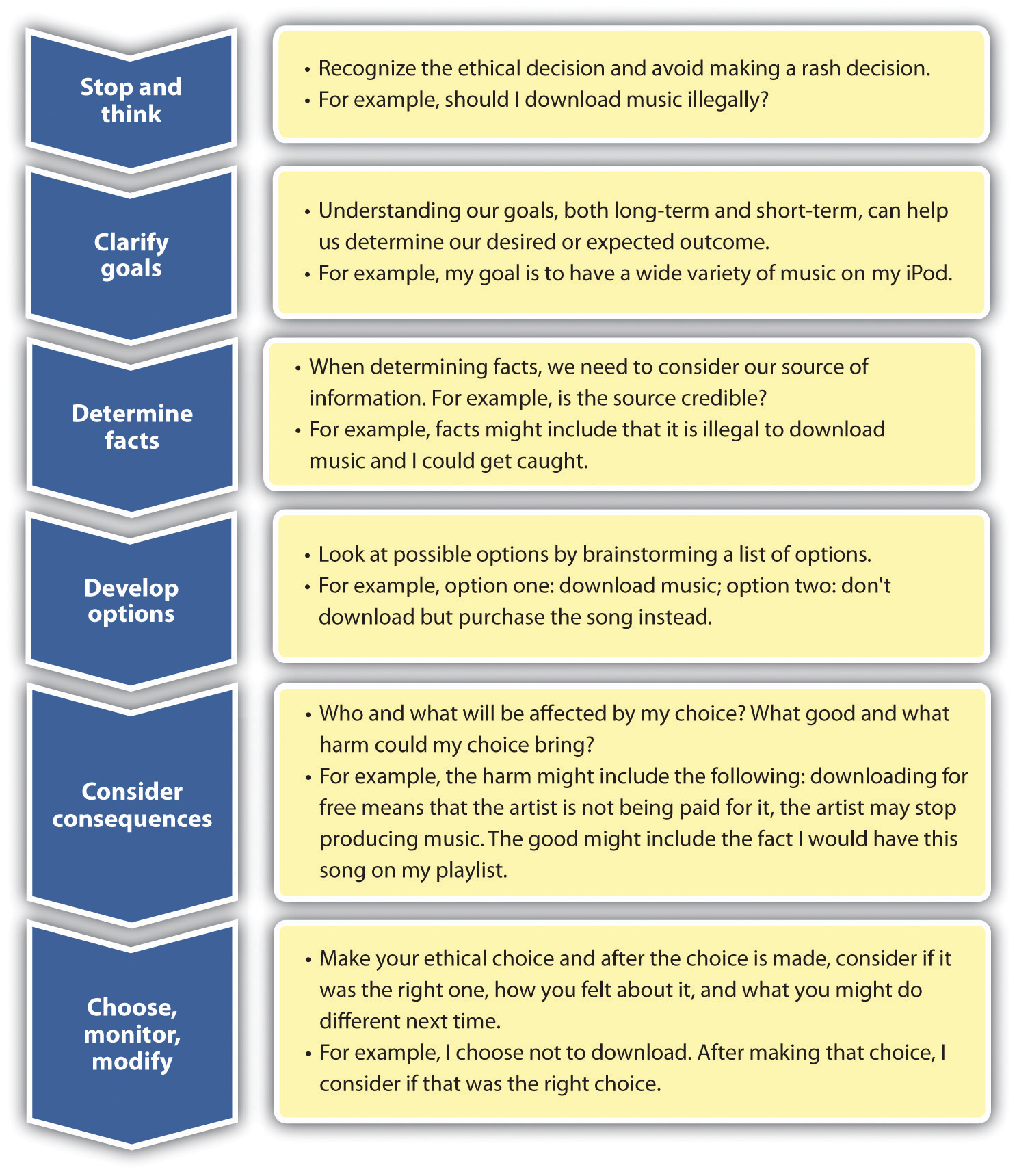
| Ethical Decision-Making Process | ||
|---|---|---|
| Identify the ethical dilemma or problem. Gather relevant information and consider different perspectives. Evaluate options, considering ethical principles and potential consequences. | ||
| 6 | ||
| Ethical Leadership | ||
|---|---|---|
| Ethical leaders demonstrate integrity, honesty, and transparency in their actions. They prioritize ethical decision-making and hold themselves accountable for their actions. Ethical leaders inspire and motivate others to act ethically and create a positive ethical culture. | ||
| 7 | ||
| Ethical Challenges in the Digital Age | ||
|---|---|---|
| Privacy and data protection: Balancing the use of personal information with individual rights. Cyberbullying and harassment: Addressing harmful behavior online while respecting freedom of speech. Artificial intelligence and automation: Ensuring ethical use and accountability in decision-making algorithms. | ||
| 8 | ||
| Cultural and Relativistic Perspectives | ||
|---|---|---|
| Cultural relativism suggests that moral ethics are subjective and vary across cultures. Ethical universalism argues that certain ethical principles are universally valid. Recognizing cultural diversity while upholding basic ethical principles is important for a global society. | ||
| 9 | ||
| Conclusion | ||
|---|---|---|
| Moral ethics play a crucial role in guiding individual and collective behavior. Understanding ethical theories, principles, and decision-making processes helps navigate complex moral dilemmas. Emphasizing ethical leadership and addressing emerging ethical challenges contributes to a more ethical society. | ||
| 10 | ||